DFS
#
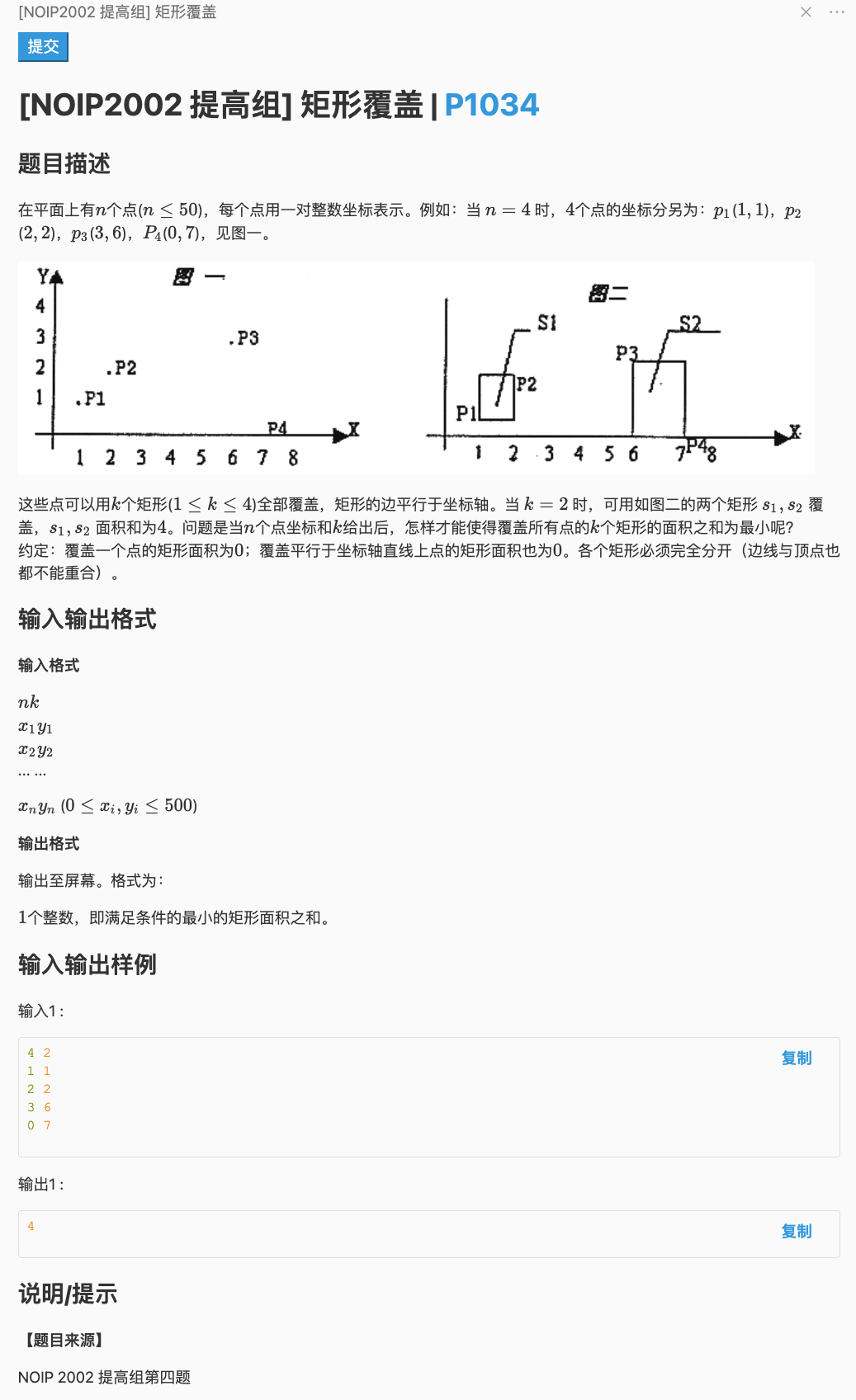
# 洛谷P1034_矩形覆盖
# 🔗
# 💡
我们必然是想将所有的点分为连续的 块
即要么双关键字 要么
单一种不行是有可能相临的两个 (或 ) 之间的 (或 )差的很大,这样的话就排一种其实也是选择得相对分散了
我们对这两个方式排过序后,每种都计算一下在这种排序方案下我们能得到的最小值,进行比较一下即可
至于怎么算最小值,我们可以枚举最多 个断点
以断点进行分割计算每一块的最大最小 和最大最小 ,他们差值的乘积就是这一个矩形的面积
# ✅
const int N = 100;
int n, k;
struct Point {
int x, y;
} pt[N];
inline void DFS ( vector<int> paus, int num, int &res ) { // 断点,我们需要的断点数量,传递答案
if ( paus.size() == num ) {
int cur = 0;
paus.push_back(n);
for ( int k = 1; k < paus.size(); k ++ ) {
int maxX = 0, maxY = 0, minX = 0x3f3f3f3f, minY = 0x3f3f3f3f;
for ( int i = paus[k - 1] + 1; i <= paus[k]; i ++ ) {
maxX = max(maxX, pt[i].x), minX = min(minX, pt[i].x),
maxY = max(maxY, pt[i].y), minY = min(minY, pt[i].y);
}
cur += (maxX - minX) * (maxY - minY);
}
res = min(res, cur);
return;
}
for ( int i = paus.back() + 1; i < n; i ++ ) {
paus.push_back(i);
DFS ( paus, num, res );
paus.pop_back();
}
}
int main () {
int res = 0x3f3f3f3f;
cin >> n >> k;
for ( int i = 1; i <= n; i ++ ) cin >> pt[i].x >> pt[i].y;
sort ( pt + 1, pt + 1 + n, [&]( Point a, Point b ) {
if ( a.x != b.x ) return a.x < b.x;
return a.y < b.y;
} );
for ( int i = 1; i <= k; i ++ ) {
DFS({0}, i, res);
}
sort ( pt + 1, pt + 1 + n, [&]( Point a, Point b ) {
if ( a.y != b.y ) return a.y < b.y;
return a.x < b.x;
} );
for ( int i = 1; i <= k; i ++ ) {
DFS({0}, i, res);
}
cout << res << endl;
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
# 洛谷P1041_传染病控制
# 🔗
# 💡
感性地理解一下,从根开始传播,每一次只能取一个点隔断
那其实就是,每一次选择一个深度的一个点进行隔断
我们可以暴力搜一下,对于一个深度,我们选择哪些点进行隔断
当然如果这个点上面有祖先已经被隔断了,那么这个点是安全的,就不需要进行隔断
我们其实要算的就是最后不安全的点数的最小值
我们先预处理出深度数组
然后 每次下潜一个深度
在这个深度下枚举我们要隔断哪个不安全的点
隔断后这个点的子树全部变为安全(通过又一种深搜 实现,当然我们要回溯一下再变成不安全代表我们不选
每一次进行隔断都会安全化整个子树,所以我们预处理时也统计一下所有节点的子树大小即可
每次走到最深的点时就维护一下 的最小值
# ✅
int res = 0x3f3f3f3f;
namespace Map {
const int M = 610;
int head[M], cnt;
struct Edge {
int nxt, to;
} edge[M];
inline void add_Edge ( int from, int to ) {
edge [ ++ cnt ] = { head[from], to };
head[from] = cnt;
}
} using namespace Map;
const int N = 310;
namespace TreeInformation {
int dep[N], fa[N], mxdep, sz[N];
inline void dfs ( int x, int fath ) {
fa[x] = fath; dep[x] = dep[fath] + 1; sz[x] = 1;
mxdep = max ( mxdep, dep[x] );
for ( int i = head[x]; i; i = edge[i].nxt ) {
int to = edge[i].to;
if ( to == fath ) continue;
dfs ( to, x );
sz[x] += sz[to];
}
}
int saf[N];
inline void Save ( int x, int is ) {
for ( int i = head[x]; i; i = edge[i].nxt ) {
int to = edge[i].to;
if ( to == fa[x] ) continue;
saf[to] = is;
Save ( to, is );
}
}
} using namespace TreeInformation;
vector<int> vec[N]; // vec[i]表示深度为i的点集合
int n, m;
map<int, int> tmp;
inline void Solve ( int d, int num ) {
bool flag = false;
if ( d > mxdep ) { res = min(res, num); return ;}
for ( auto id : vec[d] ) {
if ( saf[id] ) continue;
saf[id] = 1; Save ( id, 1 );
Solve ( d + 1, num - sz[id] );
saf[id] = 0; Save ( id, 0 );
flag = true;
}
if ( !flag ) res = min ( res, num );
}
int main () {
ios::sync_with_stdio(false);
cin >> n >> m;
for ( int i = 0, x, y; i < m; i ++ ) {
cin >> x >> y;
add_Edge ( x, y );
add_Edge ( y, x );
}
dfs ( 1, 1 );
for ( int i = 1; i <= n; i ++ ) vec[dep[i]].push_back(i);
Solve ( 2, n );
cout << res << endl;
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
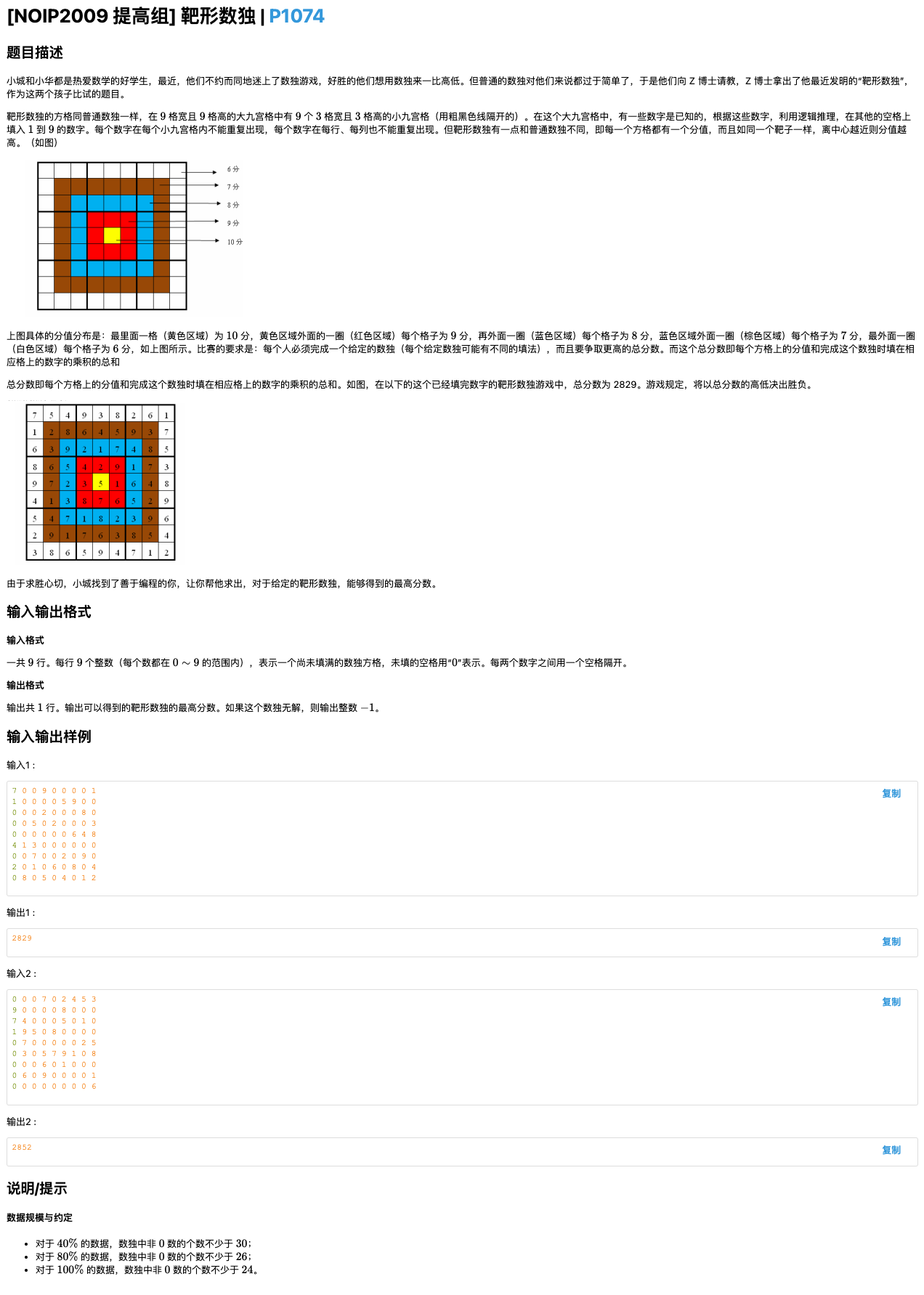
# 洛谷P1074_靶形数独
# 🔗
# 💡
大小很小,多枝多可能
于是直接开爆搜
仔细一想约束条件就有很多了
比如同行同列不能出现两个相同的
同九宫格不能出现两个相同的
那么我们开一个行数组列数组块数组
记录一下每块、每行、每列是否有
这样的话就是搜索的结果,剪枝剪下去也不会非常大
而且还能保证最后出来的都是完成的数独
# ✅
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
#define ll long long
using namespace std;
const int N = 15;
int a[N][N];
int res = -1;
bool row[N][N], col[N][N], blk[N][N]; // ()[i][j] 第 i (行、列、块) 是否有 j
inline int which ( int x, int y ) { // 第几块
if ( x < 3 ) {
if ( y < 3 ) return 1;
if ( y < 6 ) return 2;
if ( y < 9 ) return 3;
} else if ( x < 6 ) {
if ( y < 3 ) return 4;
if ( y < 6 ) return 5;
if ( y < 9 ) return 6;
} else {
if ( y < 3 ) return 7;
if ( y < 6 ) return 8;
if ( y < 9 ) return 9;
}
}
inline void DFS ( int i, int j ) {
if ( j >= 9 ) {
int cur = 0;
for ( int x = 0; x < 9; x ++ ) {
for ( int y = 0; y < 9; y ++ ) {
if ( x >= 4 && x <= 4 && y >= 4 && y <= 4 ) cur += a[x][y] * 10;
else if ( x >= 3 && x <= 5 && y >= 3 && y <= 5 ) cur += a[x][y] * 9;
else if ( x >= 2 && x <= 6 && y >= 2 && y <= 6 ) cur += a[x][y] * 8;
else if ( x >= 1 && x <= 7 && y >= 1 && y <= 7 ) cur += a[x][y] * 7;
else cur += a[x][y] * 6;
}
}
res = max ( res, cur );
return;
}
int nxtj = j + (i + 1) / 9; // 下一个的列
int nxti = (i + 1) % 9; // 下一个的行
if ( a[i][j] ) DFS ( nxti, nxtj ); // 预订了
else {
for ( int num = 9; num >= 1; num -- ) if ( !row[i][num] && !col[j][num] && !blk[which(i, j)][num] ) { // 都满足就搜下去
row[i][num] = col[j][num] = blk[which(i, j)][num] = 1;
a[i][j] = num; DFS ( nxti, nxtj ); a[i][j] = 0;
row[i][num] = col[j][num] = blk[which(i, j)][num] = 0;
}
}
}
int main () {
for ( int i = 0; i < 9; i ++ ) for ( int j = 0; j < 9; j ++ ) {
scanf("%d", &a[i][j]);
if ( a[i][j] )
row[i][a[i][j]] = col[j][a[i][j]] = blk[which(i, j)][a[i][j]] = 1;
}
DFS ( 0, 0 );
printf("%d\n", res);
return 0;
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
# 洛谷P1127_词链
# 🔗
# 💡
看到这道题第一反应应该是要想到搜索的
每一个词后面选择性接词
排个序,如果接到n个词的话第一次就一定是解,输出
我们预处理出来以每个字母开头的字符串集合
DFS,然后发现TLE两个点
考虑优化
看一下有无解的关系
如果一个字母作为首字母的次数小于作为尾字母次数-1,一定不行
如果一个字母作为首字母的数量是作为尾字母的数量+1
那么这个字母必定要作为词链首字母
如果这样的字母出现多于一个的话就一定不行,冲突了
如果是一个的话就遍历这一个就行了
如果没有的话就说明成环,每一个跑一遍就行了
# ✅
vector<int> chr[30];
int n;
string s[1100];
int vis[1100];
int asBeg[30];
int asEnd[30];
inline void dfs ( vector<int> id ) {
if ( id.size() == n ) {
for ( int i = 0; i < id.size(); i ++ ) {
if ( i ) cout << ".";
cout << s[id[i]];
}
exit(0);
}
for ( int i = 0; i < chr[s[id.back()].back() - 'a'].size(); i ++ ) {
if ( !vis[chr[s[id.back()].back() - 'a'][i]] ) {
vis[chr[s[id.back()].back() - 'a'][i]] = 1;
id.push_back(chr[s[id.back()].back() - 'a'][i]); dfs ( id ); id.pop_back();
vis[chr[s[id.back()].back() - 'a'][i]] = 0;
}
}
}
int main () {
cin >> n;
for ( int i = 0; i < n; i ++ )
cin >> s[i],
asBeg[s[i][0] - 'a'] ++,
asEnd[s[i].back() - 'a'] ++;
sort ( s, s + n );
for ( int i = 0; i < n; i ++ )
chr[s[i][0] - 'a'].push_back(i);
int num_char_can_first = 0;
char char_can_first;
for ( char i = 'a'; i <= 'z'; i ++ ) {
if ( asBeg[i - 'a'] == asEnd[i - 'a'] + 1 )
num_char_can_first ++,
char_can_first = i;
if ( asBeg[i - 'a'] < asEnd[i - 'a'] - 1 ) { cout << "***" << endl; exit(0); }
}
if ( num_char_can_first > 1 ) {
cout << "***" << endl;
} else if ( num_char_can_first == 1 ) {
for ( int i = 0; i < n; i ++ ) {
if ( s[i][0] == char_can_first ) {
vis[i] = 1;
dfs ( {i} );
vis[i] = 0;
}
}
} else {
for ( int i = 0; i < n; i ++ ) {
vis[i] = 1;
dfs ( {i} );
vis[i] = 0;
}
}
cout << "***" << endl;
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
# 洛谷P1363_幻象迷宫
# 🔗
# 💡
对于一个点,如果在两张图中且两次到达这个点,那么这个图就可以彻底连通
那么我们用一个vis数组来维护一个点是否被不折回跑地两次到达
那么就是两个变量控制不取模的原始位置,一个变量控制是否走过
如果一个取模后的位置被走过且另外两个变量有一个与当前位置不同,就代表不折回跑地到达了两次
遍历就行了
# ✅
int n, m;
string s[2000];
int flag = 0;
int dx[4] = {0, 0, -1, 1};
int dy[4] = {1, -1, 0, 0};
int vis[2000][2000][3];
inline void dfs ( int x, int y, int X, int Y ) {
if ( s[x][y] == '#' ) return;
if ( flag ) return;
if ( vis[x][y][0] && ( vis[x][y][1] != X || vis[x][y][2] != Y ) ) {flag = 1; return;} // 走过模坐标但是有一个老坐标不和新坐标相等
vis[x][y][0] = 1, vis[x][y][1] = X, vis[x][y][2] = Y; // 记录一下新坐标
for ( int i = 0; i < 4; i ++ ) {
int curx = (x + dx[i] + n) % n, cury = (y + dy[i] + m) % m;
int curX = X + dx[i], curY = Y + dy[i];
if ( vis[curx][cury][1] != curX || vis[curx][cury][2] != curY || !vis[curx][cury][0] ) // 三个变量控制是不是走的是走过的点
dfs ( curx, cury, curX, curY );
}
}
inline void Solve () {
flag = 0; memset ( vis, 0, sizeof vis );
int sttx, stty;
for ( int i = 0; i < n; i ++ ) {
cin >> s[i];
for ( int j = 0; j < m; j ++ ) {
if ( s[i][j] == 'S' ) sttx = i, stty = j;
}
}
dfs ( sttx, stty, sttx, stty );
if ( flag ) cout << "Yes" << endl;
else cout << "No" << endl;
}
int main () {
while ( cin >> n >> m ) {
Solve ();
}
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
# 洛谷P1434_滑雪
# 🔗
# 💡
对于每个点,在搜索的时候记录一下它能到达的最远距离
然后每一次搜索都是最优子问题的汇聚过程
每一个点对每一个可以转移的连接点进行连接,这些点的dfs()+1就是当前点的最优子问题之一
对每一个点都dfs一边即可
# ✅
int n, m;
int a[110][110];
int dp[110][110];
int dx[4] = {0, 0, -1, 1};
int dy[4] = {1, -1, 0, 0};
int res = 0;
inline int dfs ( int x, int y ) {
if ( dp[x][y] > 1 ) return dp[x][y];
for ( int i = 0; i < 4; i ++ ) {
if ( x + dx[i] >= 0 && x + dx[i] < n && y + dy[i] >= 0 && y + dy[i] < m && a[x + dx[i]][y + dy[i]] < a[x][y] )
dp[x][y] = max(dp[x][y], dfs ( x + dx[i], y + dy[i] ) + 1);
}
return dp[x][y];
}
int main () {
ios::sync_with_stdio(false);
cin >> n >> m;
for ( int i = 0; i < n; i ++ ) for ( int j = 0; j < m; j ++ ) cin >> a[i][j], dp[i][j] = 1;
for ( int i = 0; i < n; i ++ ) for ( int j = 0; j < m; j ++ ) res = max ( res, dfs ( i, j ) );
cout << res << endl;
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
# 洛谷P1463_反素数
# 🔗
# 💡
首先根据唯一分解定理, ,故 就是一种数量分配方式
题目就是想让我们找到 不超过 的情况下, 最大, 也最大
任何比 小的数其 都小于 ,转换一下前提就是在 相同时,反质数集内存入的是是最小的数
所以在 的分配下, 越大,被分配到的 应越小
不然在反质数集中,会有比 更小的 满足 的情况出现,这样的话只有 会被保留
用这个性质对每一个质数(前12个)出现的次数进行搜索,剪枝为当前的乘积大于 了
将搜索出来的 存入 vector 中,按上面说的任务找到 最大的情况下最大的
# ✅
int p[12] = {2, 3, 5, 7, 11, 13, 17, 19, 23, 29, 31, 37};
int n;
vector<pair<int, int> > pre_vec;
inline void dfs (int idx, int lasnum, ll x, int g) {
if (x > n || idx == 12) return;
pre_vec.push_back({x, g});
ll bas = 1;
for (int i = 0; i <= lasnum && x * bas <= n; i ++) {
dfs(idx + 1, i, x * bas, g * (i + 1));
bas *= p[idx];
}
}
int main () {
ios::sync_with_stdio(false);
cin.tie(nullptr);
cin >> n;
dfs(0, 31, 1, 1);
sort(pre_vec.begin(), pre_vec.end());
int maxg = 0, maxv = 0;
for (auto i : pre_vec) {
if (i.second > maxg) {
maxv = i.first;
maxg = i.second;
}
}
cout << maxv << endl;
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
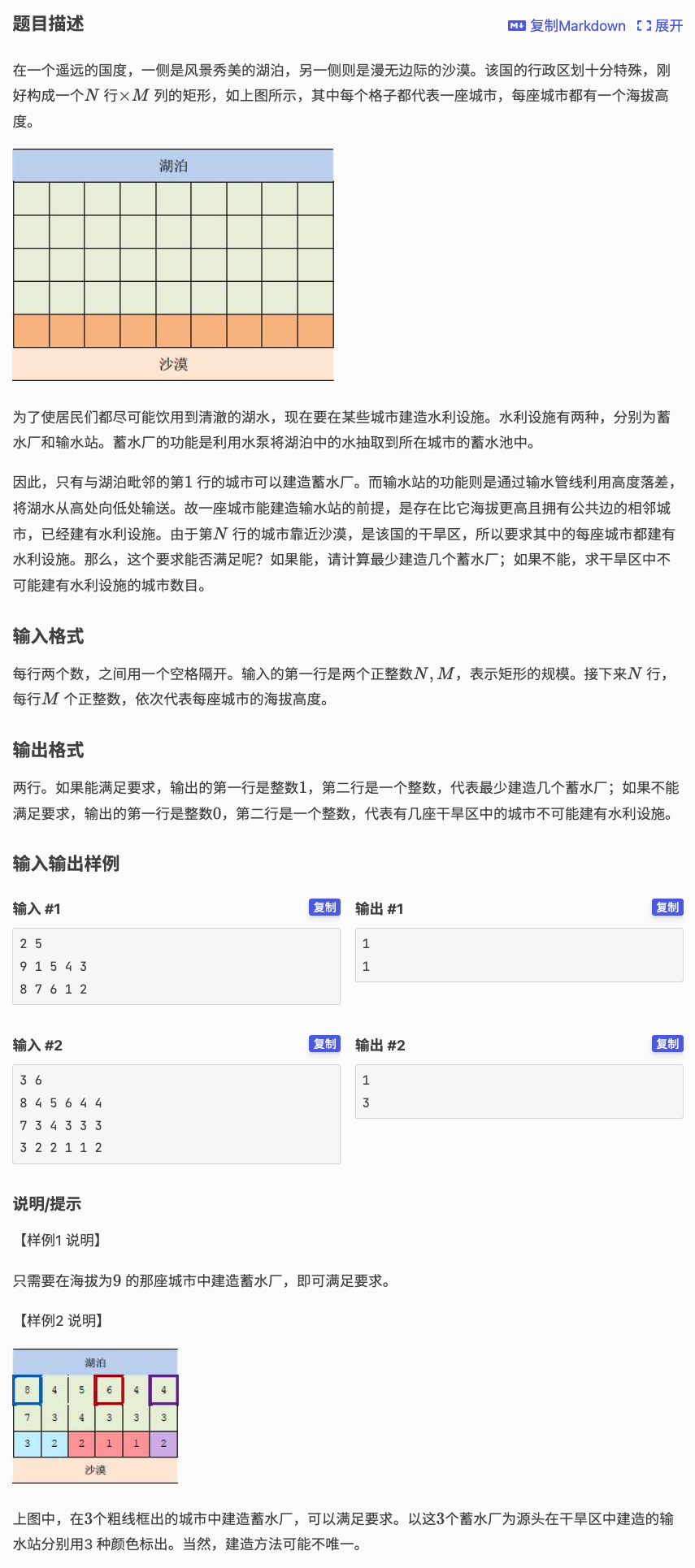
# 洛谷P1514_引水入城
# 🔗
# 💡
首先在模拟水流的时候,应该能发现,除非是有的旱区特别高导致根本流不过去输出 ,每一个蓄水站能流到的都是一段连续的区间
因为若 的水路岔开 ,可以流到 ,那么 若想被流到必须用别的蓄水站,就说明别的蓄水站的水路一定会穿过包裹住 的 水路边界,则意味着边界上的某一点可以流到 ,就意味着 能流到
故通过记搜,维护每一个点能流到旱区的左边界和右边界
最后就是看如何使用最少段铺满整个
这个通过 实现, 表示 被覆盖的需要最少的段,令 表示左边界为 的最大右边界
则 可以通过 转移给所有的
维护最小值,然后输出 即可
# ✅
int dx[] = {0, 0, 1, -1};
int dy[] = {1, -1, 0, 0};
const int N = 510;
int n, m;
int h[N][N];
int l[N][N], r[N][N];
int vis[N][N];
inline pair<int, int> dfs (int x, int y) {
if (vis[x][y]) return {l[x][y], r[x][y]}; vis[x][y] = 1;
for (int i = 0; i < 4; i ++) {
int nx = x + dx[i];
int ny = y + dy[i];
if (nx >= 1 && ny >= 1 && nx <= n && ny <= m && h[nx][ny] < h[x][y]) {
pair<int, int> nxt = dfs(nx, ny);
l[x][y] = min(l[x][y], nxt.first);
r[x][y] = max(r[x][y], nxt.second);
}
}
return {l[x][y], r[x][y]};
}
int dp[N];
int mx[N];
int main () {
scanf("%d%d", &n, &m);
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i ++) for (int j = 1; j <= m; j ++) {
scanf("%d", &h[i][j]);
l[i][j] = 0x3f3f3f3f, r[i][j] = 0;
}
for (int j = 1; j <= m; j ++) l[n][j] = r[n][j] = j;
for (int j = 1; j <= m; j ++) if (!vis[1][j]) dfs(1, j);
int cannot = 0;
for (int i = 1; i <= m; i ++) {
if (!vis[n][i]) {
cannot ++;
}
}
if (cannot) {
printf("0\n%d", cannot);
return 0;
}
// for (int i = 1; i <= m; i ++) {
// cout << l[1][i] << " " << r[1][i] << endl;
// } return 0;
for (int i = 1; i <= m; i ++) {
if (l[1][i] != 0x3f3f3f3f) mx[l[1][i]] = max(mx[l[1][i]], r[1][i]);
}
memset(dp, 0x3f, sizeof dp);
dp[0] = 0;
for (int i = 1; i <= m; i ++) {
for (int j = i; j <= mx[i]; j ++) {
dp[j] = min(dp[j], dp[i - 1] + 1);
}
}
printf("1\n%d", dp[m]);
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
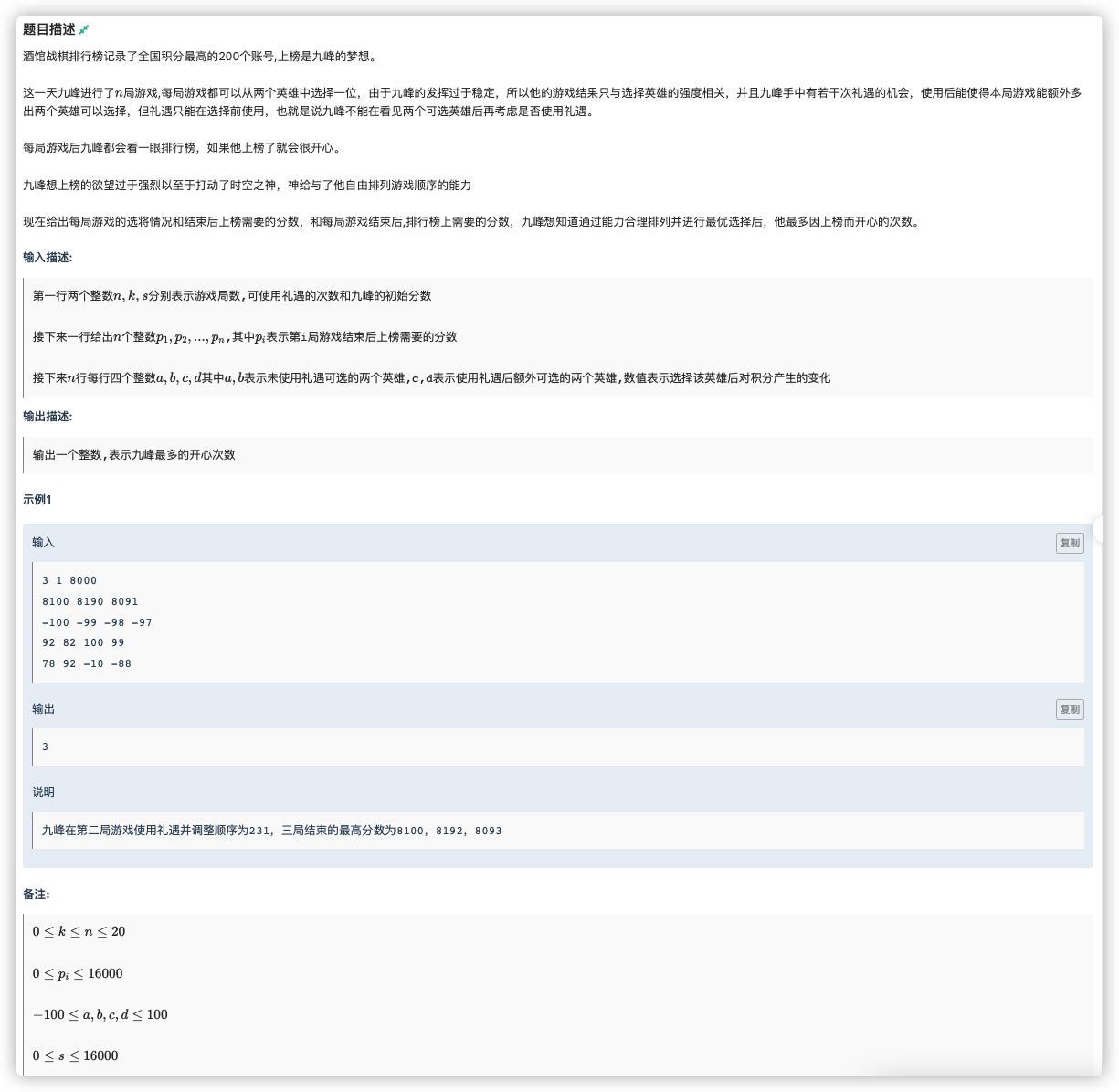
# 牛客2022寒假算法基础集训营5C_战棋小孩
# 🔗
# 💡
首先能得到的思考是
每一局游戏肯定是选能选的最大得分
如果已知所有的最大得分,我们就可以降序排序,让贡献最多的放在前面
那么问题就在于,如果去分配礼遇情况
由于游戏局数十分少,我们看一下最大复杂度即 其实也不是很大
所以我们可以 暴力搜索去分配礼遇
递归出口的时候用最大得分 sort 一下与要求得分比对一下即可
# ✅
ll n, k, s;
ll p[40];
struct node {
ll a, b, c, d;
bool chs;
inline friend bool operator < ( node a, node b ) {
int mxa, mxb;
if ( a.chs == 1 ) mxa = max(max(a.a, a.b), max(a.c, a.d));
else mxa = max(a.a, a.b);
if ( b.chs == 1 ) mxb = max(max(b.a, b.b), max(b.c, b.d));
else mxb = max(b.a, b.b);
return mxa > mxb;
}
} nd[40], tmp[40];
int RES = 0;
inline void DFS ( vector<int> chss, int num ) {
if ( chss.size() == k ) {
for ( int i = 1; i <= n; i ++ ) tmp[i] = nd[i];
for ( int i = 0; i < chss.size(); i ++ ) tmp[chss[i]].chs = 1;
sort ( tmp + 1, tmp + 1 + n );
ll cur = s; int res = 0;
for ( int i = 1; i <= n; i ++ ) {
if ( tmp[i].chs ) cur += max(max(tmp[i].a, tmp[i].b), max(tmp[i].c, tmp[i].d));
else cur += max(tmp[i].a, tmp[i].b);
if ( cur >= p[i] ) res ++;
}
RES = max(RES, res);
return;
}
for ( int i = num + 1; i <= n; i ++ ) {
chss.push_back(i);
DFS(chss, i);
chss.pop_back();
}
}
int main () {
ios::sync_with_stdio(false);
cin >> n >> k >> s;
for ( int i = 1; i <= n; i ++ ) cin >> p[i];
for ( int i = 1; i <= n; i ++ ) cin >> nd[i].a >> nd[i].b >> nd[i].c >> nd[i].d;
DFS({}, 0);
cout << RES << endl;
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
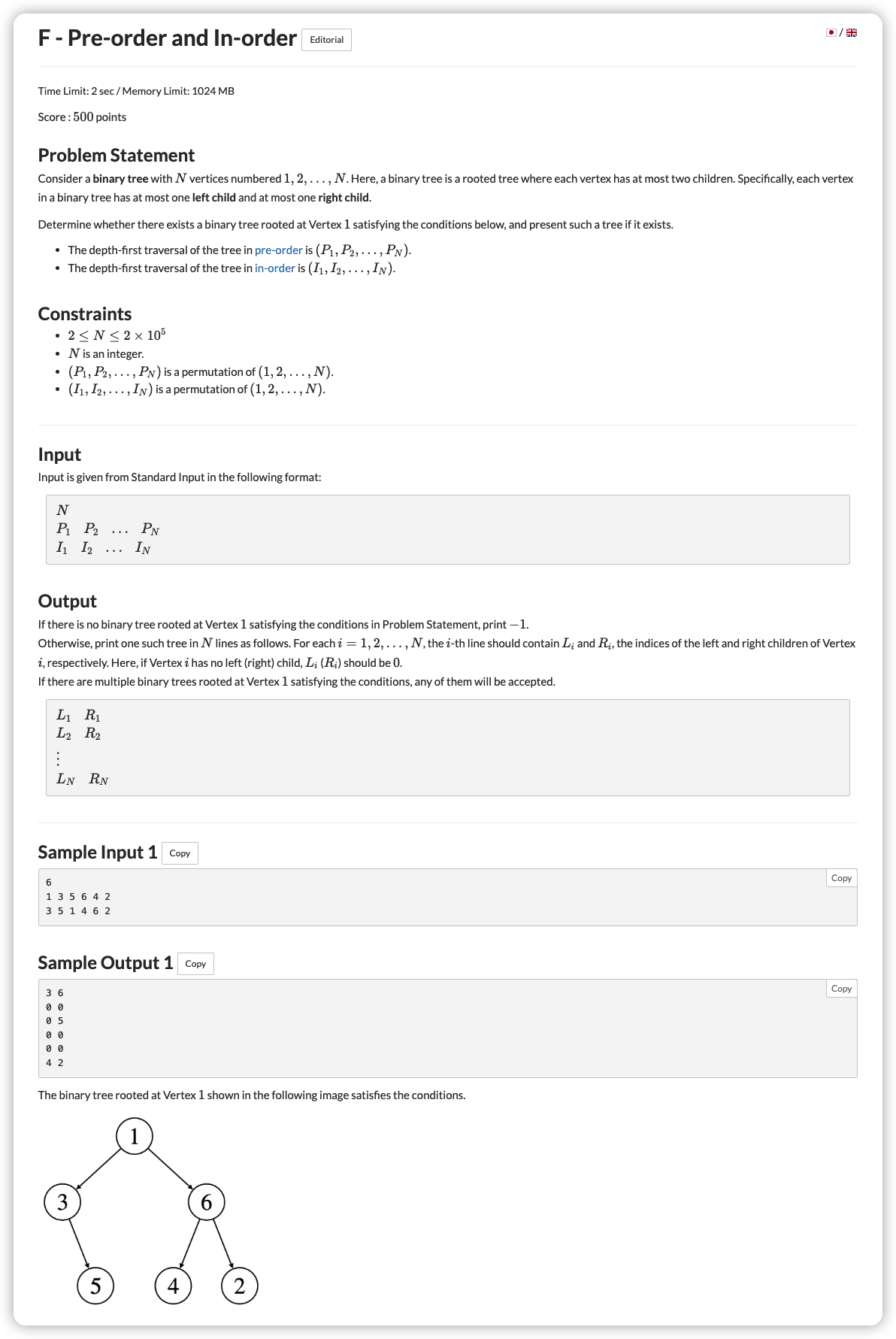
# ABC255F_Pre-orderAndIn-order
# 🔗
# 💡
考虑先序遍历和中序遍历互可取之处
中序遍历如果知道 中根的位置 ,那么左右子树为 和
先序遍历则是能快速确定根的位置
且对于一棵子树,在中序中连续的部分,必定是先序中连续一部分的排列
那么构造这棵树就两个一起用
dfs(l1, r1, l2, r2),先序区间 中序区间
那么 则是根,我们在搜索之前预处理出来 在 中出现的位置为 ,那么我们则需要将 从 处劈开
中序左区间为 右区间为
那么我们可以快速得到中序左区间的长度,也是先序左区间的长度
先序左区间为 右区间为
# ✅
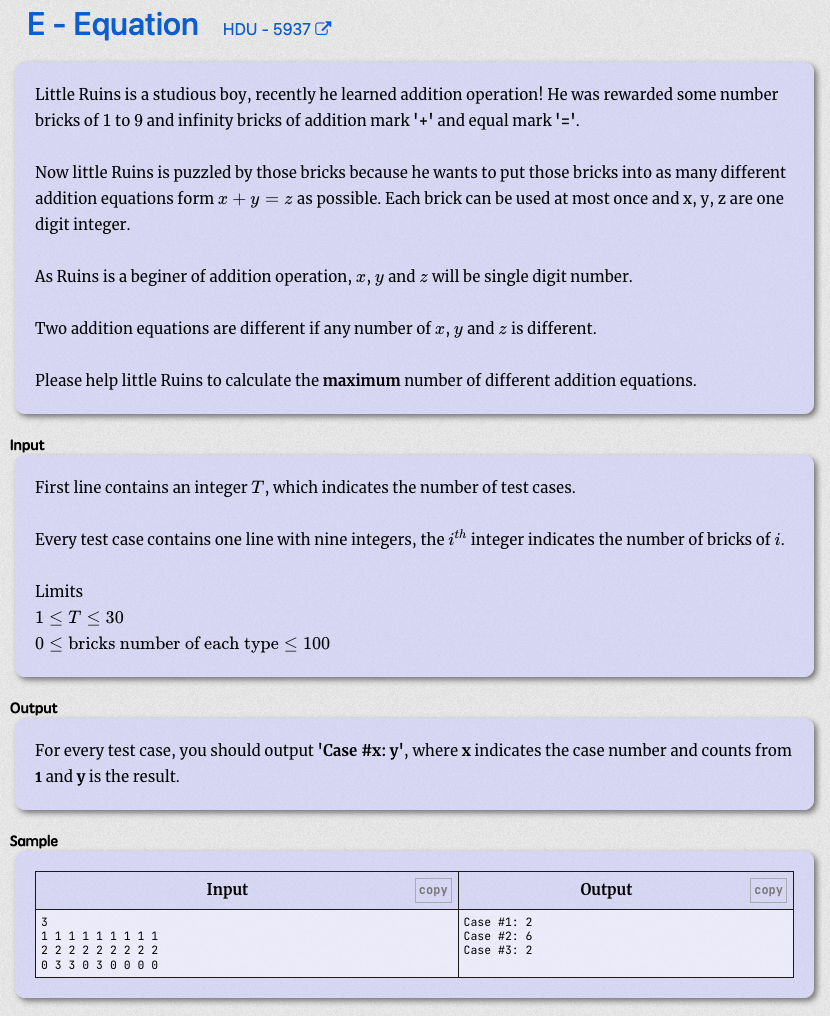
# CCPC2016杭州站E_Equation
# 🔗
# 💡
等式 如果不看交换 的话,就是 个
在三进制考虑下复杂度会有点大,但是大得不多, ( 状态是这个等式不选、选一次,交换 选两次
那么考虑一种合理的剪枝来优化,既然是求最大值且记录到最后才有最大值,且全局只有一个最大值,那么就预估到最后的步数看看如果这些步数都加到答案里面,会不会超过答案的最大值,如果可以超过那么就继续走,如果不可以就不往下进行了
// res 是当前计数,idx 是总式子数量,i 是当前遍历到第几个式子,mxres 是最大的答案
if (res + (idx - i + 1) * 2 <= mxres) return;
2
# ✅
struct node { int a, b, c; } eq[50]; int idx;
int a[10], mxres;
inline void dfs (int i, int res) {
if (res + (idx - i + 1) * 2 <= mxres) return;
if (i == idx + 1) {
mxres = max(mxres, res);
return;
}
dfs(i + 1, res);
if (eq[i].a == eq[i].b) {
if (a[eq[i].a] >= 2 && a[eq[i].c]) {
a[eq[i].a] -= 2;
a[eq[i].c] --;
dfs(i + 1, res + 1);
a[eq[i].a] += 2;
a[eq[i].c] ++;
}
} else if (a[eq[i].a] && a[eq[i].b] && a[eq[i].c]) {
a[eq[i].a] --; a[eq[i].b] --; a[eq[i].c] --;
dfs(i + 1, res + 1);
if (a[eq[i].a] && a[eq[i].b] && a[eq[i].c]) {
a[eq[i].a] --; a[eq[i].b] --; a[eq[i].c] --;
dfs(i + 1, res + 2);
a[eq[i].a] ++; a[eq[i].b] ++; a[eq[i].c] ++;
}
a[eq[i].a] ++; a[eq[i].b] ++; a[eq[i].c] ++;
}
}
int casid;
inline void Solve () {
for (int i = 1; i <= 9; i ++) scanf("%d", &a[i]);
mxres = 0;
dfs(1, 0);
printf("Case #%d: %d\n", ++casid, mxres);
}
int main () {
for (int i = 1; i <= 9; i ++) {
for (int j = i; j <= 9 && i + j <= 9; j ++) {
eq[++idx] = {i, j, i + j};
}
}
int t; scanf("%d", &t); while (t --) {
Solve();
; }
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
# CodeForces1647D_MadokaAndTheBestSchoolInRussia
# 🔗
# 💡
先将问题抽象出来
求 其中 均不为 的倍数
问我们是否可以构造出来至少两组
这个 可以采用爆搜,由于每次都是枚举的当前 的因数,所以 即可
每次填入一个 就代表 要下降一层
若下降不了就只能退出
出口可以设置为我们已经找出来了两种构造方式或者我们当前的数过大
# ✅
ll x, d;
int cnt;
map<pair<ll, ll>, bool> mp;
inline void DFS ( ll tgt, ll cur, ll bak ) {
if ( cnt == 2 || cur > tgt ) return;
if ( cur == tgt ) {
cnt ++;
return;
}
if ( mp.count({tgt, cur}) ) return; mp[{tgt, cur}] = true;
if ( tgt % d ) return; tgt /= d;
for ( ll i = bak; i * i <= tgt; i ++ ) {
if ( tgt % i == 0 ) {
if (i % d) DFS(tgt, cur * i, i);
if (i * i != tgt && (tgt / i) % d) DFS(tgt, cur * (tgt / i), tgt / i);
}
}
}
inline void Solve () {
cin >> x >> d;
cnt = 0;
mp.clear();
DFS(x, 1, 1);
if (cnt == 2) cout << "YES\n";
else cout << "NO\n";
}
int main () {
cin.tie(0)->sync_with_stdio(0);
cin.exceptions(cin.failbit);
int cass; cin >> cass; while ( cass -- ) {
Solve ();
}
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
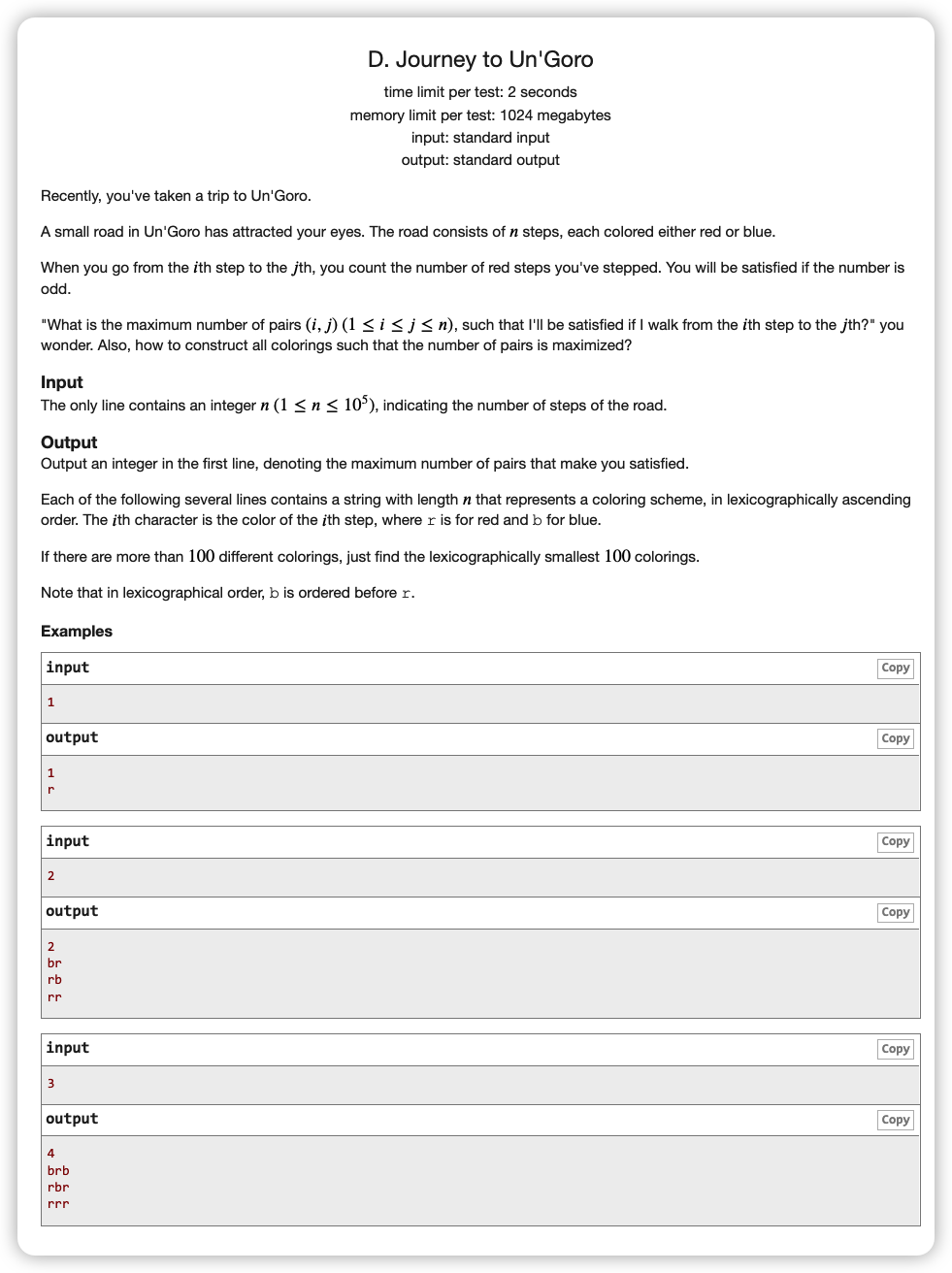
# ICPC2020沈阳D_JourneyToUn'Goro
# 🔗
# 💡
从题中要求的 的个数为奇数,我们从奇偶性入手
令 表示前缀为 的串的 的个数
为奇数,即 与 的奇偶性不同的对均满足
那么就意味着我们 的奇偶要对半开
令参数 表示 为偶数的个数, 表示 为奇数的个数,那么
利用这个条件进行前缀剪枝
要求字典序最小就优先开
开 时奇偶性不变,顺接上一层的奇偶状态
开 后奇偶变化,改变奇偶状态
# ✅
int n;
int nres;
char s[100005];
inline void DFS ( int idx, int cnt0, int cnt1, bool st ) {
if ( max(cnt0, cnt1) > (n + 2) / 2 ) return;
if ( idx == n ) {
cout << s << endl;
if ( ++ nres == 100 ) exit(0);
return;
}
s[idx] = 'b'; DFS(idx + 1, cnt0 + (!st), cnt1 + st, st);
s[idx] = 'r'; DFS(idx + 1, cnt0 + st, cnt1 + (!st), !st);
}
int main () {
cin.tie(0)->sync_with_stdio(0);
cin.exceptions(cin.failbit);
cin >> n;
ll res = 0; for ( int i = 1; i <= n; i += 2 ) res += 1ll * n - i + 1;
cout << res << endl;
DFS(0, 1, 0, 0);
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25