莫队
#
# 普通莫队
# CodeForces617E_XORAndFavoriteNumber
# 🔗
# 💡
由于异或的性质,反复异或等于0
所以求a[l]^a[l+1]^...^a[r]时
可以将a[i]标记为前缀和,然后求a[l-1]^a[r]即可
那么问题转化为记录区间里面a[l-1]^a[r]=k的个数
那么对于每个a[r]我们求一下a[r]^k的个数累加即可
# ✅
#include <iostream>
#include <algorithm>
#include <cmath>
#include <queue>
#include <cstring>
#include <vector>
#include <unordered_map>
#include <map>
#define ll long long
using namespace std;
const ll N = 1e5 + 10;
struct Q{
ll l, r, id;
}q[N];// 查询
ll a[N], res[N], RES, pos[N]; // 数列,记录答案,当前答案,块编号
ll cnt[5000010]; // 统计出现过的数的个数
ll n, m, k, len;
int main () {
ios::sync_with_stdio(false);
#ifndef ONLINE_JUDGE
freopen("in.in", "r", stdin);
freopen("out.out", "w", stdout);
#endif
auto add = [&] ( ll id ) {
RES += cnt[a[id] ^ k]; // 利用区间内出现数的个数求一下当前RES
cnt[a[id]] ++; // 前缀和出现个数++
};
auto sub = [&] ( ll id ) {
cnt[a[id]] --;
RES -= cnt[a[id] ^ k];
};
cin >> n >> m >> k; len = sqrt(n);
for ( ll i = 1; i <= n; i ++ ) {
cin >> a[i]; a[i] ^= a[i - 1];
pos[i] = i / len;
}
for ( ll i = 0; i < m; i ++ ) {
cin >> q[i].l >> q[i].r;
q[i].id = i;
}
sort ( q, q + m, []( Q a, Q b ) {
if ( pos[a.l] != pos[b.l] ) return pos[a.l] < pos[b.l];
return a.r < b.r;
});
ll l = 1, r = 0; cnt[0] = 1;
for ( ll i = 0; i < m; i ++ ) {
while ( l > q[i].l ) add ( -- l - 1 );
while ( r < q[i].r ) add ( ++ r );
while ( l < q[i].l ) sub ( l ++ - 1 );
while ( r > q[i].r ) sub ( r -- );
res[q[i].id] = RES;
}
for ( ll i = 0; i < m; i ++ ) {
cout << res[i] << endl;
}
return 0;
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
# 洛谷P3674_小清新人渣的本愿
# 🔗
# 💡
一道莫队维护bitset的好题
bitset是一个很妙的STL容器,可以实现很多优化
是否有两个数的差为,只需要判断是否存在1即可
是否有两个数的和为
可以推导一下
那么我们建立一个存放的bst2,然后查一下中是否存在1即可
是否有两个数的积为
直接暴力枚举因数然后查一下在不在就行了
# ✅
#include <iostream>
#include <cstring>
#include <cstdio>
#include <vector>
#include <algorithm>
#include <cmath>
#include <map>
#include <bitset>
#define ll long long
using namespace std;
const int N = 1e5 + 10;
int n, m, len;
int a[N];
struct Q {
int id, l, r;
int tgt, opt;
} q[N];
bitset<N> bst1, bst2;
int res[N], vis[N];
inline void add ( int x ) {
if ( !(vis[x] ++) ) bst1[x] = bst2[N - x] = true;
}
inline void del ( int x ) {
if ( !(-- vis[x]) ) bst1[x] = bst2[N - x] = false;
}
inline int get ( int x ) {
return x / len;
}
int main () {
ios::sync_with_stdio(false);
#ifndef ONLINE_JUDGE
freopen("in.in", "r", stdin);
freopen("out.out", "w", stdout);
#endif
cin >> n >> m; len = sqrt ( n );
for ( int i = 1; i <= n; i ++ ) cin >> a[i];
for ( int i = 0; i < m; i ++ ) {
int opt, l, r, x; cin >> opt >> l >> r >> x;
q[i] = {i, l, r, x, opt};
}
sort ( q, q + m, [&](Q a, Q b){
if ( get(a.l) != get(b.l) ) return get(a.l) < get(b.l);
return a.r < b.r;
});
for ( int L = 1, R = 0, i = 0; i < m; i ++ ) {
while ( L < q[i].l ) del ( a[ L ++ ] );
while ( L > q[i].l ) add ( a[ -- L ] );
while ( R > q[i].r ) del ( a[ R -- ] );
while ( R < q[i].r ) add ( a[ ++ R ] );
if ( q[i].opt == 1 ) {
res[q[i].id] = (bst1 & (bst1 << q[i].tgt)).any();
} else if ( q[i].opt == 2 ) {
res[q[i].id] = (bst1 & (bst2 >> (N - q[i].tgt))).any();
} else {
for ( int j = 1; j * j <= q[i].tgt; j ++ ) {
if ( q[i].tgt % j == 0 && bst1[j] && bst1[q[i].tgt / j] ) {
res[q[i].id] = true;
break;
}
}
}
}
for ( int i = 0; i < m; i ++ ) {
puts(res[i] ? "hana" : "bi");
}
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
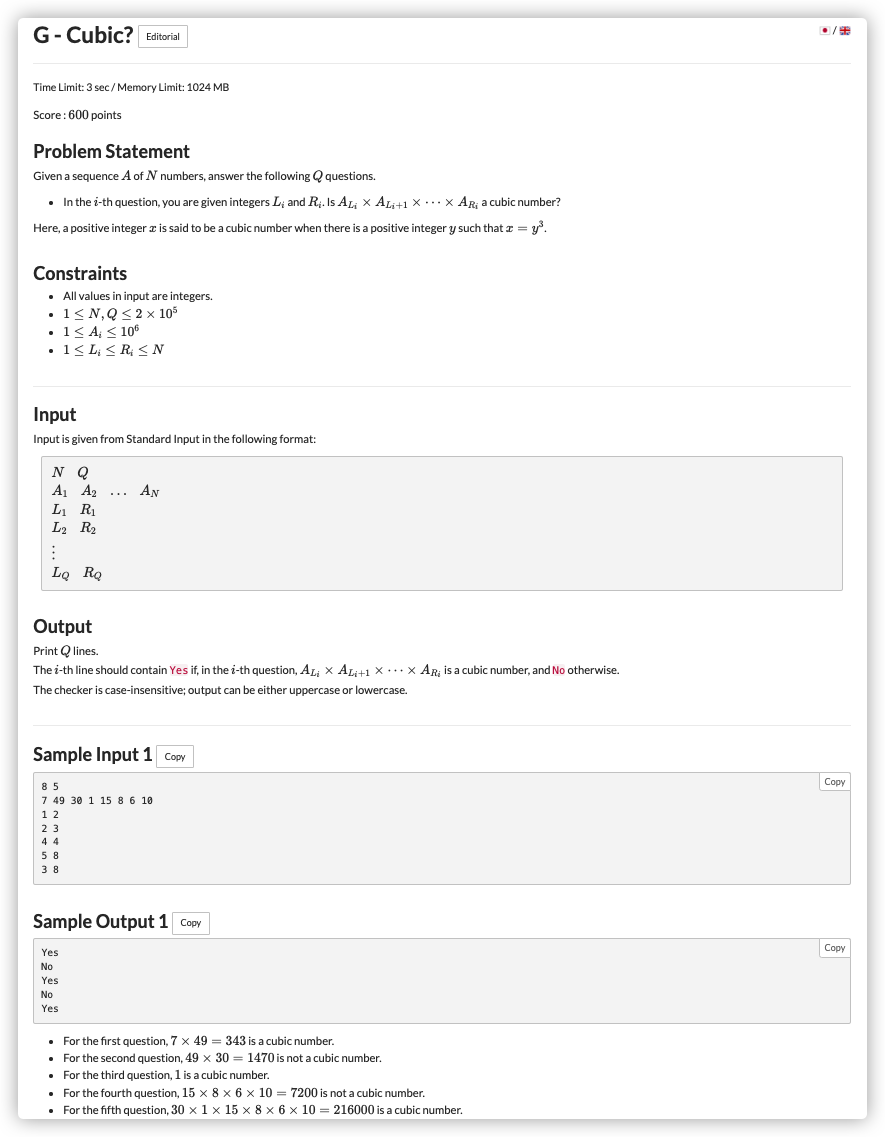
# ABC238G_Cubic?
# 🔗
# 💡
注意一下立方数的性质:分解质因数后每个质因数出现至少三的倍数次
仅有区间查询,我们可以使用莫队
对每一次移动的数,都对其质因数进行统计,如果出现操作后变得不是三的倍数,就使计数变量 ,相反的情况是
当然如果我们移动的时候都求一次,会超时
那么我们可以先对每一个位置打一个质因数表
移动的时候直接遍历这个位置的质因数表即可
带上奇偶优化,勉强卡过去
# ✅
const int N = 1e6 + 10;
namespace Number {
bool not_prime[N];
vector<ll> prime;
inline void Sieve () {
not_prime[0] = not_prime[1] = 1;
for ( int i = 2; i < N; i ++ ) {
if ( !not_prime[i] ) prime.push_back(i);
for ( ll j = 0; j < prime.size() && i * prime[j] < N; j ++ ) {
not_prime[i * prime[j]] = 1;
if ( i % prime[j] == 0 ) break;
}
}
}
inline vector<pair<ll, ll> > get_Div ( ll x ) {
vector<pair<ll, ll> > res;
for ( ll p : prime ) {
if ( p * p > x ) break;
if ( !not_prime[x] ) break;
ll num = 0;
while ( x % p == 0 ) x /= p, num ++;
if ( num ) res.push_back({p, num});
}
if ( x > 1 ) res.push_back({x, 1});
return res;
}
}
int stsz;
int cnt[N];
vector<pair<ll, ll> > divid[N];
inline void add ( int id ) {
for ( pair<ll, ll> pr : divid[id] ) {
int pre = cnt[pr.first];
cnt[pr.first] += pr.second;
int thn = cnt[pr.first];
if ( pre % 3 == 0 && thn % 3 != 0 ) stsz ++;
else if ( pre % 3 != 0 && thn % 3 == 0 ) stsz --;
}
}
inline void del ( int id ) {
for ( pair<ll, ll> pr : divid[id] ) {
int pre = cnt[pr.first];
cnt[pr.first] -= pr.second;
int thn = cnt[pr.first];
if ( pre % 3 == 0 && thn % 3 != 0 ) stsz ++;
else if ( pre % 3 != 0 && thn % 3 == 0 ) stsz --;
}
}
int n, q;
int a[N];
int len;
inline int pos ( int x ) {
return x / len;
}
struct Query {
int l, r;
int id;
inline friend bool operator < ( Query a, Query b ) {
if ( pos(a.l) != pos(b.l) ) return pos(a.l) < pos(b.l);
if ( pos(a.l) % 2 ) return a.r > b.r;
else return a.r < b.r;
}
} qry[N];
int res[N];
int main () {
Number::Sieve();
scanf("%d%d", &n, &q); len = sqrt(n);
for ( int i = 1; i <= n; i ++ )
scanf("%d", &a[i]),
divid[i] = Number::get_Div(a[i]);
for ( int i = 0; i < q; i ++ )
scanf("%d%d", &qry[i].l, &qry[i].r),
qry[i].id = i;
sort(qry, qry + q);
int L = 1, R = 0;
for ( int i = 0; i < q; i ++ ) {
while ( L < qry[i].l ) del(L ++);
while ( L > qry[i].l ) add(-- L);
while ( R > qry[i].r ) del(R --);
while ( R < qry[i].r ) add(++ R);
if ( stsz ) res[qry[i].id] = 0;
else res[qry[i].id] = 1;
}
for ( int i = 0; i < q; i ++ ) {
if ( res[i] ) puts("Yes");
else puts("No");
}
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
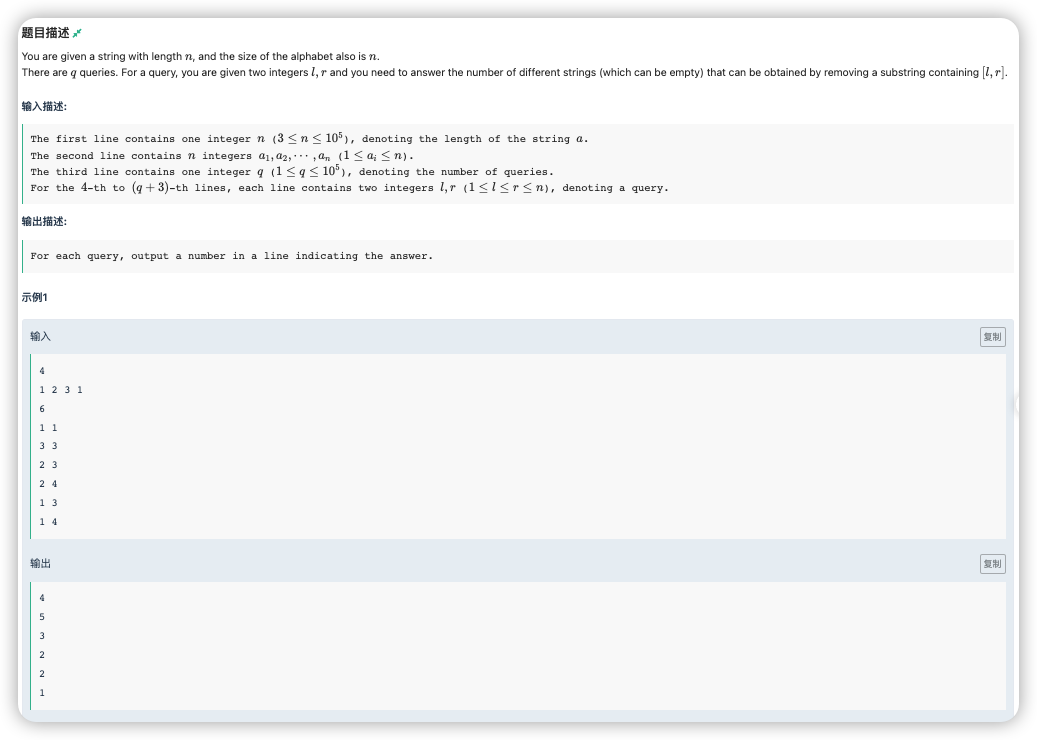
# ICPC2022昆明E_EasyStringProblem
# 🔗
# 💡
的区间问题,考虑莫队
看看在递进区间时,我们可以通过一个点得到什么需要维护的信息
要得到删去后不同串的数量比较难,正难则反,可以看看删去后相同的串的数量
删去的剩下的要相等,如果一个串两侧剩下相同的那么留谁都可以,所以定义 为右侧字符 的数量, 为左侧字符 的数量,选取区间剩余相同的数量为
所以用这个来维护莫队的动态加点删点即可
# ✅
const int N = 1e5 + 10;
struct Query {int l, r, i;} qry[N];
int n, q, sq;
int a[N];
ll res[N];
ll _res;
int num[2][N];
inline void add (int x, int op) {
num[op][a[x]] ++;
_res += num[!op][a[x]];
}
inline void del (int x, int op) {
num[op][a[x]] --;
_res -= num[!op][a[x]];
}
inline int p (int x) { return x / sq; }
int main () {
ios::sync_with_stdio(false);
cin.tie(nullptr);
cin >> n;
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i ++) cin >> a[i];
sq = sqrt(n);
cin >> q;
for (int i = 1; i <= q; i ++) cin >> qry[i].l >> qry[i].r, qry[i].i = i;
sort(qry + 1, qry + 1 + q, [&](Query a, Query b) {
if (p(a.l) != p(b.l)) return a.l < b.l;
if (p(a.l) & 1) return a.r < b.r;
return a.r > b.r;
});
int L = 1, R = n;
for (int i = 1; i <= q; i ++) {
while (L < qry[i].l) del(L ++, 0);
while (L > qry[i].l) add(-- L, 0);
while (R < qry[i].r) add(++ R, 1);
while (R > qry[i].r) del(R --, 1);
res[qry[i].i] = 1ll * L * (n - R + 1) - _res;
}
for (int i = 1; i <= q; i ++) cout << res[i] << endl;
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
# HDU2021多校(2)D_ILoveCounting
# 🔗
# 💡
看到 这类二进制的比大小,可以联想到按位比,第一个不同即出大小,那么用字典树贴着 跑就行了,然后能小于的时候过去看一眼累加一下值再接着往下走
但是如果我们字典树中存的是子树的下标集然后在上面二分出 之间的数了话,很难去保证里面都是不同的,但是如果我们对于区间相同的数只插入一个的话就会方便很多,直接加就行了
区间保证只插一个的做法很经典可以用莫队来实现,开一个 数组,减的时候就如果减到零了在字典树中删除,加的时候如果加成一了就在字典树中插入
分析一下没太大的复杂度问题,优化常数
数组下标访问很慢,且看到每一个数小于 ,字典树换成二叉树来跑,即左子树为 边,右子树为 边,在这个二叉树上做字典树的操作就能优化很多下标常数了
# ✅
int t[10000007];
inline void Insert (int x, int c) {
int root = 1;
for (int i = 18; i >= 0; i --) {
root = (root << 1) + (x >> i & 1);
t[root] += c;
}
}
inline int Query (int a, int b) {
int root = 1, res = 0;
for (int i = 18; i >= 0; i --) {
int ca = a >> i & 1;
int cb = b >> i & 1;
if (cb == 1) {
res += t[root << 1 | ca];
root = root << 1 | (!ca);
} else {
root = root << 1 | ca;
}
}
return res + t[root];
}
int num[100005];
int a[100005];
inline void add (int x) {
if (!num[x]) Insert(x, 1);
num[x] ++;
}
inline void del (int x) {
num[x] --;
if (!num[x]) Insert(x, -1);
}
int n, q, sq;
inline int get (int x) {return x / sq;}
struct query {
int l, r, a, b, id;
inline friend bool operator < (query a, query b) {
if (get(a.l) != get(b.l)) return get(a.l) < get(b.l);
if (get(a.l) & 1) return a.r > b.r;
return a.r < b.r;
}
} qry[100005];
int res[100005];
int main () {
scanf("%d", &n); sq = sqrt(n);
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i ++) scanf("%d", &a[i]);
scanf("%d", &q);
for (int i = 1; i <= q; i ++) {
int l, r, a, b; scanf("%d%d%d%d", &l, &r, &a, &b);
qry[i] = {l, r, a, b, i};
}
sort(qry + 1, qry + 1 + q);
for (int L = 1, R = 0, i = 1; i <= q; i ++) {
while (L < qry[i].l) del(a[L ++]);
while (L > qry[i].l) add(a[-- L]);
while (R < qry[i].r) add(a[++ R]);
while (R > qry[i].r) del(a[R --]);
res[qry[i].id] = Query(qry[i].a, qry[i].b);
}
for (int i = 1; i <= q; i ++) printf("%d\n", res[i]);
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
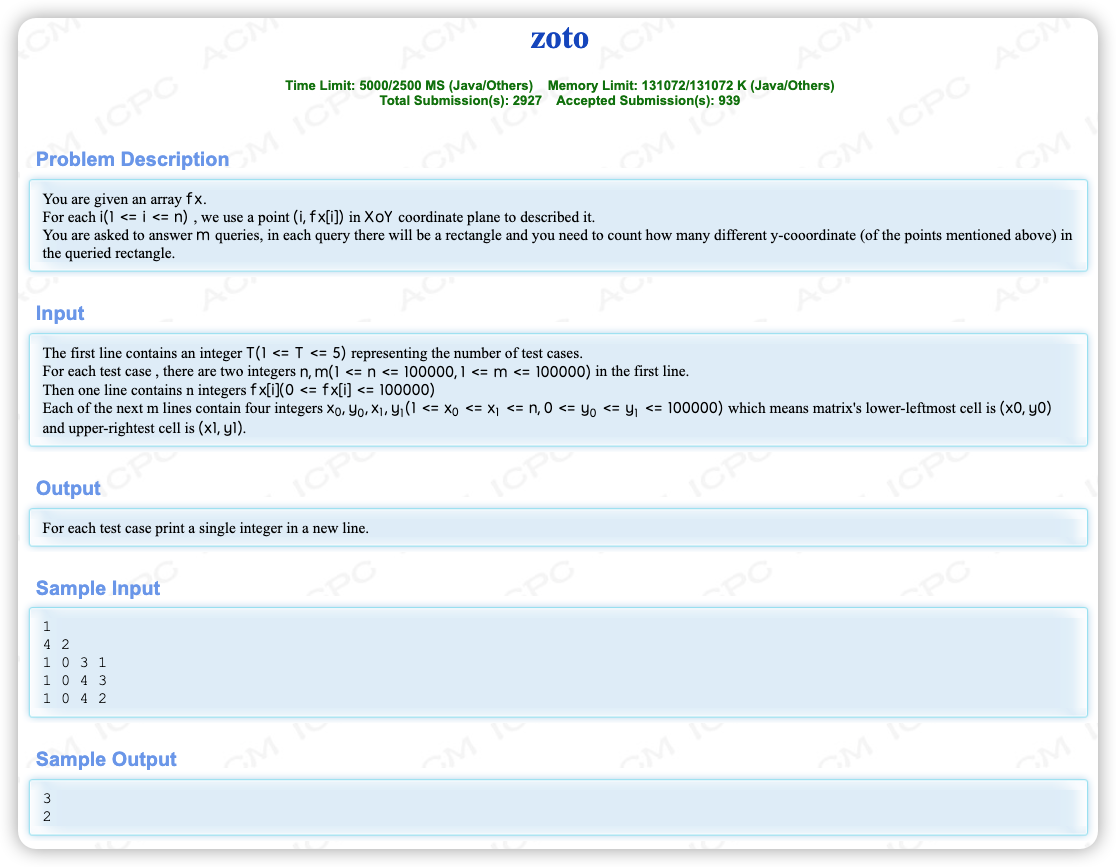
# HDU2021多校(1)J_zoto
# 🔗
# 💡
解前 $PS$
两种偏序关系,使用可持久化线段树造区间线段树吧,写了一会儿发现不行,带减法,意思是要减之后还存在的 的不同的数量,维护不了...
那么 分治的儿子纯树状数组,离线所有的点做二维前缀和,不行还是带减法...
(以上思路想和实现一共用了三个小时...)
在做不了前缀减得区间的情况下,思考另一种跑 的方式:莫队
线段树动态维护所有的 , 为零该加时插入, 为 该减时删去,对于查询求一下线段树里面 的区间和即可(TLE)
虽然它有 ,但它是 秒耶,线段树 了,试试树状数组(AC)....
(我是笨瓜)
# ✅
const int N = 2e5 + 10;
int cnt[N];
int t[N];
inline int lowbit (int x) {return x & -x;}
inline void update (int id, int va) { while (id < N) t[id] += va, id += lowbit(id);}
inline int query (int id) { int ret = 0; while (id) ret += t[id], id -= lowbit(id); return ret; }
inline int query (int l, int r) { return query(r) - query(l - 1); }
int sq;
inline int pos (int x) {return x / sq;}
struct Query {
int l, r, l1, r1, id;
inline friend bool operator < (Query a, Query b) {
if (pos(a.l) != pos(b.l)) return a.l < b.l;
if (pos(a.l) & 1) return a.r > b.r;
return a.r < b.r;
}
} qry[N];
inline void add (int x) {
if (!cnt[x]) update(x, 1);
cnt[x] ++;
}
inline void del (int x) {
cnt[x] --;
if (!cnt[x]) update(x, -1);
}
int a[N];
int res[N];
inline void Solve () {
memset(cnt, 0, sizeof cnt);
memset(t, 0, sizeof t);
int n, q; scanf("%d%d", &n, &q);
sq = sqrt(n);
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i ++) {
scanf("%d", &a[i]);
a[i] += 2;
}
for (int i = 0; i < q; i ++) {
scanf("%d%d%d%d", &qry[i].l, &qry[i].l1, &qry[i].r, &qry[i].r1), qry[i].id = i;
qry[i].l1 += 2;
qry[i].r1 += 2;
}
sort(qry, qry + q);
for (int L = 1, R = 0, i = 0; i < q; i ++) {
while (L < qry[i].l) del(a[L ++]);
while (R > qry[i].r) del(a[R --]);
while (L > qry[i].l) add(a[-- L]);
while (R < qry[i].r) add(a[++ R]);
res[qry[i].id] = query(qry[i].l1, qry[i].r1);
}
for (int i = 0; i < q; i ++) printf("%d\n", res[i]);
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
# 带修莫队
# 黑暗爆炸2120_数颜色
# 🔗
# 💡
带修莫队的模板题
add和sub也就是普通的记录一下出现次数就行
关键在于对第三个指针(时间戳)的记录
# ✅
#include <iostream>
#include <cmath>
#include <algorithm>
using namespace std;
const int N = 133350, M = 1e6 + 10;
int cnt[M], a[N], res[N];
int n, m, len;
int nq, nm, RES;
struct Q{
int l, r, t, id;
}qry[N];
struct M{
int x, y;
}mdf[N];
inline void add ( int x ) {
RES += ! cnt[x] ++;
}
inline void sub ( int x ) {
RES -= ! -- cnt[x];
}
inline int get ( int id ) {
return id / len;
}
int main () {
scanf("%d%d", &n, &m);
for ( int i = 1; i <= n; i ++ )
scanf("%d", &a[i]);
for ( int i = 1; i <= m; i ++ ) {
char op[2]; int x, y;
scanf("%s%d%d", op, &x, &y);
if ( op[0] == 'Q' ) ++ nq, qry[nq] = { x, y, nm, nq };
else ++ nm, mdf[nm] = { x, y };
}
len = cbrt ((double)n * nm) + 1;
sort ( qry + 1, qry + 1 + nm, [&]( Q a, Q b ){
if ( get(a.l) != get(b.l) ) return get(a.l) < get(b.l);
if ( get(a.r) != get(b.r) ) return get(a.r) < get(b.r);
if ( get(a.r) & 1 ) return a.t > b.t;
return a.t < b.t;
});
for ( int L = 1, R = 0, T = 0, k = 1; k <= nq; k ++ ) {
while ( L < qry[k].l ) sub ( a[L ++] );
while ( L > qry[k].l ) add ( a[-- L] );
while ( R < qry[k].r ) add ( a[++ R] );
while ( R > qry[k].r ) sub ( a[R --] );
while ( T != qry[k].t ) {
if ( T < qry[k].t ) T ++;
if ( L <= mdf[T].x && mdf[T].x <= R )
sub ( a[mdf[T].x] ),
add ( mdf[T].y );
swap ( a[mdf[T].x], mdf[T].y );
if ( T > qry[k].t ) T --;
}
res[qry[k].id] = RES;
}
for ( int i = 1; i <= nq; i ++ )
printf("%d\n", res[i]);
return 0;
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65