差分约束
#
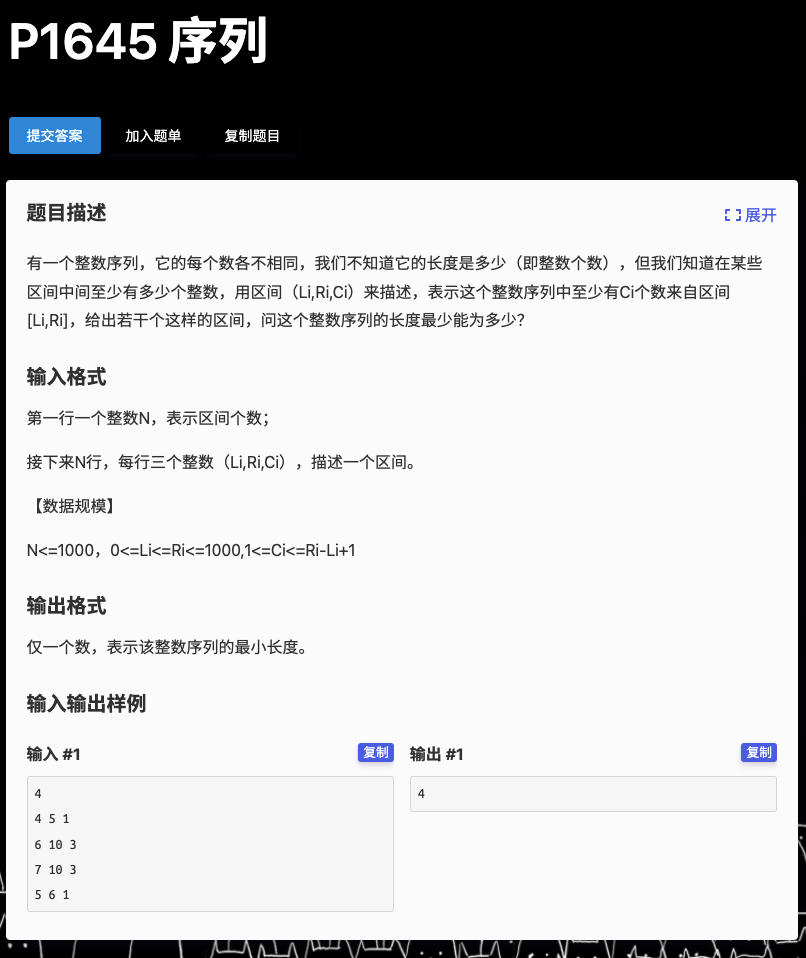
# 洛谷P1645_序列
# 🔗
# 💡
槽点
- 这个蓝题竟然是 洛谷P1250 (opens new window) 这个橙题的数据简化版
- 本意可能是贪心(虽然贪心 难度也不够),过了之后看了眼题解差分约束(好久没做差分约束了感知力下降了很多)
我们用前缀和入手
设 为 型变量的 是否被选择
为 的前缀和
那么我们可以得到约束条件
由于是问最小值,所以我们化成 后求最长路
# ✅
const int N = 1100;
const int M = 3100;
struct Edge {
int nxt, to;
int val;
} edge[M];
int head[N], cnt;
inline void add_Edge ( int from, int to, int val ) {
edge[++cnt] = { head[from], to, val };
head[from] = cnt;
}
int dis[N], vis[N];
inline void SPFA () {
for ( int i = 0; i < N; i ++ ) dis[i] = -0x3f3f3f3f;
queue<int> que;
que.push(0); vis[0] = 1; dis[0] = 0;
while ( que.size() ) {
int x = que.front(); que.pop();
vis[x] = 0;
for ( int i = head[x]; i; i = edge[i].nxt ) {
int y = edge[i].to;
if ( dis[y] < dis[x] + edge[i].val ) {
dis[y] = dis[x] + edge[i].val;
if ( !vis[y] ) vis[y] = 1, que.push(y);
}
}
}
}
int n;
int main () {
ios::sync_with_stdio(false);
cin >> n;
int mx = 0;
for ( int i = 0; i < n; i ++ ) {
int a, b, c; cin >> a >> b >> c;
add_Edge(a - 1, b, c);
mx = max(mx, b);
}
for ( int i = 0; i < mx; i ++ ) {
add_Edge(i, i + 1, 0);
add_Edge(i + 1, i, -1);
}
SPFA();
cout << dis[mx] << endl;
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
# CCPC2022上海省赛B_BracketQuery
# 🔗
# 💡
给定的区间做一下公式让它更清晰
令 为区间内左/右括号数量,则有
化简可得 ,这个是区间的数量,让相对变得绝对,换成前缀和问题
令 表示 的左括号数量 (比赛的时候用左右括号数量差的前缀和做,麻烦的要死...最终没)
则有 (必须保证 是偶数)
给定一大堆前缀和之间的差值关系,就是比较明显的并查集或者差分约束,但是并查集只可以解决是否成立的问题,构造合法解还是得差分约束
则第一个约束已经出来了:
这是给定的,按照常理一个位置不可能出两个左括号,故第二个约束
还有一个问题没有加进去,那就是最终解是一个合法括号序列,那么这就有关于每一个 的上下界
最多的时候前面都是左括号(不能超过 ),故
最少的时候前面尽可能成对,即
故第三个约束为
上面的三个约束条件统一化为 求最短路
判断是否合法。
求出来一组 后,我们要判断是否和我们已知的 成立,即在给定的时候记录 ,求完 扫描 ,看 是否等于
最后输出时由于我们 数组最多差 ,且是一组合法的前缀和,那么如果 说明 多了一个 ,否则是一个
# ✅
const int M = 1e6 + 10;
const int N = 3e3 + 10;
struct Edge {
int nxt, to, val;
} edge[M];
int head[N], cnt;
inline void add_Edge (int from, int to, int val) {
edge[++cnt] = {head[from], to, val};
head[from] = cnt;
}
int n, q;
int dis[N], vis[N], ct[N];
inline bool spfa () {
for (int i = 0; i <= n; i ++) dis[i] = 0x3f3f3f3f, vis[i] = ct[i] = 0;
deque<int> q; q.push_back(1); vis[1] = true; dis[1] = 0;
while (q.size()) {
int u = q.front(); q.pop_front();
vis[u] = false;
for (int i = head[u]; i; i = edge[i].nxt) {
int v = edge[i].to;
if (dis[v] > dis[u] + edge[i].val) {
dis[v] = dis[u] + edge[i].val;
ct[v] = ct[u] + 1;
if (ct[v] > n) return false;
if (!vis[v]) {
vis[v] = true;
if (q.size() && dis[v] > dis[q.front()]) q.push_back(v);
else q.push_front(v);
}
}
}
}
return true;
}
# define NOOOOOO {puts("?");return 0;}
int nod[N];
inline int find (int x) { return x == nod[x] ? x : nod[x] = find(nod[x]); }
inline bool is_link (int x, int y) {
x = find(x), y = find(y);
if (x == y) return true;
nod[x] = y;
return false;
}
int dif[N][N];
int main () {
for (int i = 0; i < N; i ++) {
nod[i] = i;
for (int j = 0; j < N; j ++) dif[i][j] = 0x3f3f3f3f;
}
scanf("%d%d", &n, &q);
for (int i = 0; i < q; i ++) {
int l, r, c; scanf("%d%d%d", &l, &r, &c);
if ((r - l + 1 + c) % 2) NOOOOOO
dif[l][r] = c;
if (!is_link(l - 1, r)) {
add_Edge(l - 1, r, (r - l + 1 + c) / 2);
add_Edge(r, l - 1, -(r - l + 1 + c) / 2);
}
}
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i ++) {
add_Edge(i - 1, i, 1);
add_Edge(i, i - 1, 0);
}
for (int i = 0; i <= n; i ++) {
add_Edge(0, i, min(n / 2, i));
add_Edge(i, 0, -(i + 1) / 2);
}
if (spfa()) {
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i ++) {
for (int j = i; j <= n; j ++) {
if (dif[i][j] == 0x3f3f3f3f) continue;
if ((j - i + 1 + dif[i][j]) / 2 != dis[j] - dis[i - 1]) NOOOOOO
}
}
printf("! ");
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i ++) {
printf("%c", "()"[dis[i] == dis[i - 1]]);
}
} else NOOOOOO
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
# HDUOJ3592_WorldExhibition
# 🔗
https://acm.dingbacode.com/showproblem.php?pid=3592
# 💡
一个比较明显的差分约束题型
前x个:a[i] b[i] c[i]
表示:b[i] - a[i] <= c[i]
后y个:a[i] b[i] c[i]
表示:b[i] - a[i] >= c[i]
求最大值,所以要跑最短路,标准化一下不等式得
x: b[i] - a[i] <= c[i]
y: a[i] - b[i] <= -c[i]
使用Bellman-Ford
1.距离无限大,-1
2.有负环,-2
3.不是1.2.就输出
# ✅
/*
________ _ ________ _
/ ______| | | | __ | | |
/ / | | | |__| | | |
| | | |___ _ _ _ ___ _ _____ | ___| ______ _____ ___ _ | |
| | | __ \ |_| | | | | | _\| | | ____| | |\ \ | __ | | _ | | _\| | | |
| | | | \ | _ | | | | | | \ | | \___ | | \ \ | |_/ _| | |_| | | | \ | | |
\ \______ | | | | | | \ |_| / | |_/ | ___/ | | | \ \ | /_ \__ | | |_/ | | |
Author : \________| |_| |_| |_| \___/ |___/|_| |_____| _________|__| \__\ |______| | | |___/|_| |_|
____| |
\_____/
*/
#include <unordered_map>
#include <algorithm>
#include <iostream>
#include <cstring>
#include <utility>
#include <string>
#include <vector>
#include <cstdio>
#include <stack>
#include <queue>
#include <cmath>
#include <map>
#include <set>
#define G 10.0
#define LNF 1e18
#define EPS 1e-6
#define PI acos(-1.0)
#define INF 0x7FFFFFFF
#define ll long long
#define ull unsigned long long
#define LOWBIT(x) ((x) & (-x))
#define LOWBD(a, x) lower_bound(a.begin(), a.end(), x) - a.begin()
#define UPPBD(a, x) upper_bound(a.begin(), a.end(), x) - a.begin()
#define TEST(a) cout << "---------" << a << "---------" << '\n'
#define CHIVAS_ int main()
#define _REGAL exit(0)
#define SP system("pause")
#define IOS ios::sync_with_stdio(false)
//#define map unordered_map
#define _int(a) int a; cin >> a
#define _ll(a) ll a; cin >> a
#define _char(a) char a; cin >> a
#define _string(a) string a; cin >> a
#define _vectorInt(a, n) vector<int>a(n); cin >> a
#define _vectorLL(a, b) vector<ll>a(n); cin >> a
#define PB(x) push_back(x)
#define ALL(a) a.begin(),a.end()
#define MEM(a, b) memset(a, b, sizeof(a))
#define EACH_CASE(cass) for (cass = readInt(); cass; cass--)
#define LS l, mid, rt << 1
#define RS mid + 1, r, rt << 1 | 1
#define GETMID (l + r) >> 1
using namespace std;
template<typename T> inline T MAX(T a, T b){return a > b? a : b;}
template<typename T> inline T MIN(T a, T b){return a > b? b : a;}
template<typename T> inline void SWAP(T &a, T &b){T tp = a; a = b; b = tp;}
template<typename T> inline T GCD(T a, T b){return b > 0? GCD(b, a % b) : a;}
template<typename T> inline void ADD_TO_VEC_int(T &n, vector<T> &vec){vec.clear(); cin >> n; for(int i = 0; i < n; i ++){T x; cin >> x, vec.PB(x);}}
template<typename T> inline pair<T, T> MaxInVector_ll(vector<T> vec){T MaxVal = -LNF, MaxId = 0;for(int i = 0; i < (int)vec.size(); i ++) if(MaxVal < vec[i]) MaxVal = vec[i], MaxId = i; return {MaxVal, MaxId};}
template<typename T> inline pair<T, T> MinInVector_ll(vector<T> vec){T MinVal = LNF, MinId = 0;for(int i = 0; i < (int)vec.size(); i ++) if(MinVal > vec[i]) MinVal = vec[i], MinId = i; return {MinVal, MinId};}
template<typename T> inline pair<T, T> MaxInVector_int(vector<T> vec){T MaxVal = -INF, MaxId = 0;for(int i = 0; i < (int)vec.size(); i ++) if(MaxVal < vec[i]) MaxVal = vec[i], MaxId = i; return {MaxVal, MaxId};}
template<typename T> inline pair<T, T> MinInVector_int(vector<T> vec){T MinVal = INF, MinId = 0;for(int i = 0; i < (int)vec.size(); i ++) if(MinVal > vec[i]) MinVal = vec[i], MinId = i; return {MinVal, MinId};}
template<typename T> inline pair<map<T, T>, vector<T> > DIV(T n){T nn = n;map<T, T> cnt;vector<T> div;for(ll i = 2; i * i <= nn; i ++){while(n % i == 0){if(!cnt[i]) div.push_back(i);cnt[i] ++;n /= i;}}if(n != 1){if(!cnt[n]) div.push_back(n);cnt[n] ++;n /= n;}return {cnt, div};}
template<typename T> vector<T>& operator-- (vector<T> &v){for (auto& i : v) --i; return v;}
template<typename T> vector<T>& operator++ (vector<T> &v){for (auto& i : v) ++i; return v;}
template<typename T> istream& operator>>(istream& is, vector<T> &v){for (auto& i : v) is >> i; return is;}
template<typename T> ostream& operator<<(ostream& os, vector<T> v){for (auto& i : v) os << i << ' '; return os;}
inline int readInt(){int X=0; bool flag=1; char ch=getchar();while(ch<'0'||ch>'9') {if(ch=='-') flag=0; ch=getchar();}while(ch>='0'&&ch<='9') {X=(X<<1)+(X<<3)+ch-'0'; ch=getchar();}if(flag) return X;return ~(X-1);}
inline int writeInt(int X){if(X<0) {putchar('-'); X=~(X-1);}int s[20],top=0;while(X) {s[++top]=X%10; X/=10;}if(!top) s[++top]=0;while(top) putchar(s[top--]+'0');}
inline ll readLL(){ll X=0; bool flag=1; char ch=getchar();while(ch<'0'||ch>'9') {if(ch=='-') flag=0; ch=getchar();}while(ch>='0'&&ch<='9') {X=(X<<1)+(X<<3)+ch-'0'; ch=getchar();}if(flag) return X;return ~(X-1); }
inline int writeLL(ll X){if(X<0) {putchar('-'); X=~(X-1);}ll s[20],top=0;while(X) {s[++top]=X%10; X/=10;}if(!top) s[++top]=0;while(top) putchar(s[top--]+'0');}
const int N = 1100, M = 21000;
int fr[M], to[M], vl[M];
int dis[N];
int n, x, y;
inline void Init(){
for(int i = 0; i < N; i ++) dis[i] = 1e9;
}
inline void DrawMap(){
n = readInt(); x = readInt(); y = readInt();
for(int i = 0; i < x; i ++) fr[i] = readInt(), to[i] = readInt(), vl[i] = readInt();
for(int i = 0; i < y; i ++) to[i + x] = readInt(), fr[i + x] = readInt(), vl[i + x] = -readInt();
}
inline void Bellman_Ford(){
dis[1] = 0;
for(int k = 1; k < n; k ++){
for(int i = 0; i < x + y; i ++){
dis[to[i]] = MIN(dis[fr[i]] + vl[i], dis[to[i]]);
}
}
if (dis[n] == 1e9) { puts("-2"); return; }//到不了,无限远
for(int i = 0; i < x + y; i ++){
if(dis[to[i]] > dis[fr[i]] + vl[i]){
puts("-1"); return;//还能松弛,有负环
}
}
writeInt(dis[n]); puts("");
}
CHIVAS_{
int cass;
EACH_CASE(cass){
Init();
DrawMap();
Bellman_Ford();
}
_REGAL;
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
99
100
101
102
103
104
105
106
107
108
109
110
111
112
113
114
115
116
117
118
119
120
121
122
123
# 洛谷2294_狡猾的商人
# 🔗
# 💡
对于给定的a,b,c
可以使用前缀和,(b)-(a-1)=c
那么就建边:
(b)-(a-1)<=c
(a-1)-(b)<=-c
即然检查正确性,那么就跑图,对于每个连通块看一下有没有负环
# ✅
const ll N = 1e2 + 10, M = 2e3 + 10;
int stt[M], tgt[M], val[M], cnt;
int dis[N], vis[N];
int n, m;
inline bool Bellman_Ford ( int x ) {
memset ( dis, 0x3f3f3f, sizeof dis ); dis[x] = 0;
for ( int k = 0; k < n - 1; k ++ )
for ( int i = 0; i < cnt; i ++ )
dis[tgt[i]] = min ( dis[tgt[i]], dis[stt[i]] + val[i] ),
vis[tgt[i]] = 1;
for ( int i = 0; i < cnt; i ++ )
if ( dis[tgt[i]] > dis[stt[i]] + val[i] )
return false;
return true;
}
int main () {
#ifndef ONLINE_JUDGE
freopen("in.in", "r", stdin);
freopen("out.out", "w", stdout);
#endif
int cass;
for ( scanf("%d", &cass); cass; cass -- ) {
scanf("%d%d", &n, &m);
cnt = 0; memset ( vis, 0, sizeof vis );
for ( int i = 0, a, b, c; i < m; i ++ )
scanf("%d%d%d", &a, &b, &c),
stt[cnt] = a - 1, tgt[cnt] = b, val[cnt ++] = c,
stt[cnt] = b, tgt[cnt] = a - 1, val[cnt ++] = -c;
dis[0] = 0;
bool flag = true;
for ( int i = 0; i <= n; i ++ ) {
if ( !vis[i] && !Bellman_Ford( i ) ) { flag = false; break; }
}
if ( flag ) puts("true");
else puts("false");
}
return 0;
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
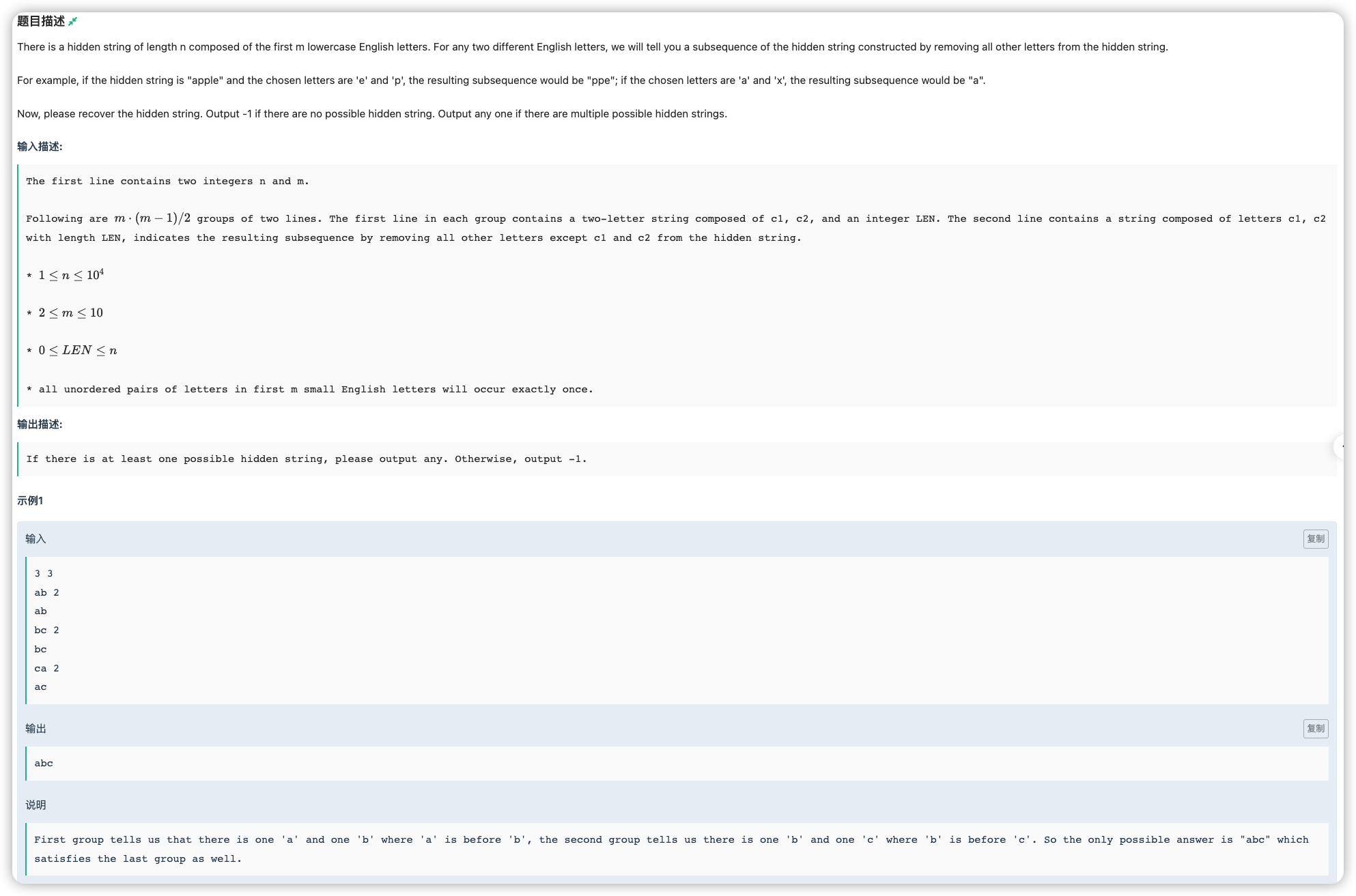
# 牛客2022国庆集训派对day3H_Subsequence2
# 🔗
# 💡
看一下给定的东西包含什么信息
- 一种字符的数量个数
- 两种字符的每一个字符的相对位置
这个相对位置就很灵性了,如果将 的第 个字符的位置映射到
在给定 的意义下,就意味着
这就是一个差分约束系统啊,如果 说明
那就用 建图就好了,对于将每一个字符每一次出现的位置映射成一个点,在跑完最短路获取到 后将每个点按 进行排序,依次输出这个点是哪个字符
但是这个 很大 与 同级,跑个 大概率寄掉,但是注意到每一个边权都是 ,故直接跑一个拓扑排序维护最短路就行了
# ✅
inline void cgets (char *s) { // 读取一行字符串
char ch;
int i = 0;
while (scanf("%c", &ch) != EOF && ch != '\n') {
s[i++] = ch;
}
s[i] = '\0';
}
const int N = 1e4 + 10;
const int M = N * 26 * 10;
int in[N * 26];
int idchar[N * 26], idx; // 第 idx 个点是哪个字符
int charid[26][N], char_num[26]; // charid[i][j]:i字符出现的第j个对应哪个点 ,char_num[i]:i字符的个数
struct Edge {
int nxt, to, val;
} edge[M];
int head[N * 26], cnt;
inline void add_Edge (int from, int to, int val) {
edge[++cnt] = {head[from], to, val};
head[from] = cnt;
in[to] ++;
}
int n, m;
int dis[N * 26];
inline bool topSort () {
for (int i = 0; i < N * 26; i ++) {
dis[i] = 0x3f3f3f3f;
}
queue<int> que;
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i ++) {
if (!in[i]) {
que.push(i);
dis[i] = 0;
}
}
while (!que.empty()) {
int u = que.front();
que.pop();
for (int i = head[u]; i; i = edge[i].nxt) {
int v = edge[i].to;
in[v] --;
dis[v] = min(dis[v], dis[u] + edge[i].val);
if (!in[v]) {
que.push(v);
}
}
}
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i ++) if (dis[i] == 0x3f3f3f3f) return false;
return true;
}
char t[4];
char s[N];
int main () {
scanf("%d%d", &n, &m);
for (int i = 0; i < m * (m - 1) / 2; i ++) {
int len;
scanf("%s%d", t, &len);
getchar(); cgets(s);
// 如果 t[0] 没获取过信息
if (!charid[t[0] - 'a'][1]) {
int id = 0;
for (int j = 0; j < len; j ++) {
if (s[j] == t[0]) {
charid[t[0] - 'a'][++id] = ++idx;
idchar[idx] = t[0] - 'a';
}
}
char_num[t[0] - 'a'] = id;
// 先是同一个字符内的大小关系
for (int j = 1; j + 1 <= id; j ++) {
add_Edge(charid[t[0] - 'a'][j + 1], charid[t[0] - 'a'][j], -1);
}
}
// 如果 t[1] 没获取过信息
if (!charid[t[1] - 'a'][1]) {
int id = 0;
for (int j = 0; j < len; j ++) {
if (s[j] == t[1]) {
charid[t[1] - 'a'][++id] = ++idx;
idchar[idx] = t[1] - 'a';
}
}
char_num[t[1] - 'a'] = id;
for (int j = 1; j + 1 <= id; j ++) {
add_Edge(charid[t[1] - 'a'][j + 1], charid[t[1] - 'a'][j], -1);
}
}
// 建边,按 s 的顺序搭建
int id1 = 0, id2 = 0;
if (s[0] == t[0]) id1 ++; else id2 ++;
for (int j = 1; j < len; j ++) {
if (s[j] == t[0]) id1 ++;
else id2 ++;
if (s[j] != s[j - 1]) {
if (s[j - 1] == t[0]) add_Edge(charid[t[1] - 'a'][id2], charid[t[0] - 'a'][id1], -1);
else add_Edge(charid[t[0] - 'a'][id1], charid[t[1] - 'a'][id2], -1);
}
}
}
if (idx != n) {
printf("-1\n");
return 0;
}
if (!topSort()) {
printf("-1\n");
} else {
vector<int> v;
for (int i = 1; i <= idx; i ++) v.push_back(i);
sort(v.begin(), v.end(), [&](int a, int b) {
return dis[a] < dis[b];
});
for (int i = 0; i < v.size(); i ++) {
printf("%c", idchar[v[i]] + 'a');
}
}
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
99
100
101
102
103
104
105
106
107
108
109
110
111
112
113
114
115
116
117
118
119
120
121
122
123
124
125
126
127
128
129
130