暴力优化
#
# 折半枚举
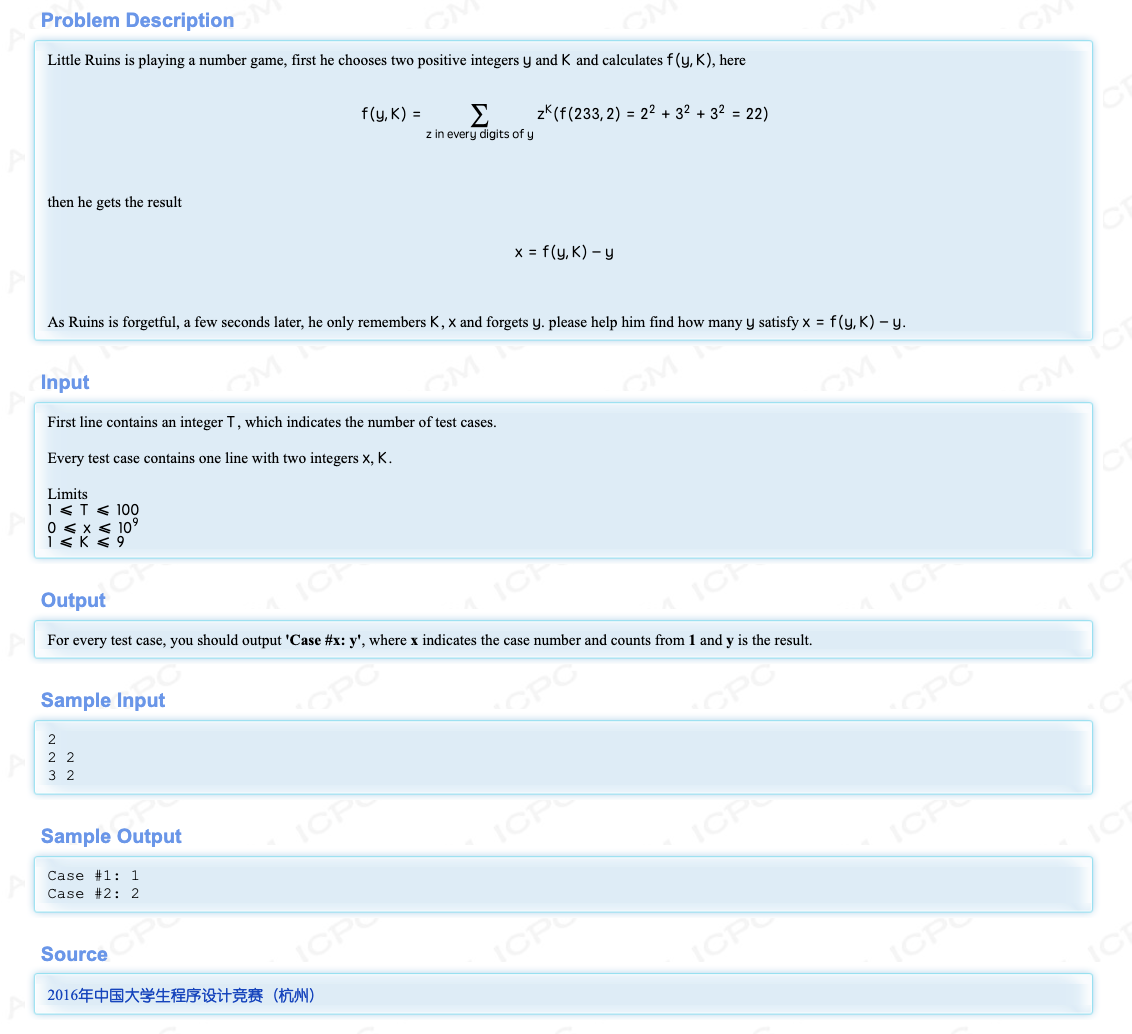
# CCPC2016杭州站D_Difference
# 🔗
# 💡
和这个题 (opens new window)的套路非常类似,本题 是十位数,因为 最大是 ,到第十位每次跳跃的范围都很大,完全补不回来
但是十位我们枚举下来也是非常过分的,考虑那个题想到的套路,我们既然走不完,就分段走
这里可以分成两个五位数,那么对于 我们拆成 和
贡献即为 和 ,就是统计有多少对 可以满足贡献和为
于是先统计 的数量,然后再遍历 ,直接去锁定 的数量,对其求和即可
# ✅
map<ll, ll> mp[10];
//ll bg[10], ed[10];
ll pw[10][10];
inline void Solve (int casid) {
int n, k; scanf("%d%d", &n, &k);
ll res = 0;
for (ll i = 0; i <= 99999; i ++) {
int ii = i;
ll f = 0;
while (ii) f += pw[ii % 10][k], ii /= 10;
ll fd = (ll)n - f + i * 100000;
//if (fd < bg[k] || fd > ed[k]) continue;
if (mp[k].count(fd)) {
res += mp[k][fd];
}
}
printf("Case #%d: %lld\n", casid, res);
}
inline ll ksm (ll a, int b) {
ll res = 1;
while (b) {
if (b & 1) res = (ll)res * a;
a = (ll)a * a;
b >>= 1;
}
return res;
}
int main () {
//for (int i = 1; i < 9; i ++) bg[i] = 2e18, ed[i] = -2e18;
for (int i = 0; i <= 9; i ++) for (int j = 1; j <= 9; j ++) pw[i][j] = ksm(i, j);
for (int i = 1; i <= 99999; i ++) {
int ii = i;
ll f[10] = {0};
while (ii) {
for (int j = 1; j < 10; j ++) f[j] += pw[ii % 10][j];
ii /= 10;
}
for (int j = 1; j < 10; j ++) {
mp[j][f[j] - i] ++;
// bg[j] = min(bg[j], f[j] - i);
// ed[j] = max(ed[j], f[j] - i);
}
}
int id = 0;
int t; scanf("%d", &t); while (t --) {
Solve(++id);
}
//cout << clock() * 1.0 / CLOCKS_PER_SEC << endl;
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
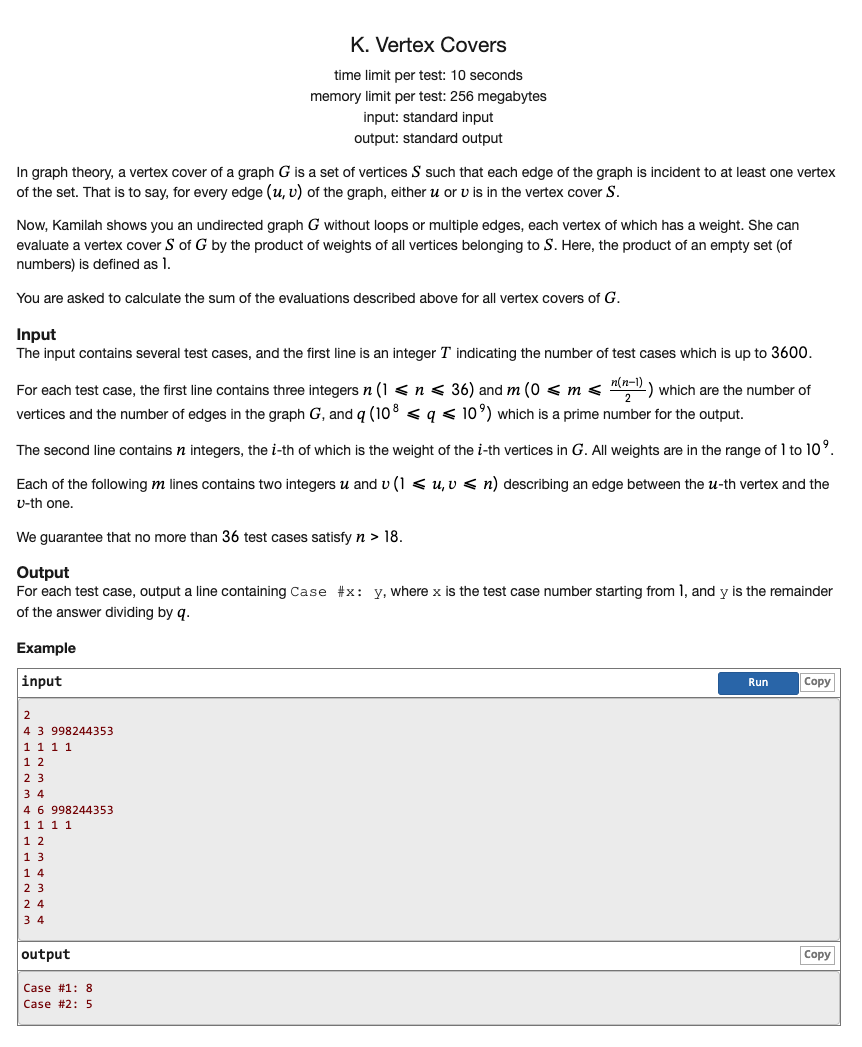
# ICPC2018银川K_VertexCovers
# 🔗
# 💡
看来还是应该多考虑 的复杂度
这里折一半之后 ,状压就可以做
首先处理出来左集合每一种情况的结果 ,处理方式为扫描左集合状态 ,在扫描左集合的点 ,对于当前 如果 ,则让当前答案乘上该点的权值,如果不在说明当且仅当集合 包含了所有与 连边的点,才可以,这里就要判断一下,如果全部包含,就继续,否则结果为
判断
判断方式可以记录一下 集合内部的连边情况,记录邻点状态,即对每一个 集合内部的点 ,如果 ,就将 加给 的邻点状态
以这样的方式处理出来两点都在 中的,都在 中的,一个在 一个在 中的
判断是否包含就直接用“与”操作看看是否为超集
每一个状态结果已经出来了,要考虑到如果 可以,那么 的所有超集也可以,故再维护一个超集和
然后就是另一半 的信息,和统计 时差不多,但是有一个要求是如果 不在 中,我们还需要保证在 集合中的邻点要都存在,故维护一个 表示我们需要的点的状态
最后在统计完乘积后,让乘积乘上 即乘上我们之前维护的超集和,累加进答案中
# ✅
const int N = 1e6 + 10;
int n, m, mod;
int a[N];
int sum[N];
int l2l[N], l2r[N], r2r[N];
inline void Solve () {
scanf("%d%d%d", &n, &m, &mod);
for (int i = 0; i < n; i ++) scanf("%d", &a[i]);
int lfn = n / 2, rtn = n - lfn;
for (int i = 0; i < 1 << lfn; i ++) l2l[i] = l2r[i] = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < 1 << rtn; i ++) r2r[i] = sum[i] = 0;
for (int i = 1; i <= m; i ++) {
int u, v; scanf("%d%d", &u, &v); u --, v --;
if (u > v) swap(u, v);
if (v < lfn) l2l[u] |= 1 << v;
else if (u >= lfn) r2r[u - lfn] |= 1 << (v - lfn);
else l2r[u] |= 1 << (v - lfn);
}
for (int s = 0; s < 1 << rtn; s ++) {
int res = 1;
for (int i = 0; i < rtn; i ++) {
if (s >> i & 1) res = 1ll * res * a[i + lfn] % mod;
else res *= (r2r[i] | s) == s;
}
sum[s] = res;
}
for (int i = 0; i < rtn; i ++) {
for (int s = 0; s < 1 << rtn; s ++) {
if (~s >> i & 1) (sum[s] += sum[s | (1 << i)]) %= mod;
}
}
int res = 0;
for (int s = 0; s < 1 << lfn; s ++) {
int need = 0, cur = 1;
for (int i = 0; i < lfn; i ++) {
if (s >> i & 1) cur = 1ll * cur * a[i] % mod;
else cur *= (l2l[i] | s) == s, need |= l2r[i];
}
(res += 1ll * cur * sum[need] % mod) %= mod;
}
printf("%d\n", res);
}
int main () {
int cass; scanf("%d", &cass);
for (int i = 1; i <= cass; i ++) {
printf("Case #%d: ", i);
Solve ();
}
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
# HDU2021多校10D_PtyHatesPrimeNumbers
# 🔗
# 💡
个质数,一眼容斥吧
依旧是遍历到 就会超,这种不大,超了一部分的,拆成两半去做
首先看看能不能处理出来前 个质数组成的所有有用信息
令前 个质数的积为 ,有一个性质是如果 可以被前八个质数整除,那么 也可以被前八个质数整除
所以这里完全可以将超过 的数压缩进
在 时我们直接容斥做就行
在 时,我们求出后八个质数的每一个容斥因子 ,那么 以内 的倍数会成为 , 是我们自带的容斥, 中的 是源于前 个, 压缩进 可以压缩成 个完整的 ,剩一个
所以我们需要知道对于 之前的,有几个不可以被前 个质数整除
直接通过埃氏筛标记后对未标记的求前缀和即可算出来 表示 中有几个不可以被前 个质数整除的
所以对于 的加操作的每一个容斥因子 ,我们累计
减操作就是
# ✅
const int N = 9699690;
int prime[] = {0, 2, 3, 5, 7, 11, 13, 17, 19, 23, 29, 31, 37, 41, 43, 47, 53};
vector<ll> add[20];
vector<ll> del[20];
inline void dfs (int idx, int cnt, ll mul, int k) {
if (idx == k + 1) {
if (cnt % 2 == 0) add[k].push_back(mul);
else del[k].push_back(mul);
return;
}
dfs(idx + 1, cnt, mul, k);
dfs(idx + 1, cnt + 1, mul * prime[idx], k);
}
int sum[N + 1];
int main () {
for (int k = 1; k <= 16; k ++) {
if (k <= 8) dfs(1, 0, 1, k);
else dfs(9, 0, 1, k);
}
for (int i = 1; i <= N; i ++) sum[i] = 1;
for (int i = 1; i <= 8; i ++) {
for (int j = prime[i]; j <= N; j += prime[i]) sum[j] = 0;
}
for (int i = 1; i <= N; i ++) sum[i] += sum[i - 1];
int cass; scanf("%d", &cass); while (cass --) {
ll n; int k; scanf("%lld%d", &n, &k);
// for (ll i : add[k]) printf("%lld ", i); puts("");
// for (ll i : del[k]) printf("%lld ", i); puts("");
ll res = 0;
if (k <= 8) {
for (ll i : add[k]) res += n / i;
for (ll i : del[k]) res -= n / i;
} else {
for (ll i : add[k]) res += n / i / N * sum[N] + sum[n / i % N];
for (ll i : del[k]) res -= n / i / N * sum[N] + sum[n / i % N];
}
printf("%lld\n", res);
}
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
# HDU2141_CanYouFindIt?
# 🔗
https://acm.dingbacode.com/showproblem.php?pid=2141
# 💡
题目让找满足 a[i] + b[j] + c[k] = x
所以我们改一下式子变成:a[i] + b[j] = x - c[k]
即我们对 a[i] + b[j] 打一个ab表
然后排序后每输入一个x
就枚举c[i]然后在ab表内二分查找元素是否存在
# ✅
/*
________ _ ________ _
/ ______| | | | __ | | |
/ / | | | |__| | | |
| | | |___ _ _ _ ___ _ _____ | ___| ______ _____ ___ _ | |
| | | __ \ |_| | | | | | _\| | | ____| | |\ \ | __ | | _ | | _\| | | |
| | | | \ | _ | | | | | | \ | | \___ | | \ \ | |_/ _| | |_| | | | \ | | |
\ \______ | | | | | | \ |_| / | |_/ | ___/ | | | \ \ | /_ \__ | | |_/ | | |
Author : \________| |_| |_| |_| \___/ |___/|_| |_____| _________|__| \__\ |______| | | |___/|_| |_|
____| |
\_____/
*/
//#include <unordered_map>
#include <algorithm>
#include <iostream>
#include <cstring>
#include <utility>
#include <string>
#include <vector>
#include <cstdio>
#include <stack>
#include <queue>
#include <cmath>
#include <map>
#include <set>
#define G 10.0
#define LNF 1e18
#define EPS 1e-6
#define PI acos(-1.0)
#define INF 0x7FFFFFFF
#define ll long long
#define ull unsigned long long
#define LOWBIT(x) ((x) & (-x))
#define LOWBD(a, x) lower_bound(a.begin(), a.end(), x) - a.begin()
#define UPPBD(a, x) upper_bound(a.begin(), a.end(), x) - a.begin()
#define TEST(a) cout << "---------" << a << "---------" << '<br>'
#define CHIVAS_ int main()
#define _REGAL exit(0)
#define SP system("pause")
#define IOS ios::sync_with_stdio(false)
//#define map unordered_map
#define PB(x) push_back(x)
#define ALL(a) a.begin(),a.end()
#define MEM(a, b) memset(a, b, sizeof(a))
#define EACH_CASE(cass) for (cass = inputInt(); cass; cass--)
#define LS l, mid, rt << 1
#define RS mid + 1, r, rt << 1 | 1
#define GETMID (l + r) >> 1
using namespace std;
/*
template<typename T> inline T MAX(T a, T b){return a > b? a : b;}
template<typename T> inline T MIN(T a, T b){return a > b? b : a;}
template<typename T> inline void SWAP(T &a, T &b){T tp = a; a = b; b = tp;}
template<typename T> inline T GCD(T a, T b){return b > 0? GCD(b, a % b) : a;}
template<typename T> inline void ADD_TO_VEC_int(T &n, vector<T> &vec){vec.clear(); cin >> n; for(int i = 0; i < n; i ++){T x; cin >> x, vec.PB(x);}}
template<typename T> inline pair<T, T> MaxInVector_ll(vector<T> vec){T MaxVal = -LNF, MaxId = 0;for(int i = 0; i < (int)vec.size(); i ++) if(MaxVal <vec[i]) MaxVal = vec[i], MaxId = i; return {MaxVal, MaxId};}
template<typename T> inline pair<T, T> MinInVector_ll(vector<T> vec){T MinVal = LNF, MinId = 0;for(int i = 0; i < (int)vec.size(); i ++) if(MinVal > vec[i])MinVal = vec[i], MinId = i; return {MinVal, MinId};}
template<typename T> inline pair<T, T> MaxInVector_int(vector<T> vec){T MaxVal = -INF, MaxId = 0;for(int i = 0; i < (int)vec.size(); i ++) if(MaxVal <vec[i]) MaxVal = vec[i], MaxId = i; return {MaxVal, MaxId};}
template<typename T> inline pair<T, T> MinInVector_int(vector<T> vec){T MinVal = INF, MinId = 0;for(int i = 0; i < (int)vec.size(); i ++) if(MinVal > vec[i])MinVal = vec[i], MinId = i; return {MinVal, MinId};}
template<typename T> inline pair<map<T, T>, vector<T> > DIV(T n){T nn = n;map<T, T> cnt;vector<T> div;for(ll i = 2; i * i <= nn; i ++){while(n % i == 0){if(!cnt[i]) div.push_back(i);cnt[i] ++;n /= i;}}if(n != 1){if(!cnt[n]) div.push_back(n);cnt[n] ++;n /= n;}return {cnt, div};}
template<typename T> vector<T>& operator-- (vector<T> &v){for (auto& i : v) --i; return v;}
template<typename T> vector<T>& operator++ (vector<T> &v){for (auto& i : v) ++i; return v;}
template<typename T> istream& operator>>(istream& is, vector<T> &v){for (auto& i : v) is >> i; return is;}
template<typename T> ostream& operator<<(ostream& os, vector<T> v){for (auto& i : v) os << i << ' '; return os;}
*/inline int inputInt(){int X=0; bool flag=1; char ch=getchar();while(ch<'0'||ch>'9') {if(ch=='-') flag=0; ch=getchar();}while(ch>='0'&&ch<='9') {X=(X<<1)+(X<<3)+ch-'0'; ch=getchar();}if(flag) return X;return ~(X-1);}
inline void outInt(int X){if(X<0) {putchar('-'); X=~(X-1);}int s[20],top=0;while(X) {s[++top]=X%10; X/=10;}if(!top) s[++top]=0;while(top) putchar(s[top--]+'0');}
inline ll inputLL(){ll X=0; bool flag=1; char ch=getchar();while(ch<'0'||ch>'9') {if(ch=='-') flag=0; ch=getchar();}while(ch>='0'&&ch<='9') {X=(X<<1)+(X<<3)+ch-'0'; ch=getchar();}if(flag) return X;return ~(X-1); }
inline void outLL(ll X){if(X<0) {putchar('-'); X=~(X-1);}ll s[20],top=0;while(X) {s[++top]=X%10; X/=10;}if(!top) s[++top]=0;while(top) putchar(s[top--]+'0');}
const int N = 550;
ll a[N], b[N], c[N];
vector<ll> ab;
ll l, n, m;
ll nQst;
int CasId;
CHIVAS_{
while ( scanf("%lld%lld%lld", &l, &n, &m) == 3 ) {
ab.clear();
for ( int i = 1; i <= l; i ++ ) a[i] = inputLL();
for ( int i = 1; i <= n; i ++ ) b[i] = inputLL();
for ( int i = 1; i <= m; i ++ ) c[i] = inputLL();
for ( int i = 1; i <= l; i ++ ) for ( int j = 1; j <= n; j ++ ) ab.push_back(a[i] + b[j]);
sort(ALL(ab));
nQst = inputLL();
printf("Case %d:\n", ++CasId);
while ( nQst -- ) {
ll x = inputLL();
bool flag = false;
for ( int i = 1; i <= m; i ++ ) {
if ( binary_search(ALL(ab), x - c[i]) ) {
flag = 1;
break;
}
}
if ( flag ) puts("YES");
else puts("NO");
}
}
_REGAL;
};
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
99
100
101
102
103
104
105
106
107
108
109
110
111
# POJ2785_4ValuesWhoseSumIs0
# 🔗
http://poj.org/problem?id=2785
# 💡
同样的,我们先枚举a[i] + b[j]并存入一个数列ab中
然后排序后枚举c[i] + d[j]
同时在数列ab中二分查找答案,用upper_bound和lower_bound模拟数字哈希过程固定其元素个数即可
# ✅
/*
________ _ ________ _
/ ______| | | | __ | | |
/ / | | | |__| | | |
| | | |___ _ _ _ ___ _ _____ | ___| ______ _____ ___ _ | |
| | | __ \ |_| | | | | | _\| | | ____| | |\ \ | __ | | _ | | _\| | | |
| | | | \ | _ | | | | | | \ | | \___ | | \ \ | |_/ _| | |_| | | | \ | | |
\ \______ | | | | | | \ |_| / | |_/ | ___/ | | | \ \ | /_ \__ | | |_/ | | |
Author : \________| |_| |_| |_| \___/ |___/|_| |_____| _________|__| \__\ |______| | | |___/|_| |_|
____| |
\_____/
*/
//#include <unordered_map>
#include <algorithm>
#include <iostream>
#include <cstring>
#include <utility>
#include <string>
#include <vector>
#include <cstdio>
#include <stack>
#include <queue>
#include <cmath>
#include <map>
#include <set>
#define G 10.0
#define LNF 1e18
#define EPS 1e-6
#define PI acos(-1.0)
#define INF 0x7FFFFFFF
#define ll long long
#define ull unsigned long long
#define LOWBIT(x) ((x) & (-x))
#define LOWBD(a, x) lower_bound(a.begin(), a.end(), x) - a.begin()
#define UPPBD(a, x) upper_bound(a.begin(), a.end(), x) - a.begin()
#define TEST(a) cout << "---------" << a << "---------" << '<br>'
#define CHIVAS_ int main()
#define _REGAL exit(0)
#define SP system("pause")
#define IOS ios::sync_with_stdio(false)
//#define map unordered_map
#define PB(x) push_back(x)
#define ALL(a) a.begin(),a.end()
#define MEM(a, b) memset(a, b, sizeof(a))
#define EACH_CASE(cass) for (cass = inputInt(); cass; cass--)
#define LS l, mid, rt << 1
#define RS mid + 1, r, rt << 1 | 1
#define GETMID (l + r) >> 1
using namespace std;
/*
template<typename T> inline T MAX(T a, T b){return a > b? a : b;}
template<typename T> inline T MIN(T a, T b){return a > b? b : a;}
template<typename T> inline void SWAP(T &a, T &b){T tp = a; a = b; b = tp;}
template<typename T> inline T GCD(T a, T b){return b > 0? GCD(b, a % b) : a;}
template<typename T> inline void ADD_TO_VEC_int(T &n, vector<T> &vec){vec.clear(); cin >> n; for(int i = 0; i < n; i ++){T x; cin >> x, vec.PB(x);}}
template<typename T> inline pair<T, T> MaxInVector_ll(vector<T> vec){T MaxVal = -LNF, MaxId = 0;for(int i = 0; i < (int)vec.size(); i ++) if(MaxVal <vec[i]) MaxVal = vec[i], MaxId = i; return {MaxVal, MaxId};}
template<typename T> inline pair<T, T> MinInVector_ll(vector<T> vec){T MinVal = LNF, MinId = 0;for(int i = 0; i < (int)vec.size(); i ++) if(MinVal > vec[i])MinVal = vec[i], MinId = i; return {MinVal, MinId};}
template<typename T> inline pair<T, T> MaxInVector_int(vector<T> vec){T MaxVal = -INF, MaxId = 0;for(int i = 0; i < (int)vec.size(); i ++) if(MaxVal <vec[i]) MaxVal = vec[i], MaxId = i; return {MaxVal, MaxId};}
template<typename T> inline pair<T, T> MinInVector_int(vector<T> vec){T MinVal = INF, MinId = 0;for(int i = 0; i < (int)vec.size(); i ++) if(MinVal > vec[i])MinVal = vec[i], MinId = i; return {MinVal, MinId};}
template<typename T> inline pair<map<T, T>, vector<T> > DIV(T n){T nn = n;map<T, T> cnt;vector<T> div;for(ll i = 2; i * i <= nn; i ++){while(n % i == 0){if(!cnt[i]) div.push_back(i);cnt[i] ++;n /= i;}}if(n != 1){if(!cnt[n]) div.push_back(n);cnt[n] ++;n /= n;}return {cnt, div};}
template<typename T> vector<T>& operator-- (vector<T> &v){for (auto& i : v) --i; return v;}
template<typename T> vector<T>& operator++ (vector<T> &v){for (auto& i : v) ++i; return v;}
template<typename T> istream& operator>>(istream& is, vector<T> &v){for (auto& i : v) is >> i; return is;}
template<typename T> ostream& operator<<(ostream& os, vector<T> v){for (auto& i : v) os << i << ' '; return os;}
*/
inline int inputInt(){int X=0; bool flag=1; char ch=getchar();while(ch<'0'||ch>'9') {if(ch=='-') flag=0; ch=getchar();}while(ch>='0'&&ch<='9') {X=(X<<1)+(X<<3)+ch-'0'; ch=getchar();}if(flag) return X;return ~(X-1);}
inline void outInt(int X){if(X<0) {putchar('-'); X=~(X-1);}int s[20],top=0;while(X) {s[++top]=X%10; X/=10;}if(!top) s[++top]=0;while(top) putchar(s[top--]+'0');}
inline ll inputLL(){ll X=0; bool flag=1; char ch=getchar();while(ch<'0'||ch>'9') {if(ch=='-') flag=0; ch=getchar();}while(ch>='0'&&ch<='9') {X=(X<<1)+(X<<3)+ch-'0'; ch=getchar();}if(flag) return X;return ~(X-1); }
inline void outLL(ll X){if(X<0) {putchar('-'); X=~(X-1);}ll s[20],top=0;while(X) {s[++top]=X%10; X/=10;}if(!top) s[++top]=0;while(top) putchar(s[top--]+'0');}
const ll N = 4010;
ll a[N], b[N], c[N], d[N];
ll cd[N * N], id;
CHIVAS_{
ll n = inputLL();
for ( ll i = 1; i <= n; i ++ ) a[i] = inputLL(), b[i] = inputLL(), c[i] = inputLL(), d[i] = inputLL();
for ( ll i = 1; i <= n; i ++ ) for ( ll j = 1; j <= n; j ++ ) cd[id ++] = -(a[i] + b[j]);
ll res = 0;
sort(cd, cd + id);
for ( ll i = 1; i <= n; i ++ ) for ( ll j = 1; j <= n; j ++ ) res += ( upper_bound(cd, cd + id, c[i] + d[j]) - cd ) - ( lower_bound(cd, cd + id, c[i] + d[j]) - cd );
outLL(res);
_REGAL;
};
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
# 对象缩减
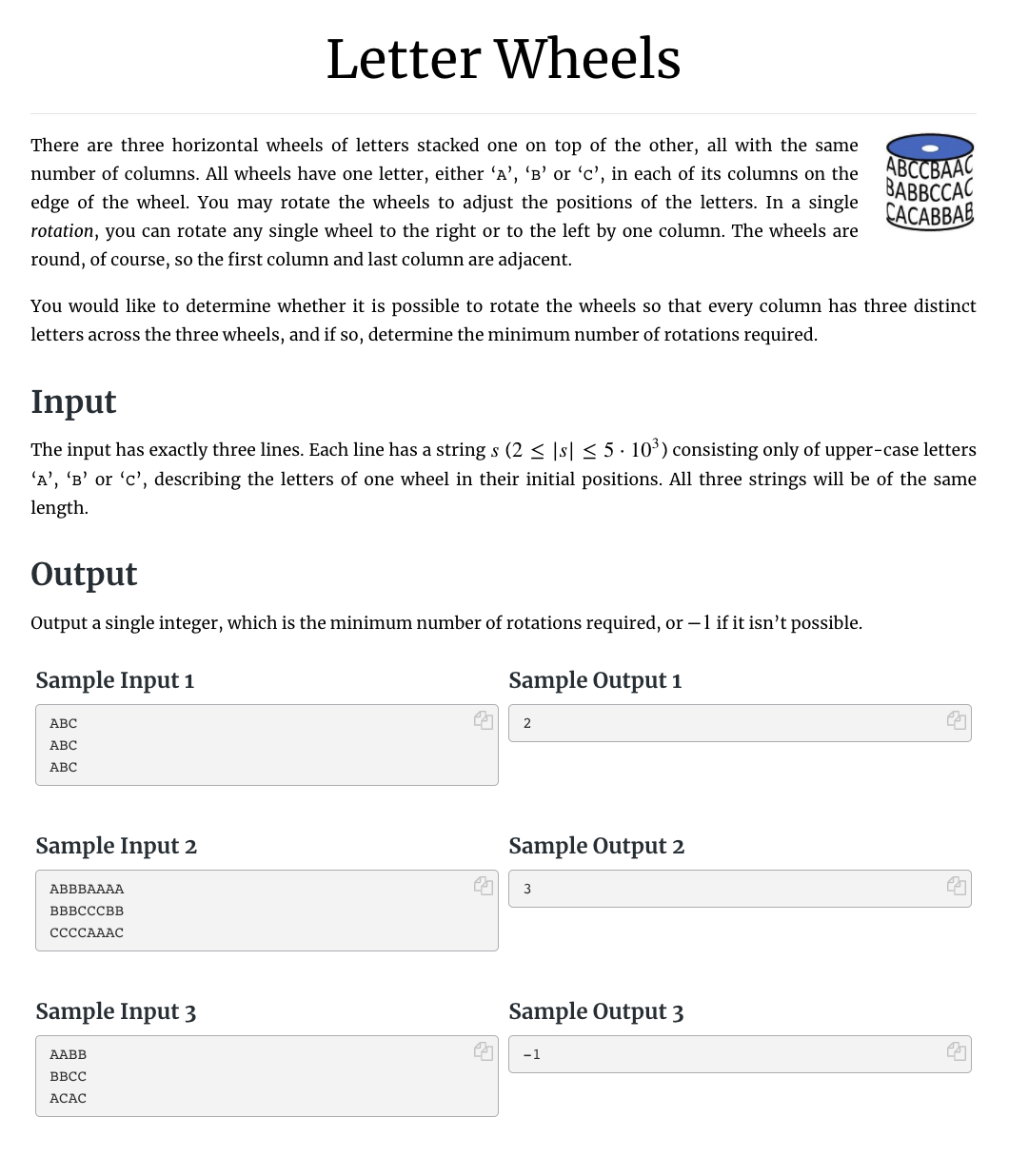
# 牛客2021训练联盟(6)I_LetterWheels
# 🔗
# 💡
首先能想到的最暴力方式:
固定s1串,然后枚举s2和s3的偏移量
一个个枚举,看是不是成立,如果成立就维护一下最小值
时间O(n^3),妥妥的TLE
那么在偏移量里面
我们要枚举双重的,不如提前建立好一个字符串偏移一定的值是不是成立
这样我们枚举一遍偏移量,然后再顺着字符串内部枚举一下在“这个偏移量之下,两个字符串之间能不能成立”
然后我们在下面维护答案的时候
枚举两个偏移量,自然就知道第三个偏移量了,就在这个基础上,如果三个字符串之间互相成立,就维护一下最小值
# ✅
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
#define INF 0x7FFFFFFF
using namespace std;
// 偏移: ->
const int N = 5e3 + 10;
int isSm[3][N]; // 0:对于1,2的偏移 1:对于2,3的偏移 2:对于1,3的偏移 =1:相同 =0:不同
int len, res = INF;
string s1, s2, s3;
int main () {
cin >> s1 >> s2 >> s3; len = s1.size();
for ( int i = 0; i < len; i ++ ) { // 偏移量
for ( int j = 0; j < len; j ++ ) { // 一位一位枚举
if ( s1[j] == s2[(i + j) % len] ) isSm[0][i] = 1;
if ( s2[j] == s3[(i + j) % len] ) isSm[1][i] = 1;
if ( s1[j] == s3[(i + j) % len] ) isSm[2][i] = 1;
}
}
for ( int i = 0; i < len; i ++ ) { // 2对于1的偏移量
for ( int j = 0; j < len; j ++ ) { // 3对于1的偏移量
if ( /*1&3*/!isSm[2][j] &&
/*2&1*/!isSm[0][i] &&
/*3&2*/!isSm[1][( j - i + len) % len] ) {
res = min(res, max(i, j));
res = min(res, max(len - i, len - j));
res = min(res, min(i, len - i) + min(j, len - j));
}
}
}
cout << (res == INF ? -1 : res) << endl;
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
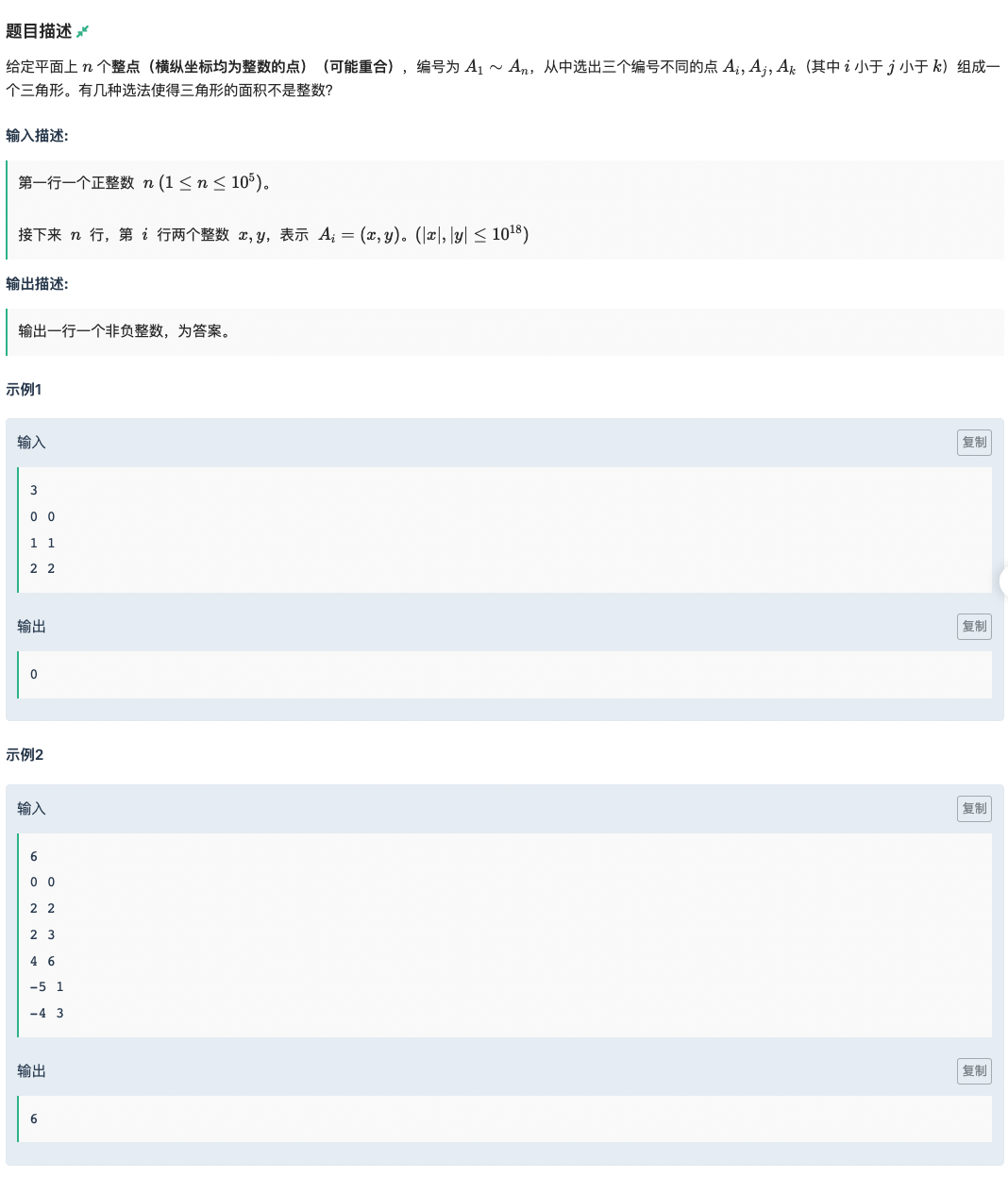
# 牛客练习赛95B_Non-interger Area
# 🔗
# 💡
矩形的面积肯定是整数,我们可以画一个三角形外接矩形的图
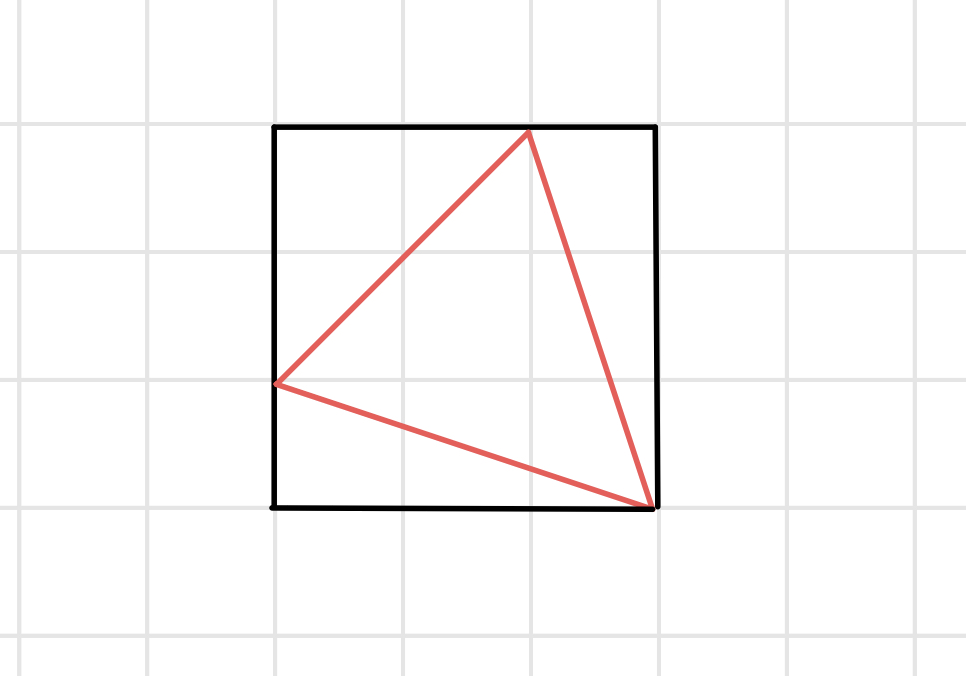
如果矩形内部三角形外部的面积总和为整数,那么这个三角形的面积也一定是整数
外面每一个三角形的面积都是 ,那么我们就要考虑奇偶了
如果三角形有两个点 是一样的奇偶性,即 同奇偶, 同奇偶
那么这三个三角形一定有一个是 偶乘偶除二
另外两个三角形是从 发射的,它的 与另外两个点的相对 的奇偶性肯定是相同或者相反
那么另外两个三角形同奇偶,他们加起来也一定是整数
所以我们需要找三个奇偶性互不相同的点
那么就不需要考虑数值了,考虑奇偶
这个可以压缩一下对象,奇数为 偶数为 ,那么我们统计一下
答案便是
# ✅
ll num[2][2];
int main () {
ios::sync_with_stdio(false);
int n; cin >> n;
for ( int i = 0; i < n; i ++ ) {
ll x, y; cin >> x >> y;
num[x & 1][y & 1] ++;
}
cout << num[1][1] * num[0][0] * (num[1][0] + num[0][1]) + num[1][0] * num[0][1] * (num[1][1] + num[0][0]);
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
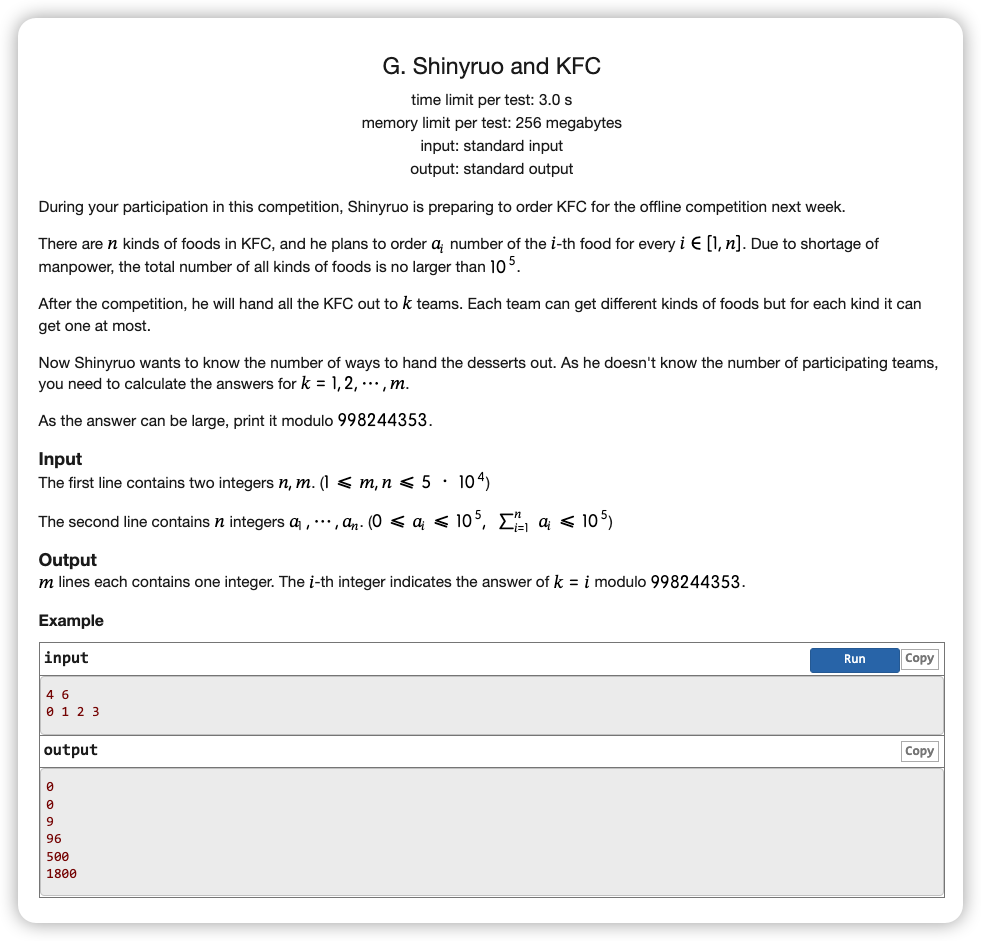
# CCPC2021威海站G_ShinyruoAndKFC
# 🔗
# 💡
比较明显的一个是在 时,会因为分不下导致一个队分了两个相同的食品,所以是
那么就只对于 时考虑
写出式子就是 ,暴力复杂度 寄了
优化一下,发现 非常小只有不到 ,这就说明会有很多重复的,且对于相同的 其 是相同的
要想没有重复也要 了,所以将对象缩减下来,然后对于每一个出现的数值求一下后算个幂即可
# ✅
const int mod = 998244353;
const int N = 1e5 + 10;
int n, m;
int f[N], ivf[N];
inline int ksm (int a, int b) {
int res = 1;
while (b) {
if (b & 1) res = (ll)res * a % mod;
a = (ll)a * a % mod;
b >>= 1;
}
return res;
}
inline int inv (int x) { return ksm(x, mod - 2); }
inline int C (int n, int m) {
return (ll)f[n] * ivf[n - m] % mod * ivf[m] % mod;
}
int a[N];
vector<int> vec;
int num[N];
int main () {
ios::sync_with_stdio(false);
cin.tie(nullptr);
f[0] = 1;
for (int i = 1; i < N; i ++) f[i] = (ll)f[i - 1] * i % mod;
ivf[N - 1] = inv(f[N - 1]);
for (int i = N - 2; i >= 0; i --) ivf[i] = (ll)ivf[i + 1] * (i + 1) % mod;
int mx = 0;
cin >> n >> m;
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i ++) {
cin >> a[i], mx = max(mx, a[i]);
if (!num[a[i]]) vec.push_back(a[i]);
num[a[i]] ++;
}
for (int k = 1; k < mx; k ++) cout << 0 << endl;
for (int k = mx; k <= m; k ++) {
int res = 1;
for (int i : vec) {
res = (ll)res * ksm(C(k, i), num[i]) % mod;
}
cout << res << endl;
}
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
# CodeForces1060C_MaximumSubrectangle
# 🔗
# 💡
首先分析问题
任意两个向量维构成的矩阵两两对应
同时子区间也能完全对应成立
所以题目就是让求a序列的某个区间和乘上b序列的某个区间和,在不超过x的情况下,两者长度相乘最大
首先区间和可以很快化为前缀和问题O(1)地减出区间和
然后可以发现,即然我们要求长度满足条件,所以我们要尽可能让ab数组的某个长度的区间和最小
这样我们才能让满足条件的区间乘起来最大
而ab的每个区间都能对应起来,所以一个区间长度的最小值就可以代表同长度的区间
处理一下ab每个长度的区间和的最小值
对象缩减为区间长度
这道题就变成了一个枚举区间长度来判断是否满足条件的问题了
# ✅
#include <iostream>
#include <algorithm>
#include <vector>
#include <cstring>
#define ll long long
using namespace std;
const ll N = 2100;
ll n, m;
ll a[N], b[N]; // 化为前缀和数组
ll lena[N], lenb[N];// lena[i]表示a的子串里面长度为i的最小值,lenb同理
ll res;
ll x;
int main () {
#ifndef ONLINE_JUDGE
freopen("../in.in", "r", stdin);
freopen("../out.out", "w", stdout);
#endif
memset(lena, 0x3f3f3f3f, sizeof lena);
memset(lenb, 0x3f3f3f3f, sizeof lenb);
cin >> n >> m;
for ( ll i = 1; i <= n; i ++ )
cin >> a[i],
a[i] += a[i - 1];
for ( ll i = 1; i <= m; i ++ )
cin >> b[i],
b[i] += b[i - 1];
// 预处理这个最小值
for ( ll len = 1; len <= n; len ++ )
for ( ll i = len; i <= n; i ++ )
lena[len] = min ( lena[len], a[i] - a[i - len] );
for ( ll len = 1; len <= m; len ++ )
for ( ll i = len; i <= m; i ++ )
lenb[len] = min ( lenb[len], b[i] - b[i - len] );
// 如果最小值对应相乘小于x,那么就可以取最大值
cin >> x;
for ( ll lna = 1; lna <= n; lna ++ )
for ( ll lnb = 1; lnb <= m; lnb ++ )
if ( lena[lna] * lenb[lnb] <= x )
res = max ( res, lna * lnb );
cout << res << endl;
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
# CodeForces1579F_ArrayStabilization(ANDversion)
# 🔗
# 💡
首先应该很明显看到的是,每一个1在遇到0后都会变成0
即一次次滚动,每滚动一次,都有一些1变成0进行下一次滚动
可以想到会有很多0具有一样的作用,所以没必要全部都算,考虑对象缩减
同层内0碰到0不用管,因为后面那个0足够有代表性:它都碰不到1,前面的那个也没必要继续走它的路;它能碰到的1也已经开始进入下一次滚动了
之前的0也不用管了,因为它们已经尽力了,每次只考虑他们中新晋的0
那么问题就成为了:
每次将上一次得到的新0进行滚动
每产生一个新0,就加入下一次滚动的数组内
下一次就利用这些新0进行滚动
如果最后没有新得到的0了就开始遍历,如果存在“漏网之1”,那么就输出-1
否则就输出滚动次数-1(最后一轮没有对碰,所以不算
# ✅
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
#include <algorithm>
#include <cstring>
#include <map>
#include <cstdio>
#include <queue>
#include <set>
#define ll long long
#define INF 0x3f3f3f3f
using namespace std;
inline void Solve () {
int n, k; scanf("%d%d", &n, &k); int a[n];
vector<int> vec;
for ( int i = 0; i < n; i ++ ) {
scanf("%d", &a[i]);
if ( !a[i] ) vec.push_back(i);
}
int res = 0;
while ( vec.size() ) {
vector<int> cur;
for ( auto i : vec ) {
int nxt = (i + k) % n;
if ( a[nxt] ) a[nxt] = 0, cur.push_back(nxt); // 新变成的0
}
vec.clear(); for ( auto i : cur ) vec.push_back(i); // 新晋的0塞入数组
res ++;
}
for ( int i = 0; i < n; i ++ ) if ( a[i] ) { printf("-1\n"); return; }
printf("%d\n", res - 1 ); // 最后一轮是没有对碰的,所以最后一轮不算
}
int main () {
#ifndef ONLINE_JUDGE
freopen("in.in", "r", stdin);
freopen("out.out", "w", stdout);
#endif
int cass;
for ( scanf("%d", &cass); cass; cass -- ) {
Solve();
}
return 0;
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
# 区间跳跃
# 洛谷P1050_循环
# 🔗
# 💡
暴力地求k位成为循环节非常麻烦
那么考虑两点:
1.每次对于一位求得循环节很简单
2.对于同一个n,k从小到大得到的结果互相有联系
首先第一个考虑:
在一位的基础上求,这一位每次乘一个数,如果十次之后不成循环就不行了
然后第二个考虑:
比如k=3时,循环节长度为len3,k=2,循环节长度为len2
len3必定是len2的倍数,因为k=3时,为了保证k=2成循环节,那么len3必定是在基于k=2上跳多少次len2
所以len3是len2的倍数
而这个倍数就是在只针对第3位时求得的结果
那么对于n就从[1,k]枚举后面的长度
每次我们可以将当前求得的这个循环节长度作为指数累放到n每次要乘的数上
这样可以实现直接跳跃过这个区间,从而保证之前算过的位保持循环节
我们就可以只专心管理当前计算的位
n = 8123, k = 4
8123 1
8123*8123=3129 2
3129*8123=6867 3
6867*8123=0641 4
0641*8123=6843 #
8123^4=0641
8123 1
8123*0641=6843 2
6843*0641=6363 3
6363*0641=8683 4
8683*0641=5803 5
5803*0641=9723 #
0641^5=9201
(注意此时最后一位就是一直不变)
8123 1
8123*9201=9723 2
9723*9201=1323 3
1323*9201=2923 4
2923*9201=4523 5
4523*9201=6123 #
9201^5=6001
(注意此时最后两位不变)
8123 1
8123*6001=6123 2
6123*6001=4123 3
4123*6001=2123 4
2123*6001=0123 5
0123*6001=8123 #
(最后就是后三位不变了)
res=4*5*5*5=500
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
当然如果在某一位出现-1了那么整个就不行
就输出-1
# ✅
public class Main {
public static BigInteger one = BigInteger.ONE;
public static BigInteger zero = BigInteger.ZERO;
public static BigInteger two = BigInteger.valueOf(2);
public static BigInteger ten = BigInteger.TEN;
public static BigInteger ksm ( BigInteger a, BigInteger b ) {
BigInteger res = BigInteger.ONE;
while ( b.compareTo(zero) == 1 ) {
if ( b.mod(two).compareTo(one) == 0 ) {
res = res.multiply(a);
}
a = a.multiply(a);
b = b.divide(two);
}
return res;
}
public static BigInteger Solve ( BigInteger n, BigInteger k, BigInteger mul /* 每次乘的数,实现跳步 */ ) { // 针对第k位得到的分解后的循环节长度
BigInteger mo = ksm(ten, k);
n = n.mod(mo);
BigInteger nn = n;
for ( int i = 1; i <= 100; i ++ ) {
n = n.multiply(mul).mod(mo);
if ( n.compareTo(nn) == 0 ) return BigInteger.valueOf(i);
}
return BigInteger.valueOf(-1);
}
public static void main (String[] args) {
Scanner input = new Scanner(System.in);
BigInteger n = input.nextBigInteger ();
BigInteger k = input.nextBigInteger ();
BigInteger lst = one; // 实时更新每一位得到的结果
BigInteger res = one; // 总答案
BigInteger cur = n; // 每次n要乘的数(区间跳跃
for ( BigInteger i = one; i.compareTo(k) <= 0; i = i.add(one) ) {
cur = ksm(cur, lst).mod(ksm(ten, k));
lst = Solve(n, i, cur);
if ( i.compareTo(k) == 0 ) {
if ( lst.compareTo(zero) < 0 ) System.out.println("-1");
else System.out.println(lst.multiply(res));
return;
}
if ( lst.compareTo(zero) < 0 ) {
System.out.println("-1");
return;
}
res = res.multiply(lst);
}
input.close();
}
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
# AcWing3639_数组延伸
# 🔗
https://www.acwing.com/problem/content/description/3639/
# 💡
暴力优化进行模拟
我们每次把一个区间压缩为一个块表示一连串相等的数
这个块由两部分组成,一部分表示这一块都是什么数和这一块有多少个数
然后我们在累加的时候对每一块的乘积(这一块所有元素的和)进行累加即可
# ✅
#pragma region
/*
________ _ ________ _
/ ______| | | | __ | | |
/ / | | | |__| | | |
| | | |___ _ _ _ ___ _ _____ | ___| ______ _____ ___ _ | |
| | | __ \ |_| | | | | | _\| | | ____| | |\ \ | __ | | _ | | _\| | | |
| | | | \ | _ | | | | | | \ | | \___ | | \ \ | |_/ _| | |_| | | | \ | | |
\ \______ | | | | | | \ |_| / | |_/ | ___/ | | | \ \ | /_ \__ | | |_/ | | |
Author : \________| |_| |_| |_| \___/ |___/|_| |_____| _________|__| \__\ |______| | | |___/|_| |_|
____| |
\_____/
*/
#include <unordered_map>
#include <algorithm>
#include <iostream>
#include <cstring>
#include <utility>
#include <string>
#include <vector>
#include <cstdio>
#include <stack>
#include <queue>
#include <cmath>
#include <map>
#include <set>
#define G 10.0
#define LNF 1e18
#define EPS 1e-6
#define PI acos(-1.0)
#define INF 0x7FFFFFFF
#define ll long long
#define ull unsigned long long
#define LOWBIT(x) ((x) & (-x))
#define LOWBD(a, x) lower_bound(a.begin(), a.end(), x) - a.begin()
#define UPPBD(a, x) upper_bound(a.begin(), a.end(), x) - a.begin()
#define TEST(a) cout << "---------" << a << "---------" << '\n'
#define CHIVAS_ int main()
#define _REGAL exit(0)
#define SP system("pause")
#define IOS ios::sync_with_stdio(false)
//#define map unordered_map
//#define push_back emplace_back
#define _int(a) int a; cin >> a
#define _ll(a) ll a; cin >> a
#define _char(a) char a; cin >> a
#define _string(a) string a; cin >> a
#define _vectorInt(a, n) vector<int>a(n); cin >> a
#define _vectorLL(a, b) vector<ll>a(n); cin >> a
#define PB(x) push_back(x)
#define ALL(a) a.begin(),a.end()
#define MEM(a, b) memset(a, b, sizeof(a))
#define EACH_CASE(cass) for (cin >> cass; cass; cass--)
#define LS l, mid, rt << 1
#define RS mid + 1, r, rt << 1 | 1
#define GETMID (l + r) >> 1
using namespace std;
template<typename T> inline void Read(T &x){T f = 1; x = 0;char s = getchar();while(s < '0' || s > '9'){if(s == '-') f = -1; s = getchar();}while('0'<=s&&s<='9'){x=(x<<3)+(x<<1)+(s^48);s=getchar();}x*=f;}
template<typename T> inline T MAX(T a, T b){return a > b? a : b;}
template<typename T> inline T MIN(T a, T b){return a > b? b : a;}
template<typename T> inline void SWAP(T &a, T &b){T tp = a; a = b; b = tp;}
template<typename T> inline T GCD(T a, T b){return b > 0? GCD(b, a % b) : a;}
template<typename T> inline void ADD_TO_VEC_int(T &n, vector<T> &vec){vec.clear(); cin >> n; for(int i = 0; i < n; i ++){T x; cin >> x, vec.PB(x);}}
template<typename T> inline pair<T, T> MaxInVector_ll(vector<T> vec){T MaxVal = -LNF, MaxId = 0;for(int i = 0; i < (int)vec.size(); i ++) if(MaxVal < vec[i]) MaxVal = vec[i], MaxId = i; return {MaxVal, MaxId};}
template<typename T> inline pair<T, T> MinInVector_ll(vector<T> vec){T MinVal = LNF, MinId = 0;for(int i = 0; i < (int)vec.size(); i ++) if(MinVal > vec[i]) MinVal = vec[i], MinId = i; return {MinVal, MinId};}
template<typename T> inline pair<T, T> MaxInVector_int(vector<T> vec){T MaxVal = -INF, MaxId = 0;for(int i = 0; i < (int)vec.size(); i ++) if(MaxVal < vec[i]) MaxVal = vec[i], MaxId = i; return {MaxVal, MaxId};}
template<typename T> inline pair<T, T> MinInVector_int(vector<T> vec){T MinVal = INF, MinId = 0;for(int i = 0; i < (int)vec.size(); i ++) if(MinVal > vec[i]) MinVal = vec[i], MinId = i; return {MinVal, MinId};}
template<typename T> inline pair<map<T, T>, vector<T> > DIV(T n){T nn = n;map<T, T> cnt;vector<T> div;for(ll i = 2; i * i <= nn; i ++){while(n % i == 0){if(!cnt[i]) div.push_back(i);cnt[i] ++;n /= i;}}if(n != 1){if(!cnt[n]) div.push_back(n);cnt[n] ++;n /= n;}return {cnt, div};}
template<typename T> vector<T>& operator-- (vector<T> &v){for (auto& i : v) --i; return v;}
template<typename T> vector<T>& operator++ (vector<T> &v){for (auto& i : v) ++i; return v;}
template<typename T> istream& operator>>(istream& is, vector<T> &v){for (auto& i : v) is >> i; return is;}
template<typename T> ostream& operator<<(ostream& os, vector<T> v){for (auto& i : v) os << i << ' '; return os;}
#pragma endregion
//全局变量
#pragma region
#pragma endregion
//主体------------------------------------------
inline void solve(){
int n; scanf("%d", &n);
int x; scanf("%d", &x);
vector<int> a;
for(int i = 0, x; i < n; i ++) scanf("%d", &x), a.push_back(x);
ll res = 0;
vector<pair<int, int> > vec;//first表示元素,second表示个数
for(int i = 0; i < n; i ++) vec.push_back({a[i], 1});//预存:a中的每一个元素都存入1个
for(int i = 0; i < vec.size(); i ++){
if(vec[i].first % x == 0)
vec.push_back({vec[i].first / x, vec[i].second * x});//之后这一块的值是当前块的值/x,个数是当前块*x,因为当前块的每一个数都可以分出来x个
else break;
}
for(int i = 0; i < vec.size(); i ++) res += vec[i].first * vec[i].second;//延伸完数组进行累加
printf("%lld\n", res);
}
CHIVAS_{
int cass;
scanf("%d", &cass);
while(cass --){
solve();
}
_REGAL;
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
99
100
101
102
103
104
105
106
107
108
109
110
111
112
113
114
115
116
117
118
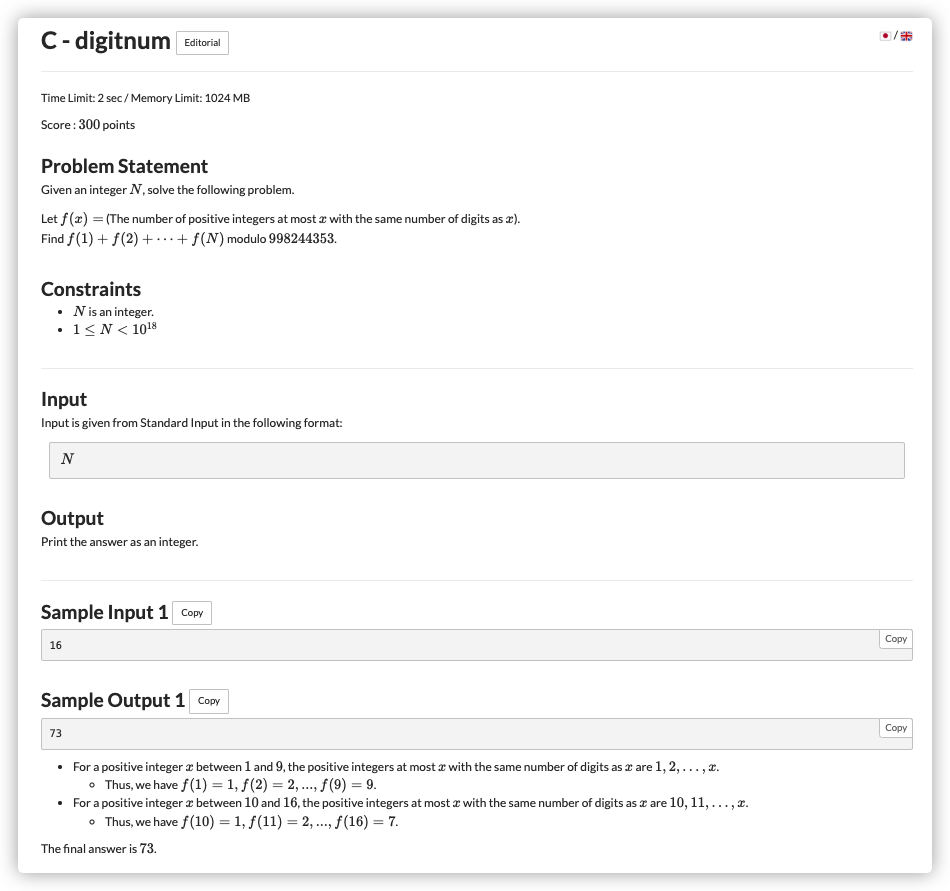
# ABC238C_Digitnum
# 🔗
# 💡
我们具像化一下公式
对于前两部分可以在同位数上一起求
- 第一部分为 的等差数列
- 第二部分为 的个数
最后求第三部分,即
本题难点2在取模上,写一个add(a,b)和sub(a,b)函数即可
# ✅
// 代码为非取模版本
int main () {
ios::sync_with_stdio(false);
ll n; cin >> n;
ll sz = to_string(n).size();
ll res = 0;
for ( ll i = 0; i < sz - 1; i ++ ) {
ll a = ksm(10, i);
ll b = ksm(10, i + 1) - 1;
res += (a + b) * (b - a + 1) / 2;
res -= (b - a + 1) * ksm(10, i);
}
ll a = ksm(10, sz - 1);
ll b = n;
res += (a + b) * (b - a + 1) / 2;
res -= (b - a + 1) * ksm(10, sz - 1);
cout << res + n << endl;
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
# CodeForces813B_TheGoldenAge
# 🔗
https://codeforces.com/problemset/problem/813/B
# 💡
本题让统计连续的unluckyNumber区间长度
那么可以在整个[l, r]序列中先把luckyNumber抠掉
然后在两个luckNumber中跳区间
同时对跳过的区间维护一下区间最长值即可
PS:要开__int128
# ✅
/*
________ _ ________ _
/ ______| | | | __ | | |
/ / | | | |__| | | |
| | | |___ _ _ _ ___ _ _____ | ___| ______ _____ ___ _ | |
| | | __ \ |_| | | | | | _\| | | ____| | |\ \ | __ | | _ | | _\| | | |
| | | | \ | _ | | | | | | \ | | \___ | | \ \ | |_/ _| | |_| | | | \ | | |
\ \______ | | | | | | \ |_| / | |_/ | ___/ | | | \ \ | /_ \__ | | |_/ | | |
Author : \________| |_| |_| |_| \___/ |___/|_| |_____| _________|__| \__\ |______| | | |___/|_| |_|
____| |
\_____/
*/
//#include <unordered_map>
#include <algorithm>
#include <iostream>
#include <cstring>
#include <utility>
#include <string>
#include <vector>
#include <cstdio>
#include <stack>
#include <queue>
#include <cmath>
#include <map>
#include <set>
#define G 10.0
#define LNF 1e18
#define EPS 1e-6
#define PI acos(-1.0)
#define INF 0x7FFFFFFF
#define ll long long
#define ull unsigned long long
#define INT __int128
#define LOWBIT(x) ((x) & (-x))
#define LOWBD(a, x) lower_bound(a.begin(), a.end(), x) - a.begin()
#define UPPBD(a, x) upper_bound(a.begin(), a.end(), x) - a.begin()
#define TEST(a) cout << "---------" << a << "---------" << '<br>'
#define CHIVAS_ int main()
#define _REGAL exit(0)
#define SP system("pause")
#define IOS ios::sync_with_stdio(false)
//#define map unordered_map
#define _int(a) int a; cin >> a
#define _ll(a) ll a; cin >> a
#define _char(a) char a; cin >> a
#define _string(a) string a; cin >> a
#define _vectorInt(a, n) vector<int>a(n); cin >> a
#define _vectorLL(a, b) vector<ll>a(n); cin >> a
#define PB(x) push_back(x)
#define ALL(a) a.begin(),a.end()
#define MEM(a, b) memset(a, b, sizeof(a))
#define EACH_CASE(cass) for (cass = inputInt(); cass; cass--)
#define LS l, mid, rt << 1
#define RS mid + 1, r, rt << 1 | 1
#define GETMID (l + r) >> 1
using namespace std;
template<typename T> inline T MAX(T a, T b){return a > b? a : b;}
template<typename T> inline T MIN(T a, T b){return a > b? b : a;}
template<typename T> inline void SWAP(T &a, T &b){T tp = a; a = b; b = tp;}
template<typename T> inline T GCD(T a, T b){return b > 0? GCD(b, a % b) : a;}
template<typename T> inline void ADD_TO_VEC_int(T &n, vector<T> &vec){vec.clear(); cin >> n; for(int i = 0; i < n; i ++){T x; cin >> x, vec.PB(x);}}
template<typename T> inline pair<T, T> MaxInVector_ll(vector<T> vec){T MaxVal = -LNF, MaxId = 0;for(int i = 0; i < (int)vec.size(); i ++) if(MaxVal < vec[i]) MaxVal = vec[i], MaxId = i; return make_pair(MaxVal, MaxId);}
template<typename T> inline pair<T, T> MinInVector_ll(vector<T> vec){T MinVal = LNF, MinId = 0;for(int i = 0; i < (int)vec.size(); i ++) if(MinVal > vec[i]) MinVal = vec[i], MinId = i; return make_pair(MinVal, MinId);}
template<typename T> inline pair<T, T> MaxInVector_int(vector<T> vec){T MaxVal = -INF, MaxId = 0;for(int i = 0; i < (int)vec.size(); i ++) if(MaxVal < vec[i]) MaxVal = vec[i], MaxId = i; return make_pair(MaxVal, MaxId);}
template<typename T> inline pair<T, T> MinInVector_int(vector<T> vec){T MinVal = INF, MinId = 0;for(int i = 0; i < (int)vec.size(); i ++) if(MinVal > vec[i]) MinVal = vec[i], MinId = i; return make_pair(MinVal, MinId);}
template<typename T> inline pair<map<T, T>, vector<T> > DIV(T n){T nn = n;map<T, T> cnt;vector<T> div;for(ll i = 2; i * i <= nn; i ++){while(n % i == 0){if(!cnt[i]) div.push_back(i);cnt[i] ++;n /= i;}}if(n != 1){if(!cnt[n]) div.push_back(n);cnt[n] ++;n /= n;}return make_pair(cnt, div);}
inline int inputInt(){int X=0; bool flag=1; char ch=getchar();while(ch<'0'||ch>'9') {if(ch=='-') flag=0; ch=getchar();}while(ch>='0'&&ch<='9') {X=(X<<1)+(X<<3)+ch-'0'; ch=getchar();}if(flag) return X;return ~(X-1);}
inline void outInt(int X){if(X<0) {putchar('-'); X=~(X-1);}int s[20],top=0;while(X) {s[++top]=X%10; X/=10;}if(!top) s[++top]=0;while(top) putchar(s[top--]+'0');}
inline ll inputLL(){ll X=0; bool flag=1; char ch=getchar();while(ch<'0'||ch>'9') {if(ch=='-') flag=0; ch=getchar();}while(ch>='0'&&ch<='9') {X=(X<<1)+(X<<3)+ch-'0'; ch=getchar();}if(flag) return X;return ~(X-1); }
inline void outLL(ll X){if(X<0) {putchar('-'); X=~(X-1);}ll s[20],top=0;while(X) {s[++top]=X%10; X/=10;}if(!top) s[++top]=0;while(top) putchar(s[top--]+'0');}
inline INT ksm(INT a, INT b) { // 快速幂
INT res = 1;
while ( b ) {
if ( b & 1 ) res = res * a;
a = a * a;
b >>= 1;
}return res;
}
CHIVAS_{
ll xx, yy, l_l, r_r; cin >> xx >> yy >> l_l >> r_r;
INT x = xx, y = yy, l = l_l, r = r_r;
vector<INT> vec;
for ( INT a = 0; ksm(x, a) <= 1e20; a ++ ) {
for ( INT b = 0; ksm(y, b) + ksm(x, a) <= 1e20; b ++ ) {
if ( ksm(x, a) + ksm(y, b) >= l &&
ksm(x, a) + ksm(y, b) <= r )
vec.push_back(ksm(x, a) + ksm(y, b)); // 将满足条件的插入到表里面
}
}
sort ( ALL(vec) );
if ( vec.size() == 0 ) { // 特判会不会根本没有数插进去
cout << (ll)(r - l + 1) << endl;
return 0;
}
INT res = vec[0] - l; // 初始为左端点到左侧第一个unlucky数
for ( INT i = 1; i < vec.size(); i ++ ) {
if ( vec[i] == vec[i - 1] ) continue; // 防止爆负数
res = MAX( res, vec[i] - vec[i - 1] - 1 ); // 对区间维护最大值
}
res = MAX ( res, r - vec.back() ); // 再维护一下右端点到右侧第一个unlucky数
cout << (ll)res << endl;
_REGAL;
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
99
100
101
102
103
104
105
106
107
108
109
110
111
112
113
114
115
116
117
118
119
120
# CodeForces1511C_YetAnotherCardDeck
# 🔗
# 💡
可以看做是一类区间跳跃
题目说过,数字编号最多到50
同时因为每次我们都把数值固定位置最前的元素移动到整个数组最前面
所以我们每次移动的就那最多50个数字
暴力就行了,一个位置的数字代表整个同数字的元素,每次挑选出那个元素x后,从1到50判断一下哪个的位置小于x,都向后推1即可
# ✅
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int n, q;
int id[51];
int main () {
cin >> n >> q;
for ( int i = 1, a; i <= n; i ++ ) {
cin >> a;
if ( !id[a] ) id[a] = i;
}
for ( int i = 1, t; i <= q; i ++ ) {
cin >> t;
cout << id[t] << " ";
for ( int j = 1; j <= 50; j ++ ) if ( id[j] < id[t] ) id[j] ++;
id[t] = 1;
}
return 0;
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
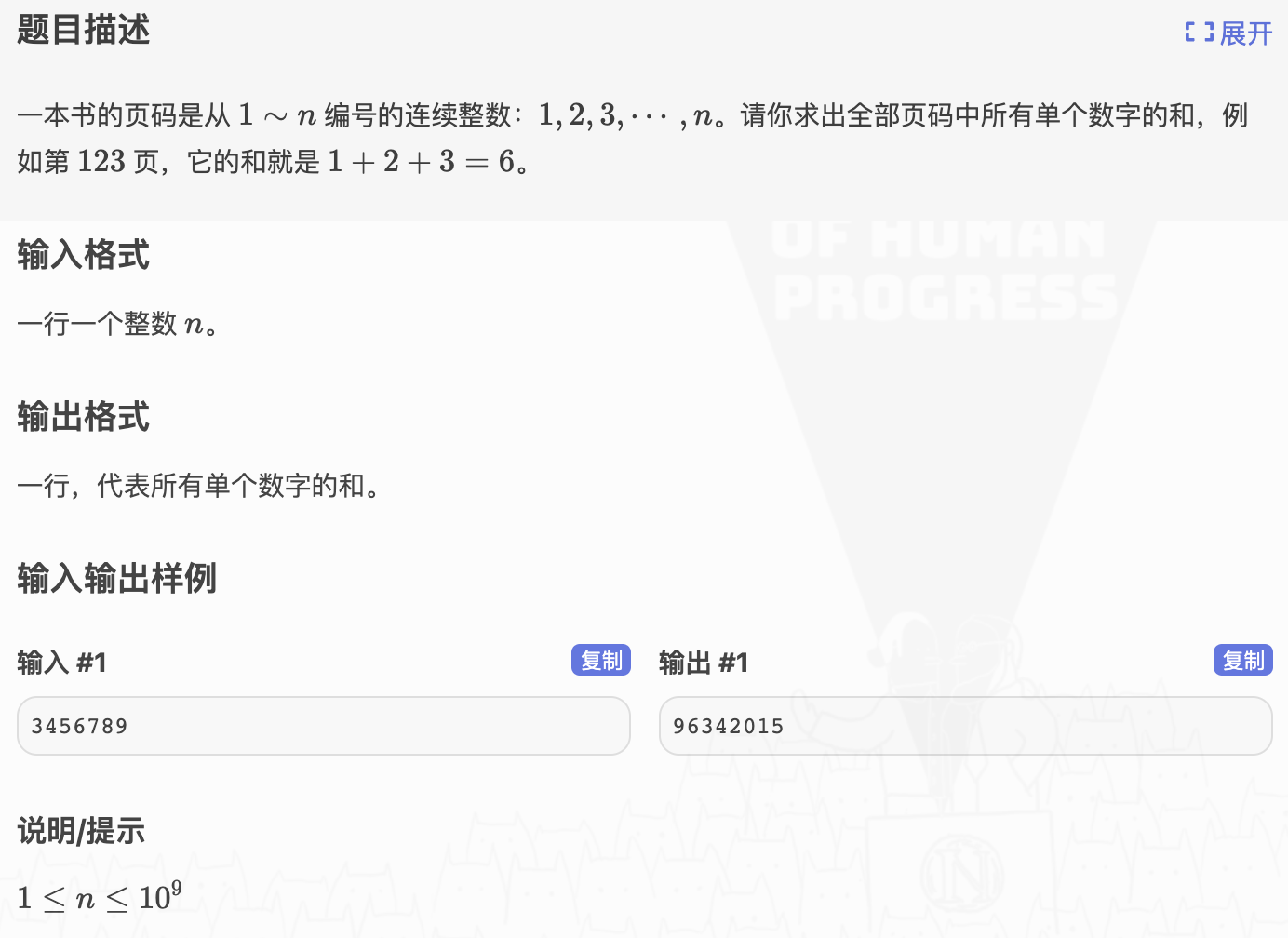
# 区间打表
# 洛谷P1836_数页码
# 🔗
# 💡
一类浅显的数位问题,可以直接分段打表
我们设置 表示 所有数的数位和
直接递推打表就可以造出来
在推 时, 会出现 次,而 会各自出现 次
所以直接
我们观测一个数
可以拆成 这样算
但是要思考好每一位上每个数出现的次数
如第一位 ,出现过 次
第二位 ,出现过 次
第三位 ,出现过 次
输入按字符串 处理
第 位也就是 会出现 次,这便是贡献:
后面的跟着第 位往上跳 次,这便是贡献:
出现次数算过了, 出现的次数也要算一下,这便是贡献:
# ✅
#### include <iostream>
#### include <vector>
#### include <map>
#### include <algorithm>
#### define ll long long
using namespace std;
ll s[15];
inline ll ksm ( ll a, ll b ) {
ll res = 1;
while ( b ) {
if ( b & 1 ) res = res * a;
a = a * a;
b >>= 1;
}
return res;
}
inline ll back_num ( string s, int id ) {
ll res = 0;
for ( int i = id + 1; i < s.size(); i ++ ) {
res = res * 10 + (s[i] - '0');
}
return res + 1;
}
int main () {
s[0] = 0;
for ( int i = 1; i <= 10; i ++ ) {
s[i] = s[i - 1] * 10 + 45 * ksm(10, i - 1);
}
ll res = 0;
string str; cin >> str;
for ( int i = 0; i < str.size(); i ++ ) {
// 贡献1:str[i] 这个数在后面出现了多少次
res += (ll)(str[i] - '0') * back_num(str, i);
// 贡献2:str[i] 后面的[0, 99...99] 跳了多少次
res += (ll)(str[i] - '0') * s[str.size() - i - 1];
// 贡献3:str[i] 以下的数出现过多少次
res += max(0, str[i] - '0' - 1) * (str[i] - '0') / 2 * ksm(10, str.size() - i - 1);
}
cout << res << endl;
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49