栈
#
# 河南萌新联赛2022(6)I_打工装货
# 🔗
# 💡
这个比较明显是 首先分析一下转移, 由于 过大这个 可以用区间查询
而里面的 则需要一个能表示出来一组可以作为区间极值的点,这就是一个典型的单调栈维护了
两组区间极值,那必然是一个单调递增栈和一个单调递减栈,在退栈的时候,对于退出的 其需要撤回的作用为新栈顶 到 这一段,它们会被更换为 , 是加法,那么应该减完原始的贡献然后加上新的贡献,即 区间减 然后加上 ,对于 则相反,因为本身是减,应该加上原始贡献再减新贡献,即 区间加 然后减 (注意着两个 是分别在不同栈下退出的栈顶)
区间减后查询区间最小值加 就是 的结果,但是注意到还有一个条件为区间和不能超过 ,这个就意味着只有有限的 可以转移到 , 用一个双指针保证 不超过 就行了,然后区间查询最小值
得到 后单点更新一下 即可
# ✅
const int N = 5e5 + 10;
struct node {
ll mn, lazy;
} t[N << 2];
inline void pushup (int rt) {
t[rt].mn = min(t[rt << 1].mn, t[rt << 1 | 1].mn);
}
inline void pushdown (int l, int r, int rt) {
if (!t[rt].lazy) return;
t[rt << 1].lazy += t[rt].lazy;
t[rt << 1 | 1].lazy += t[rt].lazy;
t[rt << 1].mn += t[rt].lazy;
t[rt << 1 | 1].mn += t[rt].lazy;
t[rt].lazy = 0;
}
inline void update (int a, int b, ll c, int l, int r, int rt) {
if (a <= l && r <= b) {
t[rt].lazy += c;
t[rt].mn += c;
return;
}
int mid = (l + r) >> 1;
pushdown(l, r, rt);
if (a <= mid) update(a, b, c, l, mid, rt << 1);
if (b > mid) update(a, b, c, mid + 1, r, rt << 1 | 1);
pushup(rt);
}
inline ll query (int a, int b, int l, int r, int rt) {
if (a <= l && r <= b) return t[rt].mn;
pushdown(l, r, rt);
int mid = (l + r) >> 1;
ll res = 1e18;
if (a <= mid) res = min(res, query(a, b, l, mid, rt << 1));
if (b > mid) res = min(res, query(a, b, mid + 1, r, rt << 1 | 1));
return res;
}
int n, m;
ll M, W;
ll w[N], sumw[N];
int stk_min[N], mintop;
int stk_max[N], maxtop;
ll dp[N];
int main () {
ios::sync_with_stdio(false);
cin.tie(nullptr);
cin >> n >> m >> M >> W;
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i ++) cin >> w[i], sumw[i] = sumw[i - 1] + w[i];
while (m --) {
int l, r; cin >> l >> r;
if (sumw[r] - sumw[l - 1] > W) cout << "N0\n";
else cout << "YE5\n";
}
int j = 0; ll sum = 0;
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i ++) {
sum += w[i]; while (sum > W) sum -= w[j ++];
while (mintop && w[stk_min[mintop]] > w[i]) {
update(stk_min[mintop - 1], stk_min[mintop] - 1, + w[stk_min[mintop]] - w[i], 0, n, 1);
mintop --;
} stk_min[++mintop] = i;
while (maxtop && w[stk_max[maxtop]] < w[i]) {
update(stk_max[maxtop - 1], stk_max[maxtop] - 1, - w[stk_max[maxtop]] + w[i], 0, n, 1);
maxtop --;
} stk_max[++maxtop] = i;
dp[i] = query(j - 1, i - 1, 0, n, 1) + M;
update(i, i, dp[i], 0, n, 1);
}
cout << dp[n] << endl;
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
# 蓝桥杯2021_双向排序
# 🔗
# 💡
首先在相同种类的操作重叠时
除了最大长度的,别的都没有作用
所以可以把操作种类变为一个个01来回跳的操作
然后还可以进行下面的优化
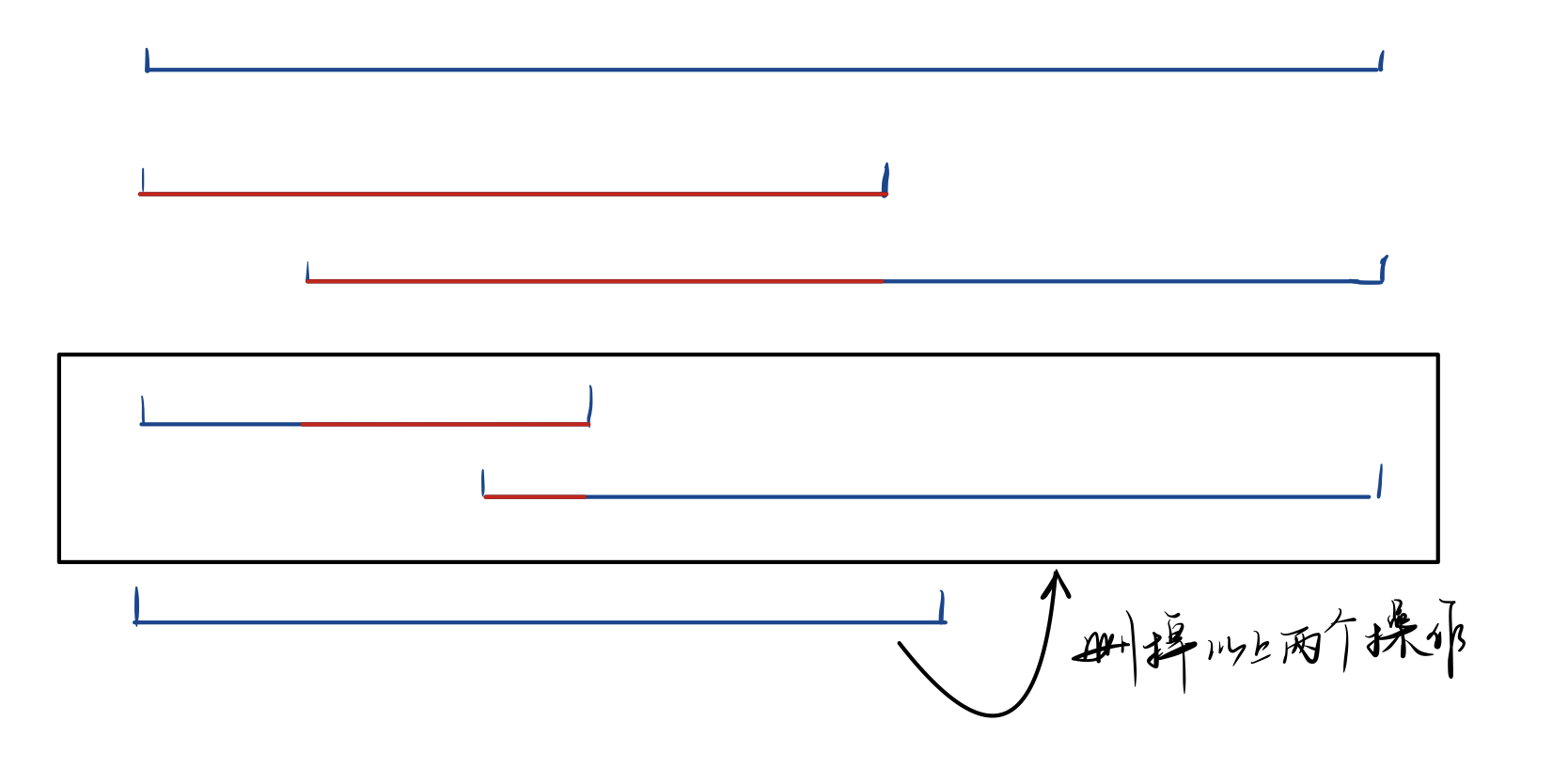 可以通过栈来维护有效操作
可以通过栈来维护有效操作
可以发现[l, r]不断缩进,那么有效操作确定之后可以进行赋值了
# ✅
#include <iostream>
#include <algorithm>
#include <vector>
#include <map>
#include <stack>
using namespace std;
const int N = 1e5 + 10;
#define x first
#define y second
#define pii pair<int, int>
int n, m;
vector<pair<int, int> > stk; // first = op, second = x
int res[N];
int main () {
#ifndef ONLINE_JUDGE
freopen("in.in", "r", stdin);
freopen("out.out", "w", stdout);
#endif
stk.push_back({0, 100});
cin >> n >> m;
while ( m -- ) {
int p, q; cin >> p >> q;
if ( p == 0 ) { // 前缀
while ( stk.size() && stk.back().x == 0 ) // 同种操作
q = max ( q, stk.back().y ),
stk.pop_back();
while ( stk.size() >= 2 && stk[stk.size() - 2].y <= q ) // 若这次操作区间覆盖了上次同类操作的区间,可以完整删掉前两次操作
stk.pop_back(),
stk.pop_back();
} else if ( stk.size() ) { // 后缀
while ( stk.size() && stk.back().x == 1 )
q = min ( q, stk.back().y ),
stk.pop_back();
while ( stk.size() >= 2 && stk[stk.size() - 2].y >= q )
stk.pop_back(),
stk.pop_back();
}
stk.push_back({p, q});
}
int k = n, l = 1, r = n;
for ( int i = 0; i < stk.size(); i ++ ) { // 一个个缩进区间并赋值
if ( stk[i].x == 0 ) {
while ( r > stk[i].y && l <= r ) res[ r -- ] = k --;
} else {
while ( l < stk[i].y && l <= r ) res[ l ++ ] = k --;
}
if ( l > r ) break;
}
if ( stk.size() % 2 ) // 漏了一个
while ( l <= r ) res[ l ++ ] = k --;
else
while ( l <= r ) res[ r -- ] = k --;
for ( int i = 1; i <= n; i ++ ) cout << res[i] << " ";
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
# GYM102174E_只有一端开口的瓶子
# 🔗
https://codeforces.com/gym/102174/problem/E
# 💡
需要知道的一个信息,一列数组必定能被两个栈排序
因为可以倒来倒去让需要的元素暴露出来
然后就是一个判断用一个栈还是两个栈的过程
如果这列数组不能被一个栈排序,我们就用两个栈
判断过程在《README.md》
# ✅
/*
________ _ ________ _
/ ______| | | | __ | | |
/ / | | | |__| | | |
| | | |___ _ _ _ ___ _ _____ | ___| ______ _____ ___ _ | |
| | | __ \ |_| | | | | | _\| | | ____| | |\ \ | __ | | _ | | _\| | | |
| | | | \ | _ | | | | | | \ | | \___ | | \ \ | |_/ _| | |_| | | | \ | | |
\ \______ | | | | | | \ |_| / | |_/ | ___/ | | | \ \ | /_ \__ | | |_/ | | |
Author : \________| |_| |_| |_| \___/ |___/|_| |_____| _________|__| \__\ |______| | | |___/|_| |_|
____| |
\_____/
*/
//#include <unordered_map>
#include <algorithm>
#include <iostream>
#include <cstring>
#include <utility>
#include <string>
#include <vector>
#include <cstdio>
#include <stack>
#include <queue>
#include <cmath>
#include <map>
#include <set>
#define G 10.0
#define LNF 1e18
#define EPS 1e-6
#define PI acos(-1.0)
#define INF 0x7FFFFFFF
#define ll long long
#define ull unsigned long long
#define LOWBIT(x) ((x) & (-x))
#define LOWBD(a, x) lower_bound(a.begin(), a.end(), x) - a.begin()
#define UPPBD(a, x) upper_bound(a.begin(), a.end(), x) - a.begin()
#define TEST(a) cout << "---------" << a << "---------" << '<br>'
#define CHIVAS_ int main()
#define _REGAL exit(0)
#define SP system("pause")
#define IOS ios::sync_with_stdio(false)
//#define map unordered_map
#define PB(x) push_back(x)
#define ALL(a) a.begin(),a.end()
#define MEM(a, b) memset(a, b, sizeof(a))
#define EACH_CASE(cass) for (cass = inputInt(); cass; cass--)
#define LS l, mid, rt << 1
#define RS mid + 1, r, rt << 1 | 1
#define GETMID (l + r) >> 1
using namespace std;
template<typename T> inline T MAX(T a, T b){return a > b? a : b;}
template<typename T> inline T MIN(T a, T b){return a > b? b : a;}
template<typename T> inline void SWAP(T &a, T &b){T tp = a; a = b; b = tp;}
template<typename T> inline T GCD(T a, T b){return b > 0? GCD(b, a % b) : a;}
template<typename T> inline void ADD_TO_VEC_int(T &n, vector<T> &vec){vec.clear(); cin >> n; for(int i = 0; i < n; i ++){T x; cin >> x, vec.PB(x);}}
template<typename T> inline pair<T, T> MaxInVector_ll(vector<T> vec){T MaxVal = -LNF, MaxId = 0;for(int i = 0; i < (int)vec.size(); i ++) if(MaxVal <vec[i]) MaxVal = vec[i], MaxId = i; return {MaxVal, MaxId};}
template<typename T> inline pair<T, T> MinInVector_ll(vector<T> vec){T MinVal = LNF, MinId = 0;for(int i = 0; i < (int)vec.size(); i ++) if(MinVal > vec[i])MinVal = vec[i], MinId = i; return {MinVal, MinId};}
template<typename T> inline pair<T, T> MaxInVector_int(vector<T> vec){T MaxVal = -INF, MaxId = 0;for(int i = 0; i < (int)vec.size(); i ++) if(MaxVal <vec[i]) MaxVal = vec[i], MaxId = i; return {MaxVal, MaxId};}
template<typename T> inline pair<T, T> MinInVector_int(vector<T> vec){T MinVal = INF, MinId = 0;for(int i = 0; i < (int)vec.size(); i ++) if(MinVal > vec[i])MinVal = vec[i], MinId = i; return {MinVal, MinId};}
template<typename T> inline pair<map<T, T>, vector<T> > DIV(T n){T nn = n;map<T, T> cnt;vector<T> div;for(ll i = 2; i * i <= nn; i ++){while(n % i == 0){if(!cnt[i]) div.push_back(i);cnt[i] ++;n /= i;}}if(n != 1){if(!cnt[n]) div.push_back(n);cnt[n] ++;n /= n;}return {cnt, div};}
template<typename T> vector<T>& operator-- (vector<T> &v){for (auto& i : v) --i; return v;}
template<typename T> vector<T>& operator++ (vector<T> &v){for (auto& i : v) ++i; return v;}
template<typename T> istream& operator>>(istream& is, vector<T> &v){for (auto& i : v) is >> i; return is;}
template<typename T> ostream& operator<<(ostream& os, vector<T> v){for (auto& i : v) os << i << ' '; return os;}
inline int inputInt(){int X=0; bool flag=1; char ch=getchar();while(ch<'0'||ch>'9') {if(ch=='-') flag=0; ch=getchar();}while(ch>='0'&&ch<='9') {X=(X<<1)+(X<<3)+ch-'0'; ch=getchar();}if(flag) return X;return ~(X-1);}
inline void outInt(int X){if(X<0) {putchar('-'); X=~(X-1);}int s[20],top=0;while(X) {s[++top]=X%10; X/=10;}if(!top) s[++top]=0;while(top) putchar(s[top--]+'0');}
inline ll inputLL(){ll X=0; bool flag=1; char ch=getchar();while(ch<'0'||ch>'9') {if(ch=='-') flag=0; ch=getchar();}while(ch>='0'&&ch<='9') {X=(X<<1)+(X<<3)+ch-'0'; ch=getchar();}if(flag) return X;return ~(X-1); }
inline void outLL(ll X){if(X<0) {putchar('-'); X=~(X-1);}ll s[20],top=0;while(X) {s[++top]=X%10; X/=10;}if(!top) s[++top]=0;while(top) putchar(s[top--]+'0');}
inline void solve ( ) {
int n = inputInt();
int a[n + 10], Want = 1;
for ( int i = 1; i <= n; i ++ ) a[i] = inputInt();
stack<int> stk;
//压栈
for ( int i = 1; i <= n; i ++ ) {
while ( stk.size() && stk.top() == Want ) Want ++, stk.pop(); // 实时抛一下
stk.push(a[i]);
}
//抛栈
while ( stk.size() && stk.top() == Want ) Want ++, stk.pop();
outInt( 1 + (!stk.empty()) );
}
CHIVAS_{
int cass;
EACH_CASE ( cass ) {
solve();
}
};
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
99
100
101
102
103
# PTA_列车厢调度
# 🔗
https://pintia.cn/problem-sets/1378951666713001984/problems/1378951732962107393
# 💡
用STL库函数以及一个期望变量对我们想要插入的元素选择合适的插入时间以及顺序
# ✅
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
vector<string>path;
int main()
{
string a;
string b;
cin>>a>>b;
string c;
int id=0;
for(int i=0;i<a.size();i++)
{
if(a[i]==b[id])
{
path.push_back("1->2");
id++;
}
else c+=a[i],path.push_back("1->3");
while(c.size()&&c[c.size()-1]==b[id]) c.erase(c.end()-1,c.end()),id++,path.push_back("3->2");
}
if(c.size())
{
printf("Are you kidding me?\n");
return 0;
}
for(int i=0;i<path.size();i++) cout<<path[i]<<endl;
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
# PTA_特殊堆栈
# 🔗
https://pintia.cn/problem-sets/1384757951243542528/problems/1384758301778305038
# 💡
使用STL库函数快速模拟栈的存储过程
# ✅
#pragma GCC optimize(3,"Ofast","inline")
#include <algorithm>
#include <iostream>
#include <cstring>
#include <string>
#include <vector>
#include <cstdio>
#include <stack>
#include <queue>
#include <cmath>
#include <map>
#include <set>
#define G 10.0
#define LNF 1e18
#define eps 1e-6
#define PI acos(-1.0)
#define ll long long
#define INF 0x7FFFFFFF
#define Regal exit(0)
#define Chivas int main()
#define pb(x) push_back(x)
#define SP system("pause")
#define Max(a,b) ((a)>(b)?(a):(b))
#define Min(a,b) ((a)<(b)?(a):(b))
#define IOS ios::sync_with_stdio(false)
#define mm(a, b) memset(a, b, sizeof(a))
#define each_cass(cass) for (cin>>cass; cass; cass--)
#define test(a) cout << "---------" << a << "---------" << '\n'
using namespace std;
inline void solve(){
int n;
cin>>n;
vector<int>vec;
vector<int>stvc;
//priority_queue<int>up;
//priority_queue<int,vector<int>,greater<int> >down;
while(n--){
string s;
cin>>s;
if(s=="Pop"){
if(vec.size()==0){
cout<<"Invalid"<<endl;
}else{
cout<<vec.back()<<endl;
int id = lower_bound(stvc.begin(),stvc.end(),vec.back())-stvc.begin();
stvc.erase(stvc.begin()+id,stvc.begin()+id+1);
vec.pop_back();
}
}else if(s=="Push"){
int x;
cin>>x;
vec.push_back(x);
if(stvc.size()){
if(x>=stvc[stvc.size()-1]) stvc.push_back(x);
else{
int id=lower_bound(stvc.begin(),stvc.end(),x)-stvc.begin();
stvc.insert(stvc.begin()+id,x);
}
}
else{
stvc.push_back(x);
}
}else{
if(vec.size()==0){
cout<<"Invalid"<<endl;
continue;
}else{
if(stvc.size() & 1) cout<<stvc[stvc.size()/2]<<endl;
else cout<<stvc[stvc.size()/2-1]<<endl;
}
}
}
}
Chivas{
solve();
Regal;
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80