最小生成树
#
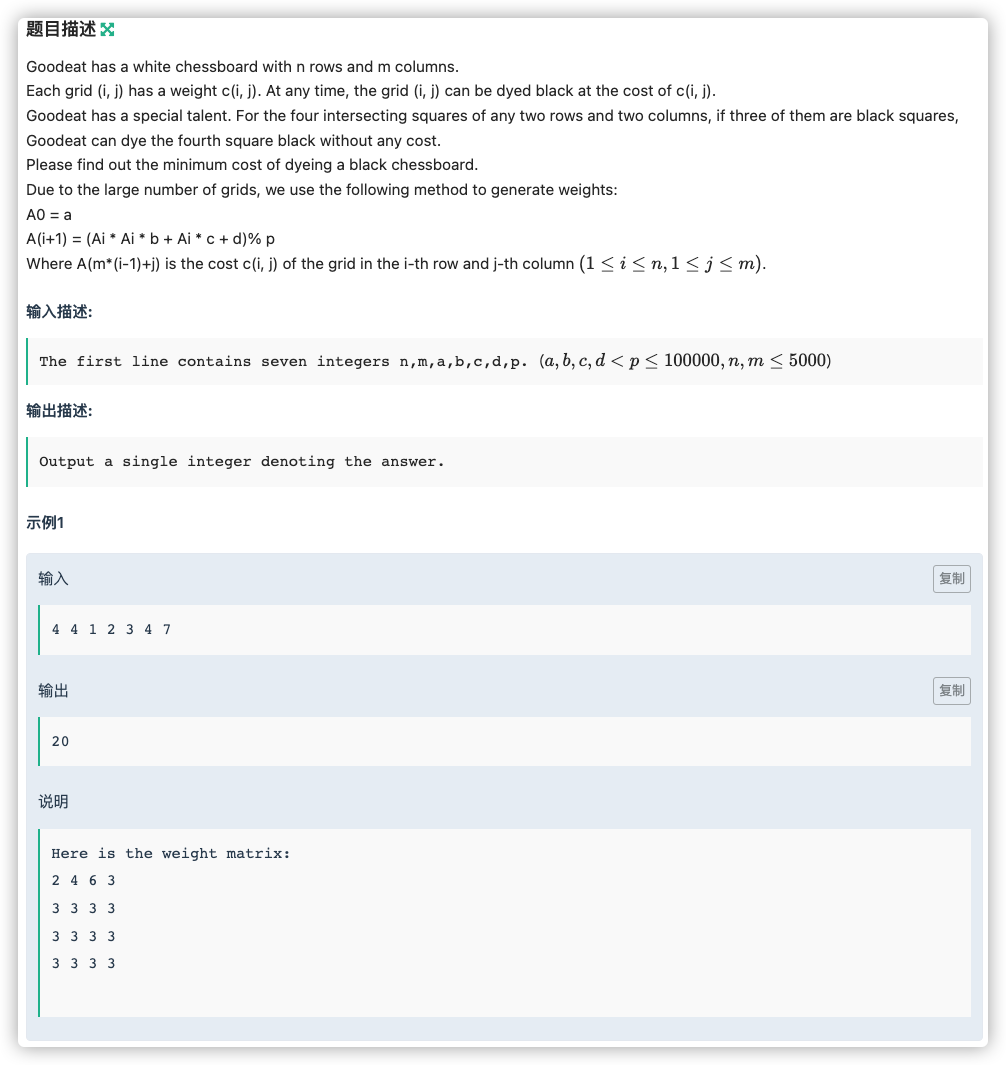
# 牛客2021多校(3)B_BlackAndWhite
# 🔗
# 💡
神仙模型~
肯定是需要尽可能去做白嫖操作,如果我们根据矩阵 的思想,在第一列和第一行都涂黑,那么剩下的都是可以白嫖的
但是一画就能发现其实把任意一行任意一列都涂黑也是可以白嫖别的所有的
关键来了,如果我们不是涂完整一行完整一列的话是否可行,类似于 的矩阵上涂 也是可以的
也就是说我们只需要涂 个就可以实现白嫖,但这可不是随便涂的啊,分析一下什么样的涂了不浪费
在有 时再涂 显然是浪费的,且注意 和 是贴着的,可以看做 和 通过 连在了一起, 和 通过 连在了一起,因此 已然连通,发现这是一个连通性问题
我们只要让所有的行和所有的列连通即可,这也对应了我们需要涂 个是为什么
故这就是一个最小生成树了, 行转化为点 , 行转化为点 ,最终目的是让 连通
# ✅
const int N = 5002 * 5002;
int nod[10004];
inline void init () { for (int i = 0; i < 10004; i ++) nod[i] = i; }
inline int find (int x) { return x == nod[x] ? x : nod[x] = find(nod[x]); }
vector<pair<int, int> > v[100005];
int A[N];
int main () {
init();
int n, m, a, b, c, d, mod;
scanf("%d%d%d%d%d%d%d", &n, &m, &a, &b, &c, &d, &mod);
A[0] = a;
for (int x = 1; x <= n; x ++) {
for (int y = 1; y <= m; y ++) {
int i = m * (x - 1) + y;
A[i] = (1ll * A[i - 1] * A[i - 1] % mod * b % mod + 1ll * A[i - 1] * c % mod + d) % mod;
v[A[i]].push_back({x, y + n});
}
}
ll res = 0, cnt = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < 100000; i ++) {
for (auto [u, v] : v[i]) {
int fu = find(u);
int fv = find(v);
if (fu == fv) continue;
res += i; cnt ++;
nod[fu] = fv;
if (cnt == n + m + 1) break;
}
if (cnt == n + m - 1) break;
}
printf("%lld\n", res);
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
# ABC235E_MST+1
# 🔗
# 💡
回想一下 kruskal 树的构建过程
从权值小到大枚举边,如果不构成回路就插入
那么我们可以对固定的边和询问的边分别排个序
从权值小到大枚举询问边
递进地让每个小于当前询问边的所有点都按 kruskal 的构建方式进行构建
对于当前询问的边,如果插进去不具有回路,那么证明这个边是可以存在于最小生成树的,反之不行。
这样我们就可以离线地求出所有询问边的答案了,然后把它按顺序输出即可
# ✅
const int N = 2e5 + 10;
int n, m, q;
struct Query {
int a, b, l;
bool res;
int id;
inline friend bool operator < ( Query a, Query b ) {
return a.l < b.l;
}
} qry[N], edg[N];
int nod[N];
inline int Find ( int x ) {
return x == nod[x] ? x : nod[x] = Find(nod[x]);
}
inline void Merge ( int x, int y ) {
int fx = Find(x), fy = Find(y);
if ( fx != fy ) nod[fx] = fy;
}
inline bool is_Similar ( int x, int y ) {
int fx = Find(x), fy = Find(y);
return fx == fy;
}
int res[N];
int main () {
for ( int i = 0; i < N; i ++ ) nod[i] = i;
scanf("%d%d%d", &n, &m, &q);
for ( int i = 0; i < m; i ++ ) {
scanf("%d%d%d", &edg[i].a, &edg[i].b, &edg[i].l);
}
for ( int i = 0; i < q; i ++ ) {
scanf("%d%d%d", &qry[i].a, &qry[i].b, &qry[i].l);
qry[i].id = i;
}
sort ( edg, edg + m );
sort ( qry, qry + q );
int ide = 0;
for ( int i = 0; i < q; i ++ ) {
while ( ide < m && edg[ide] < qry[i] ) {
if ( !is_Similar(edg[ide].a, edg[ide].b) ) {
Merge(edg[ide].a, edg[ide].b);
}
ide ++;
}
if ( is_Similar(qry[i].a, qry[i].b) ) res[qry[i].id] = false;
else res[qry[i].id] = true;
}
for ( int i = 0; i < q; i ++ ) {
if ( res[i] ) puts("Yes");
else puts("No");
}
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
# POJ1258_AgriNet
# 🔗
http://poj.org/problem?id=1258
# 💡
# ✅
//#pragma GCC optimize(3,"Ofast","inline")
#include <algorithm>
#include <iostream>
#include <cstring>
#include <string>
#include <vector>
#include <cstdio>
#include <stack>
#include <queue>
#include <cmath>
#include <map>
#include <set>
#define G 10.0
#define LNF 1e18
#define eps 1e-6
#define PI acos(-1.0)
#define ll long long
#define INF 0x7FFFFFFF
#define Regal exit(0)
#define Chivas int main()
#define pb(x) push_back(x)
#define SP system("pause")
#define Max(a,b) ((a)>(b)?(a):(b))
#define Min(a,b) ((a)<(b)?(a):(b))
#define IOS ios::sync_with_stdio(false)
#define mm(a, b) memset(a, b, sizeof(a))
#define each_cass(cass) for (cin>>cass; cass; cass--)
#define test(a) cout << "---------" << a << "---------" << '\n'
using namespace std;
const int maxn = 110;
struct Node{
int x, y;
int dis;
};
int nod[maxn];
int n;
inline bool cmp(Node a, Node b){
return a.dis < b.dis;
}
inline void init(){
for(int i = 0; i < maxn; i++) nod[i] = i;
}
inline int find(int x){
return nod[x] == x? x : nod[x] = find(nod[x]);
}
inline bool isFamily(int x, int y){
int fx = find(x);
int fy = find(y);
if(fx == fy) return true;
else return false;
}
inline void Merge(int x, int y){
int fx = find(x);
int fy = find(y);
if(fx != fy){
nod[fx] = fy;
}
}
Chivas{
while(scanf("%d", &n) == 1){
init();
vector<Node> vec;
for(int i = 1; i <= n; i++){
for(int j = 1; j <= n; j++){
int len;
scanf("%d", &len);
vec.push_back({i, j, len});
}
}
sort(vec.begin(), vec.end(), cmp);
int cnt = 0;
int sum = 0;
for(int i = 0; i < vec.size(); i++){
if(!isFamily(vec[i].x, vec[i].y))
Merge(vec[i].x, vec[i].y),
cnt++,
sum += vec[i].dis;
if(cnt == n - 1)
break;
}
printf("%d\n", sum);
}
Regal;
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
# POJ2349_ArcticNetwork
# 🔗
http://poj.org/problem?id=2349
# 💡
首先分析一下题目,我们需要让所有点连通,且可以省去 s - 1 条边
所以我们要搭建出一棵可以连通所有的点的最小生成树,并且将最大的 s - 1 条边去掉,选择这里面最大的长度
给定了各个位置的坐标,那么我们可以两两建一条边,边长也有了
剩余的就是 Kruskal 的基本操作
# ✅
/*
________ _ ________ _
/ ______| | | | __ | | |
/ / | | | |__| | | |
| | | |___ _ _ _ ___ _ _____ | ___| ______ _____ ___ _ | |
| | | __ \ |_| | | | | | _\| | | ____| | |\ \ | __ | | _ | | _\| | | |
| | | | \ | _ | | | | | | \ | | \___ | | \ \ | |_/ _| | |_| | | | \ | | |
\ \______ | | | | | | \ |_| / | |_/ | ___/ | | | \ \ | /_ \__ | | |_/ | | |
Author : \________| |_| |_| |_| \___/ |___/|_| |_____| _________|__| \__\ |______| | | |___/|_| |_|
____| |
\_____/
*/
//#include <unordered_map>
#include <algorithm>
#include <iostream>
#include <cstring>
#include <utility>
#include <string>
#include <vector>
#include <cstdio>
#include <stack>
#include <queue>
#include <cmath>
#include <map>
#include <set>
#define G 10.0
#define LNF 1e18
#define EPS 1e-6
#define PI acos(-1.0)
#define INF 0x7FFFFFFF
#define ll long long
#define ull unsigned long long
#define LOWBIT(x) ((x) & (-x))
#define LOWBD(a, x) lower_bound(a.begin(), a.end(), x) - a.begin()
#define UPPBD(a, x) upper_bound(a.begin(), a.end(), x) - a.begin()
#define TEST(a) cout << "---------" << a << "---------" << endl
#define CHIVAS_ int main()
#define _REGAL exit(0)
#define SP system("pause")
#define IOS ios::sync_with_stdio(false)
//#define map unordered_map
#define PB(x) push_back(x)
#define ALL(a) a.begin(),a.end()
#define MEM(a, b) memset(a, b, sizeof(a))
#define EACH_CASE(cass) for (cass = inputInt(); cass; cass--)
#define LS l, mid, rt << 1
#define RS mid + 1, r, rt << 1 | 1
#define GETMID (l + r) >> 1
using namespace std;
/*
template<typename T> inline T MAX(T a, T b){return a > b? a : b;}
template<typename T> inline T MIN(T a, T b){return a > b? b : a;}
template<typename T> inline void SWAP(T &a, T &b){T tp = a; a = b; b = tp;}
template<typename T> inline T GCD(T a, T b){return b > 0? GCD(b, a % b) : a;}
template<typename T> inline void ADD_TO_VEC_int(T &n, vector<T> &vec){vec.clear(); cin >> n; for(int i = 0; i < n; i ++){T x; cin >> x, vec.PB(x);}}
template<typename T> inline pair<T, T> MaxInVector_ll(vector<T> vec){T MaxVal = -LNF, MaxId = 0;for(int i = 0; i < (int)vec.size(); i ++) if(MaxVal <vec[i]) MaxVal = vec[i], MaxId = i; return {MaxVal, MaxId};}
template<typename T> inline pair<T, T> MinInVector_ll(vector<T> vec){T MinVal = LNF, MinId = 0;for(int i = 0; i < (int)vec.size(); i ++) if(MinVal > vec[i])MinVal = vec[i], MinId = i; return {MinVal, MinId};}
template<typename T> inline pair<T, T> MaxInVector_int(vector<T> vec){T MaxVal = -INF, MaxId = 0;for(int i = 0; i < (int)vec.size(); i ++) if(MaxVal <vec[i]) MaxVal = vec[i], MaxId = i; return {MaxVal, MaxId};}
template<typename T> inline pair<T, T> MinInVector_int(vector<T> vec){T MinVal = INF, MinId = 0;for(int i = 0; i < (int)vec.size(); i ++) if(MinVal > vec[i])MinVal = vec[i], MinId = i; return {MinVal, MinId};}
template<typename T> inline pair<map<T, T>, vector<T> > DIV(T n){T nn = n;map<T, T> cnt;vector<T> div;for(ll i = 2; i * i <= nn; i ++){while(n % i == 0){if(!cnt[i]) div.push_back(i);cnt[i] ++;n /= i;}}if(n != 1){if(!cnt[n]) div.push_back(n);cnt[n] ++;n /= n;}return {cnt, div};}
template<typename T> vector<T>& operator-- (vector<T> &v){for (auto& i : v) --i; return v;}
template<typename T> vector<T>& operator++ (vector<T> &v){for (auto& i : v) ++i; return v;}
template<typename T> istream& operator>>(istream& is, vector<T> &v){for (auto& i : v) is >> i; return is;}
template<typename T> ostream& operator<<(ostream& os, vector<T> v){for (auto& i : v) os << i << ' '; return os;}
*/inline int inputInt(){int X=0; bool flag=1; char ch=getchar();while(ch<'0'||ch>'9') {if(ch=='-') flag=0; ch=getchar();}while(ch>='0'&&ch<='9') {X=(X<<1)+(X<<3)+ch-'0'; ch=getchar();}if(flag) return X;return ~(X-1);}
inline void outInt(int X){if(X<0) {putchar('-'); X=~(X-1);}int s[20],top=0;while(X) {s[++top]=X%10; X/=10;}if(!top) s[++top]=0;while(top) putchar(s[top--]+'0');}
inline ll inputLL(){ll X=0; bool flag=1; char ch=getchar();while(ch<'0'||ch>'9') {if(ch=='-') flag=0; ch=getchar();}while(ch>='0'&&ch<='9') {X=(X<<1)+(X<<3)+ch-'0'; ch=getchar();}if(flag) return X;return ~(X-1); }
inline void outLL(ll X){if(X<0) {putchar('-'); X=~(X-1);}ll s[20],top=0;while(X) {s[++top]=X%10; X/=10;}if(!top) s[++top]=0;while(top) putchar(s[top--]+'0');}
const int N = 250010;
int nod[600];
/*边*/struct node { int x, y; double val; inline node(int xx, int yy, double vall) {x = xx; y = yy; val = vall;}friend bool operator < (node a, node b) { return a.val < b.val; }};
/*点*/struct point { int x; int y; } pt[600];
int cass, s, p;
inline void Init ( ) {for ( int i = 0; i < 600; i ++ ) nod[i] = i; }
inline int Find ( int x ) { return x == nod[x] ? x : nod[x] = Find(nod[x]); }
inline bool Check ( int x, int y ) {
int fx = Find(x), fy = Find(y);
return fx == fy;
}
inline void Merge ( int x, int y ) {
int fx = Find(x), fy = Find(y);
if ( fx != fy ) nod[fx] = fy;
}
inline double Dis ( point a, point b ) { // 计算距离
double dir_x = abs(a.x - b.x);
double dir_y = abs(a.y - b.y);
return sqrt(dir_x * dir_x + dir_y * dir_y);
}
inline void solve () {
Init(); vector<node> vec;
int s = inputInt(), p = inputInt();
for ( int i = 0; i < p; i ++ ) pt[i].x = inputInt(), pt[i].y = inputInt();
for ( int i = 0; i < p; i ++ ) for ( int j = i + 1; j < p; j ++ ) vec.push_back(node(i, j, Dis(pt[i], pt[j]))); // 两两建一条边
sort (ALL(vec));
int cnt = 0; vector<double> res;
for ( int i = 0; i < vec.size(); i ++ ) { // Kruskal的选边流程
if ( !Check(vec[i].x, vec[i].y )) {
cnt ++;
Merge(vec[i].x, vec[i].y);
res.push_back(vec[i].val);
}
if ( cnt == p - 1 ) break;
}
s --; // 第一条边需要两个点才能成立,其余都是需要一个点
while ( s ) res.pop_back(), s --;
printf("%.2f\n", res.size()? res.back() : 0);
}
CHIVAS_{
EACH_CASE ( cass ) {
solve();
}
_REGAL;
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
99
100
101
102
103
104
105
106
107
108
109
110
111
112
113
114
115
116
117
118
119
120
121
122
123
124
125
126
127
128
129
130