Trie树
#
# 牛客NC50992_前缀统计
# 🔗
https://ac.nowcoder.com/acm/contest/1010/A
# 💡
# ✅
#include <algorithm>
#include <iostream>
#include <cstring>
#include <string>
#include <vector>
#include <cstdio>
#include <stack>
#include <queue>
#include <cmath>
#include <map>
#include <set>
#define G 10.0
#define LNF 1e18
#define eps 1e-6
#define ll long long
#define INF 0x7FFFFFFF
#define PI acos(-1.0)
#define pb(x) push_back(x)
#define SP system("pause")
#define mm(a, b) memset(a, b, sizeof(a))
#define fir(i, a, n) for (int i = a; i <= n; i++)
#define rif(i, a, n) for (int i = a; i >= n; i--)
#define each_cass(cass) for (cin >> cass; cass; cass--)
using namespace std;
const int maxn = 1e6+10;
struct Trie{
int nxt;
int cnt;
}trie[maxn][26];
int tot = 1;
void insert(string s){
int deep = 1;
for (int i = 0; i < s.size(); i++){
int cur_c = s[i] - 'a';
if(!trie[deep][cur_c].nxt)
trie[deep][cur_c].nxt = ++tot;
deep = trie[deep][cur_c].nxt;
if (i == s.size() - 1)
trie[deep][cur_c].cnt++;
}
}
int search(string s){
int deep = 1;
int num=0;
for (int i = 0; i < s.size(); i++){
deep = trie[deep][s[i] - 'a'].nxt;
if(deep==0)
break;
num += trie[deep][s[i] - 'a'].cnt;
}
return num;
}
int main()
{
int n, m;
cin >> n >> m;
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++){
string s;
cin >> s;
insert(s);
}
for (int i = 0; i < m; i++){
string s;
cin >> s;
cout<<search(s)<<endl;
}
return 0;
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
# AcWing145_最大异或对
# 🔗
https://www.acwing.com/problem/content/145/
# 💡
用字典树储存 x 二进制后每一位的数
在查找时都尽量找每一位与当前查找元素相反的数
维护最大值即可
# ✅
/*
________ _ ________ _
/ ______| | | | __ | | |
/ / | | | |__| | | |
| | | |___ _ _ _ ___ _ _____ | ___| ______ _____ ___ _ | |
| | | __ \ |_| | | | | | _\| | | ____| | |\ \ | __ | | _ | | _\| | | |
| | | | \ | _ | | | | | | \ | | \___ | | \ \ | |_/ _| | |_| | | | \ | | |
\ \______ | | | | | | \ |_| / | |_/ | ___/ | | | \ \ | /_ \__ | | |_/ | | |
Author : \________| |_| |_| |_| \___/ |___/|_| |_____| _________|__| \__\ |______| | | |___/|_| |_|
____| |
\_____/
*/
//#include <unordered_map>
#include <algorithm>
#include <iostream>
#include <cstring>
#include <utility>
#include <string>
#include <vector>
#include <cstdio>
#include <stack>
#include <queue>
#include <cmath>
#include <map>
#include <set>
#define G 10.0
#define LNF 1e18
#define EPS 1e-6
#define PI acos(-1.0)
#define INF 0x7FFFFFFF
#define ll long long
#define ull unsigned long long
#define LOWBIT(x) ((x) & (-x))
#define LOWBD(a, x) lower_bound(a.begin(), a.end(), x) - a.begin()
#define UPPBD(a, x) upper_bound(a.begin(), a.end(), x) - a.begin()
#define TEST(a) cout << "---------" << a << "---------" << '<br>'
#define CHIVAS_ int main()
#define _REGAL exit(0)
#define SP system("pause")
#define IOS ios::sync_with_stdio(false)
//#define map unordered_map
#define PB(x) push_back(x)
#define ALL(a) a.begin(),a.end()
#define MEM(a, b) memset(a, b, sizeof(a))
#define EACH_CASE(cass) for (cass = inputInt(); cass; cass--)
#define LS l, mid, rt << 1
#define RS mid + 1, r, rt << 1 | 1
#define GETMID (l + r) >> 1
using namespace std;
template<typename T> inline T MAX(T a, T b){return a > b? a : b;}
template<typename T> inline T MIN(T a, T b){return a > b? b : a;}
template<typename T> inline void SWAP(T &a, T &b){T tp = a; a = b; b = tp;}
template<typename T> inline T GCD(T a, T b){return b > 0? GCD(b, a % b) : a;}
template<typename T> inline void ADD_TO_VEC_int(T &n, vector<T> &vec){vec.clear(); cin >> n; for(int i = 0; i < n; i ++){T x; cin >> x, vec.PB(x);}}
template<typename T> inline pair<T, T> MaxInVector_ll(vector<T> vec){T MaxVal = -LNF, MaxId = 0;for(int i = 0; i < (int)vec.size(); i ++) if(MaxVal < vec[i]) MaxVal = vec[i], MaxId = i; return {MaxVal, MaxId};}
template<typename T> inline pair<T, T> MinInVector_ll(vector<T> vec){T MinVal = LNF, MinId = 0;for(int i = 0; i < (int)vec.size(); i ++) if(MinVal > vec[i]) MinVal = vec[i], MinId = i; return {MinVal, MinId};}
template<typename T> inline pair<T, T> MaxInVector_int(vector<T> vec){T MaxVal = -INF, MaxId = 0;for(int i = 0; i < (int)vec.size(); i ++) if(MaxVal < vec[i]) MaxVal = vec[i], MaxId = i; return {MaxVal, MaxId};}
template<typename T> inline pair<T, T> MinInVector_int(vector<T> vec){T MinVal = INF, MinId = 0;for(int i = 0; i < (int)vec.size(); i ++) if(MinVal > vec[i]) MinVal = vec[i], MinId = i; return {MinVal, MinId};}
template<typename T> inline pair<map<T, T>, vector<T> > DIV(T n){T nn = n;map<T, T> cnt;vector<T> div;for(ll i = 2; i * i <= nn; i ++){while(n % i == 0){if(!cnt[i]) div.push_back(i);cnt[i] ++;n /= i;}}if(n != 1){if(!cnt[n]) div.push_back(n);cnt[n] ++;n /= n;}return {cnt, div};}
template<typename T> vector<T>& operator-- (vector<T> &v){for (auto& i : v) --i; return v;}
template<typename T> vector<T>& operator++ (vector<T> &v){for (auto& i : v) ++i; return v;}
template<typename T> istream& operator>>(istream& is, vector<T> &v){for (auto& i : v) is >> i; return is;}
template<typename T> ostream& operator<<(ostream& os, vector<T> v){for (auto& i : v) os << i << ' '; return os;}
inline int inputInt(){int X=0; bool flag=1; char ch=getchar();while(ch<'0'||ch>'9') {if(ch=='-') flag=0; ch=getchar();}while(ch>='0'&&ch<='9') {X=(X<<1)+(X<<3)+ch-'0'; ch=getchar();}if(flag) return X;return ~(X-1);}
inline void outInt(int X){if(X<0) {putchar('-'); X=~(X-1);}int s[20],top=0;while(X) {s[++top]=X%10; X/=10;}if(!top) s[++top]=0;while(top) putchar(s[top--]+'0');}
inline ll inputLL(){ll X=0; bool flag=1; char ch=getchar();while(ch<'0'||ch>'9') {if(ch=='-') flag=0; ch=getchar();}while(ch>='0'&&ch<='9') {X=(X<<1)+(X<<3)+ch-'0'; ch=getchar();}if(flag) return X;return ~(X-1); }
inline void outLL(ll X){if(X<0) {putchar('-'); X=~(X-1);}ll s[20],top=0;while(X) {s[++top]=X%10; X/=10;}if(!top) s[++top]=0;while(top) putchar(s[top--]+'0');}
const int N = 1e5 + 10;
int trie[40 * N][2], tot, a[N];
inline void Insert ( int x ) {
int p = 0;
for ( int i = 30; i >= 0; i -- ) {
int u = x >> i & 1; // 取出那一位的数
if( ! trie[p][u] ) trie[p][u] = ++ tot;
p = trie[p][u];
}
}
inline int Query ( int x ) {
int p = 0, res = 0;
for ( int i = 30; i >= 0; i -- ) {
int u = x >> i & 1;
if ( trie[p][!u] ) p = trie[p][!u], res = res << 1 | 1;
else p = trie[p][u], res = res << 1;
}return res;
}
CHIVAS_{
int n = inputInt(), res = 0;
for ( int i = 0; i < n; i ++ ) a[i] = inputInt(), Insert(a[i]);
for ( int i = 0; i < n; i ++ ) res = MAX(res, Query(a[i]));
outInt(res);
_REGAL;
};
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
99
100
101
102
103
104
105
106
107
# CodeForces817E_ChoosingTheCommander
# 🔗
# 💡
本题是让所有的士兵的 的个数,且又有插入又有删除又有询问,比较明显使用字典树
字典树每个节点要表示这个节点的编号与这个节点被插入数字的数量
询问小于的太广泛了,我们可以用 也就是 划一根字典树上的分界线,我们只需要计算在“小于”这个分界线的一侧的即可
而根据二进制的高位优越性,即如果两个二进制串的前缀都相同,那么第一个不同的位便可决定谁大谁小
所以我们从高到低将一个数字分解二进制插入字典树中,对于当前位 ,则我们保证我们选择的子树根当前位是 便可以保证这个子树下的所有点异或 都小于 ,便直接累加上这个子节点被插入的数量,
然后我们走 位为 的子树来保证我们走的是相等的分界线
# ✅
const int N = 1e5 + 10;
struct node {
int val;
int num;
};
struct Trie {
node t[N * 40][2];
int idx;
inline void Insert (int x) {
int p = 0;
for (int i = 30; i >= 0; i --) {
int u = x >> i & 1;
if (!t[p][u].val) t[p][u] = {++idx, 1};
else t[p][u].num ++;
p = t[p][u].val;
}
}
inline void Delete (int x) {
int p = 0;
for (int i = 30; i >= 0; i --) {
int u = x >> i & 1;
t[p][u].num --;
int tmp = p;
p = t[p][u].val;
if (!t[tmp][u].num) t[tmp][u].val = 0;
}
}
inline int Calc (int x, int y) {
int res = 0;
int p = 0;
for (int i = 30; i >= 0; i --) {
int xi = x >> i & 1;
int yi = y >> i & 1;
if (yi == 1) res += t[p][xi].num;
p = t[p][xi ^ yi].val;
if (p == 0) return res;
}
return res;
}
}trie;
int main () {
ios::sync_with_stdio(false);
cin.tie(nullptr);
int m; cin >> m;
while (m --) {
int op; cin >> op;
if (op == 1) {
int x; cin >> x;
trie.Insert(x);
} else if (op == 2) {
int x; cin >> x;
trie.Delete(x);
} else {
int x, y; cin >> x >> y;
cout << trie.Calc(x, y) << endl;
}
}
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
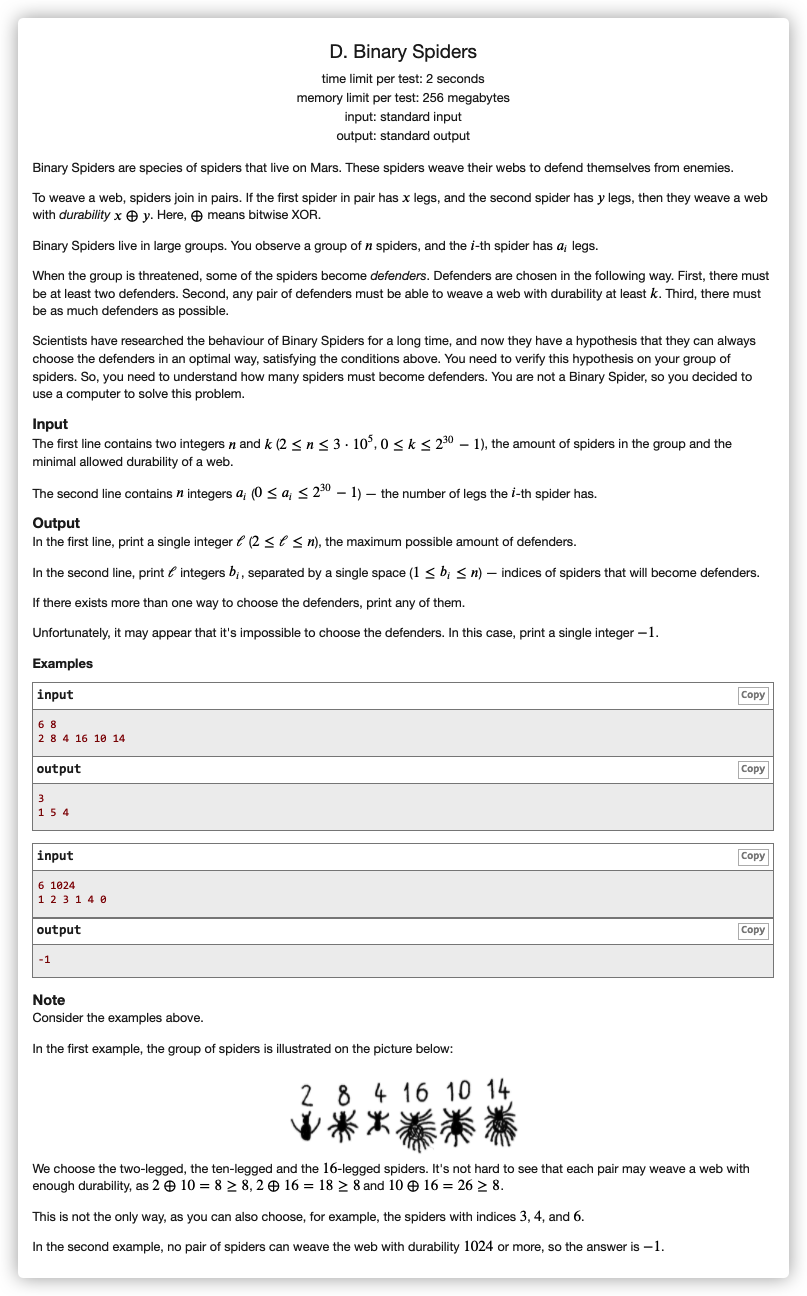
# CodeForces1625D_BinarySpiders
# 🔗
# 💡
考虑 有 位,若一对数 以上的位存在不同的,那么必然可以
若一对数 以上的位相同,那么去检查相同的内部是否存在两者
那么存 以上的前缀
- 不同,随便选
- 相同,考虑 ,所以此时最多可以选两个,但至少可以选一个
同前缀内可以用 数去查每个数的最大异或
# ✅
const int N = 3e5 + 10;
int n, k, m;
map<int, int> id;
map<int, vector<int> > pres;
inline int Bits ( int x ) {
int res = 0;
while ( x ) x >>= 1, res ++;
return res;
}
namespace Trie {
int t[N * 30][2], idx;
inline void Init () { memset(t, 0, sizeof (int) * 2 * (idx + 1)); idx = 0; }
inline void Insert ( int x ) {
int p = 0;
for ( int i = 30; i >= 0; i -- ) {
int u = x >> i & 1;
if ( !t[p][u] ) t[p][u] = ++ idx;
p = t[p][u];
}
}
inline int Query ( int x ) {
int res = 0, p = 0;
for ( int i = 30; i >= 0; i -- ) {
int u = x >> i & 1;
if ( !t[p][!u] ) {
res = res << 1 | u;
p = t[p][u];
} else {
res = res << 1 | (!u);
p = t[p][!u];
}
}
return res;
}
}
int main () {
ios::sync_with_stdio(false);
cin >> n >> k; m = Bits(k);
for ( int i = 1; i <= n; i ++ ) {
int x; cin >> x;
pres[x >> m].push_back(x);
id[x] = i;
}
if ( k == 0 ) {
cout << n << endl;
for ( int i = 1; i <= n; i ++ ) cout << i << " ";
return 0;
}
vector<int> res;
for ( auto pre : pres ) {
bool flag = false;
Trie::Init();
for ( auto x : pre.second ) {
int t = Trie::Query(x);
if ( (t ^ x) >= k ) {
res.push_back(id[t]);
res.push_back(id[x]);
flag = true;
break;
}
Trie::Insert(x);
}
if ( !flag ) res.push_back(id[pre.second[0]]);
}
if ( res.size() <= 1 ) cout << "-1" << endl;
else {
cout << res.size() << endl;
for ( auto i : res ) cout << i << " ";
cout << endl;
}
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
# CodeForces1658D2_388535(Hard Version)
# 🔗
# 💡
首先 中一定存在一个
那么枚举 看谁是就可以
但问题是如果去检查是否可以
考虑 固定了一个最小值一个最大值
且由于不同的数异或同一个数得出的数也是不同的,那么如果知道最大值最小值我们就可以得到整个区间
而在字典树中我们可以去查找异或的最小值最大值
我们去检查对应的 即 在整个字典树中的最小值最大值是不是 和 即可
# ✅
const int N = 2e5 + 10;
namespace Trie {
int t[N * 5][2], idx;
inline void Init () {
memset(t, 0, idx * 2 * sizeof(int));
idx = 0;
}
inline void Insert ( int val ) {
int p = 0;
for ( int i = 17; i >= 0; i -- ) {
int u = val >> i & 1;
if ( !t[p][u] ) t[p][u] = ++ idx;
p = t[p][u];
}
}
inline int Query_Max ( int val ) {
int p = 0, res = 0;
for ( int i = 17; i >= 0; i -- ) {
int u = val >> i & 1;
if ( t[p][!u] ) {
res = res << 1 | 1;
p = t[p][!u];
} else {
res = res << 1;
p = t[p][u];
}
}
return res;
}
inline int Query_Min ( int val ) {
int p = 0, res = 0;
for ( int i = 17; i >= 0; i -- ) {
int u = val >> i & 1;
if ( t[p][u] ) {
res = res << 1;
p = t[p][u];
} else {
res = res << 1 | 1;
p = t[p][!u];
}
}
return res;
}
}
inline void Solve() {
int l, r; cin >> l >> r;
Trie::Init();
vector<int> a(r - l + 1); for ( int &i : a ) cin >> i, Trie::Insert(i);
for ( int i : a ) {
int mn = Trie::Query_Min(i ^ l);
int mx = Trie::Query_Max(i ^ l);
if ( mn == l && mx == r ) {
cout << (i ^ l) << endl;
return;
}
}
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
# HDU2021多校(1)F_XorSum
# 🔗
# 💡
区间异或的问题,转化为前缀异或
我们一步步往某种容器内放入前缀异或,在放 之前,要看所有容器内的元素 ,满足 的 的最大下标
问题转化之后,要研究一下在二进制下 的条件
如果 就是所有位都相等。如果 则说明第一个不相等的位置 一定满足
再看一下当前条件 的性质
时如果 可以从容器中挑出来一个 满足 ,说明之后不管怎么选都可以让 ,如果挑不出来就要往 走
时说明 必须要挑一个 满足 ,挑不出来就寄了
似乎既要根据位固定出来所有位置,又要根据划定的位置找出来位是否存在,有些蒙圈,先把异或容器的常用数据结构思考一下
树、线性基...(等等, 树好像和上面列的条件有点像)
对每一个前缀异或插入,由于是要最短区间,所以多维护一个这个节点被插入的最大下标 ,插入 的时候更新这条路上的
查询的时候,维护一下信息 ,如果 那么若当前节点存在 孩子,说明走了之后就永远大于了,就维护一下这个孩子的子树最大 和 比较的最大值 ,然后顺着 的 孩子继续往下走
走到底了说明走完了一条 满足 ,依旧是满足要求的,维护一下当前节点的 和 比较的最大值
也就是说:在 树上沿着 的 每一位向下走,遇到可以让 的分支时累计一下那个分支下的 最大值,当彻底走不动时返回 ,如果能走完全程返回
# ✅
const int N = 1e5 + 10;
int a[N];
int n, k;
struct node {
int child[2];
int mxid;
} t[10000007]; int idx;
inline void Insert (int x, int id) {
int p = 0;
for (int i = 40; i >= 0; i --) {
ll c = ll(x) >> i & 1;
if (!t[p].child[c]) t[p].child[c] = ++idx;
p = t[p].child[c];
t[p].mxid = id;
}
}
int ii;
inline int query (int A, int K) {
int ret = -1;
int p = 0;
for (int i = 40; i >= 0; i --) {
ll cA = ll(A) >> i & 1;
ll cK = ll(K) >> i & 1;
if (cK == 0) {
if (t[p].child[!cA]) ret = max(ret, t[t[p].child[!cA]].mxid);
if (!t[p].child[cA]) return ret;
p = t[p].child[cA];
} else {
if (!t[p].child[!cA]) return ret;
p = t[p].child[!cA];
}
}
ret = max(ret, t[p].mxid);
return ret;
}
inline void Solve () {
for (int i = 0; i <= idx; i ++) t[i].child[0] = t[i].child[1] = 0, t[i].mxid = -1;
idx = 0;
cin >> n >> k;
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i ++) cin >> a[i];
pair<int, int> res = {-1, n + 1};
Insert(0, 0);
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i ++) {
ii = i;
a[i] ^= a[i - 1];
int qry = query(a[i], k);
if (qry != -1) {
if (i - qry < res.second - res.first + 1) res = {qry + 1, i};
else if (i - qry == res.second - res.first + 1) res = min(res, {qry + 1, i});
}
Insert(a[i], i);
}
if (res.first == -1) cout << "-1\n";
else cout << res.first << " " << res.second << endl;
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
# HDU2021多校(2)D_ILoveCounting
# 🔗
# 💡
看到 这类二进制的比大小,可以联想到按位比,第一个不同即出大小,那么用字典树贴着 跑就行了,然后能小于的时候过去看一眼累加一下值再接着往下走
但是如果我们字典树中存的是子树的下标集然后在上面二分出 之间的数了话,很难去保证里面都是不同的,但是如果我们对于区间相同的数只插入一个的话就会方便很多,直接加就行了
区间保证只插一个的做法很经典可以用莫队来实现,开一个 数组,减的时候就如果减到零了在字典树中删除,加的时候如果加成一了就在字典树中插入
分析一下没太大的复杂度问题,优化常数
数组下标访问很慢,且看到每一个数小于 ,字典树换成二叉树来跑,即左子树为 边,右子树为 边,在这个二叉树上做字典树的操作就能优化很多下标常数了
(话说贴着字典树往下走上一场出过很类似的操作啊 传送门 )
# ✅
int t[10000007];
inline void Insert (int x, int c) {
int root = 1;
for (int i = 18; i >= 0; i --) {
root = (root << 1) + (x >> i & 1);
t[root] += c;
}
}
inline int Query (int a, int b) {
int root = 1, res = 0;
for (int i = 18; i >= 0; i --) {
int ca = a >> i & 1;
int cb = b >> i & 1;
if (cb == 1) {
res += t[root << 1 | ca];
root = root << 1 | (!ca);
} else {
root = root << 1 | ca;
}
}
return res + t[root];
}
int num[100005];
int a[100005];
inline void add (int x) {
if (!num[x]) Insert(x, 1);
num[x] ++;
}
inline void del (int x) {
num[x] --;
if (!num[x]) Insert(x, -1);
}
int n, q, sq;
inline int get (int x) {return x / sq;}
struct query {
int l, r, a, b, id;
inline friend bool operator < (query a, query b) {
if (get(a.l) != get(b.l)) return get(a.l) < get(b.l);
if (get(a.l) & 1) return a.r > b.r;
return a.r < b.r;
}
} qry[100005];
int res[100005];
int main () {
scanf("%d", &n); sq = sqrt(n);
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i ++) scanf("%d", &a[i]);
scanf("%d", &q);
for (int i = 1; i <= q; i ++) {
int l, r, a, b; scanf("%d%d%d%d", &l, &r, &a, &b);
qry[i] = {l, r, a, b, i};
}
sort(qry + 1, qry + 1 + q);
for (int L = 1, R = 0, i = 1; i <= q; i ++) {
while (L < qry[i].l) del(a[L ++]);
while (L > qry[i].l) add(a[-- L]);
while (R < qry[i].r) add(a[++ R]);
while (R > qry[i].r) del(a[R --]);
res[qry[i].id] = Query(qry[i].a, qry[i].b);
}
for (int i = 1; i <= q; i ++) printf("%d\n", res[i]);
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67