并查集
#
# 洛谷9月月赛2Div2C_Rabbit
# 🔗
# 💡
如果是在原树上考虑的话,一个点要找两个比自己小的子节点,还要找一个子节点一个父节点,如果将最大值踢到根节点,那么它只需要任选两个“不同子树内”的节点(保证没有被选过的)
这样肯定是从下往上处理,可是在原树上一边边找最大值然后换根十分麻烦
既然卡着子树找最值很麻烦,两个同级的限制条件对调一下,变成卡着最值找子树
每次枚举的点可以成为之前枚举所有点的最大值的话,之前的点如果在当前建边的子树中的话就可以用
所以从 到 枚举节点,然后用已知连边合并比自己小的节点,看看是否存在两个子树里面都有没有被标记过的点,如果存在的话就让答案加一,该点代表子树的没标记点数 减三(去掉两个子树中的点和自己)
合并可以用并查集合并
# ✅
const int N = 200005;
int num[N], nod[N];
inline int find (int x) { return x == nod[x] ? x : nod[x] = find(nod[x]); }
inline void Solve () {
int n; cin >> n;
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i ++) nod[i] = i, num[i] = 1;
vector<vector<int> > g(n + 1);
for (int i = 1; i < n; i ++) {
int u, v; cin >> u >> v;
g[u].push_back(v);
g[v].push_back(u);
}
int res = 0;
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i ++) {
int hasSon = 0;
for (int j : g[i]) {
if (j > i) continue;
hasSon += num[find(j)] > 0;
num[i] += num[find(j)];
nod[find(j)] = i;
}
if (hasSon >= 2)
num[i] -= 3,
res ++;
}
cout << res << endl;
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
# ABC238E_RangeSums
# 🔗
# 💡
考虑一下,在拥有 的情况下,拥有了 ,我们会获得
如果是拥有了 ,我们会获得
这是一个传递性的关系
可以通过建图完成
建立并查集,每次连通 ,如果最后 与 连通,就可以传递过去
反之不能
# ✅
const int N = 2e5 + 10;
namespace UnionSet {
int nod[N];
inline int Find ( int x ) { return x == nod[x] ? x : nod[x] = Find(nod[x]); }
inline void Merge ( int x, int y ) {
int fx = Find(x), fy = Find(y);
if ( fx != fy ) nod[fx] = fy;
}
}
int n, q;
int main () {
ios::sync_with_stdio(false);
cin >> n >> q;
for ( int i = 0; i <= n; i ++ ) UnionSet::nod[i] = i;
for ( int i = 0; i < q; i ++ ) {
int l, r; cin >> l >> r;
UnionSet::Merge(l - 1, r);
}
if ( UnionSet::Find(0) == UnionSet::Find(n) ) cout << "Yes" << endl;
else cout << "No" << endl;
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
# 洛谷P2391_白雪皑皑
# 🔗
# 💡
看一下题,什么鬼就是一个 吧,再看一眼数据量,要么每次 操作,要么总复杂度不高
总复杂度很容易想到
这种覆盖性质的染色问题,基本上都是倒着染,每染一个之后就不看这个点了
这种删除、不遍历的操作可以使用链表来解决
但是考虑到如果确定操作 了话,从哪里开始呢,找了话还是要 ?
思考了一下也就是说我们用链表删除后,这个点的后继在之后的操作不会被修改了,所以我们没法找到它的存在后继
但是每一块被删除的部分,一定有一个最后被删的元素,其前驱后继就是这一块所有点的前驱后继
这种认贼作父(啊不是)的操作,就是并查集的根啊
所以我们开一个标记记录是否存在,再开一套并查集
在删除一个点的时候,我们看它前后是否有删除的点,如果有,就让它们的并查集根认作这个即将删除的点
然后在操作时,对于 更改为它并查集根的后继, 更改为它并查集根的前驱
然后让 一直按链表向后跑并不断删除访问过的点直到 即可
# ✅
const int N = 1000006;
int n, m, p, q;
struct node { int pre, nxt; } a[N];
int fa[N], vis[N], res[N];
inline int find (int x) { return x == fa[x] ? x : fa[x] = find(fa[x]); }
inline void del (int x) {
a[a[x].nxt].pre = a[x].pre;
a[a[x].pre].nxt = a[x].nxt;
int fx = find(x);
if (vis[x - 1]) {
int fxd1 = find(x - 1);
fa[fxd1] = fx;
}
if (vis[x + 1]) {
int fxa1 = find(x + 1);
fa[fxa1] = fx;
}
vis[x] = 1;
}
int main () {
ios::sync_with_stdio(false);
cin.tie(nullptr);
cin >> n >> m >> p >> q;
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i ++) {
fa[i] = i;
a[i].pre = i - 1;
a[i].nxt = i + 1;
}
for (int i = m; i >= 1; i --) {
int l = ((ll)i * p + q) % n + 1;
int r = ((ll)i * q + p) % n + 1;
if (l > r) swap(l, r);
l = vis[l] ? a[find(l)].nxt : l;
r = vis[r] ? a[find(r)].pre : r;
while (l <= r) {
res[l] = i;
int tmp = l;
l = a[l].nxt;
del(tmp);
}
}
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i ++) cout << res[i] << endl;
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
# CodeForces659F_PolycarpAndHay
# 🔗
# 💡
注意到如果我们选 ,那么
一个连通块都要相同且有一个必须等于原始值,就意味着该连通快的每一个数值要么是 要么是最小值,即它由最小值确定
那么我们将每一个位置存入,从大到小排序
然后遍历中维护一个连通块的个数、最小值
如果 并且连通块数量足够,就意味着可以构造出来,构造方式以最小值为中心开始 即可
# ✅
const int N = 1e3 + 10;
const int dx[] = {0, 0, 1, -1};
const int dy[] = {1, -1, 0, 0};
int n, m;
ll k;
int a[N][N];
struct node {
int val;
int x, y;
inline friend bool operator < ( node a, node b ) {
return a.val > b.val;
}
}; vector<node> vec;
namespace UnionSet {
const int SZ_NOD = 1e6 + 1e3 + 10;
int nod[SZ_NOD];
int val_nod[SZ_NOD];
int num_nod[SZ_NOD];
inline int Hash ( int x, int y ) { return x * 1000 + y; }
inline pair<int, int> hsaH ( int val ) { return {val / 10000, val % 1000}; }
inline void Init () {
for ( int i = 1; i <= n; i ++ ) {
for ( int j = 1; j <= m; j ++ ) {
int hsh = Hash(i, j);
nod[hsh] = hsh;
num_nod[hsh] = 1;
val_nod[hsh] = a[i][j];
}
}
}
inline int Find ( int x ) {
return x == nod[x] ? x : nod[x] = Find(nod[x]);
}
inline void Merge ( int x, int y ) {
int fx = Find(x), fy = Find(y);
if ( fx != fy)
nod[fx] = fy,
val_nod[fy] = min(val_nod[fy], val_nod[fx]),
num_nod[fy] += num_nod[fx];
}
inline bool Check ( int x, int y ) {
int fx = Find(x), fy = Find(y);
return fx == fy;
}
} using namespace UnionSet;
int res[N][N];
int vis[N][N];
inline void Solve ( int sx, int sy, ll val, int root ) {
queue<pair<int, int> > que;
que.push({sx, sy});
while ( !que.empty() ) {
auto [x, y] = que.front(); que.pop();
if ( vis[x][y] || !k ) continue;
vis[x][y] = 1; res[x][y] = val; k -= val;
for ( int d = 0; d < 4; d ++ ) {
int nx = x + dx[d];
int ny = y + dy[d];
if ( nx < 1 || nx > n || ny < 1 || ny > m ) continue;
if ( Find(Hash(nx, ny)) != root ) continue;
que.push({nx, ny});
}
}
for ( int i = 1; i <= n; i ++, cout << "\n") for ( int j = 1; j <= m; j ++ ) cout << res[i][j] << ' ';
}
int main () {
cin.tie(0)->sync_with_stdio(0);
cin.exceptions(cin.failbit);
cin >> n >> m >> k;
for ( int i = 1; i <= n; i ++ ) for ( int j = 1; j <= m; j ++ ) cin >> a[i][j], vec.push_back({a[i][j], i, j});
sort ( vec.begin(), vec.end() );
Init();
for ( int i = 0; i < vec.size(); i ++ ) {
auto [x, y, v] = vec[i];
int hsh = Hash(x, y);
for ( int d = 0; d < 4; d ++ ) {
int nx = x + dx[d], ny = y + dy[d];
if ( nx < 1 || nx > n || ny < 1 || ny > m ) continue;
if ( a[nx][ny] < v ) continue;
int nhsh = Hash(nx, ny);
Merge(hsh, nhsh);
}
if ( k % v == 0 && k / v <= num_nod[Find(hsh)] ) {
cout << "YES\n";
Solve ( x, y, v, Find(hsh) );
exit(0);
}
}
cout << "NO\n";
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
99
# CodeForces1209D_CowAndSnacks
# 🔗
# 💡
肯定是希望更多的人只吃一个点心
同时喜欢两个东西,可以将这两个点相连,这样在一个大小超过 的连通块里面必定只会出现一次有人吃两个的情况,别的都是只吃一个
所以使用并查集获取到每一个连通块的大小,对于大于等于 的连通块,我们将
这样会得到最多能有几个人有吃的,输出 即可
# ✅
const int N = 1e5 + 10;
int fa[N], sz[N];
inline int find (int x) {return x == fa[x] ? x : fa[x] = find(fa[x]);}
inline void merge (int x, int y) {
int fx = find(x);
int fy = find(y);
if (fx == fy) return;
sz[fy] += sz[fx];
fa[fx] = fy;
}
int main () {
int n, m; scanf("%d%d", &n, &m);
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i ++) {
fa[i] = i;
sz[i] = 1;
}
for (int i = 1; i <= m; i ++) {
int x, y; scanf("%d%d", &x, &y);
merge(x, y);
}
int res = 0;
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i ++) {
if (find(i) == i && sz[find(i)] >= 2) {
res += sz[find(i)] - 1;
}
}
printf("%d\n", m - res);
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
# CodeForces1475F_UnusualMatrix
# 🔗
# 💡
就是一个奇偶翻转次数的问题
若 ,说明 要翻转奇数次,也就意味着两种可能: 行翻转奇数次 列翻转偶数次、 行偶数次 列奇数次
若 ,说明 翻转偶数次,意味着: 行 列都翻转偶数次、 行 列都翻转奇数次
而最终表现情况,希望存在一组解,这一组解肯定不能同时存在 行或者 列既翻转奇数次也翻转偶数次
所以用一组 大小的并查集储存行在 奇数次为 偶数次为 的情况、列在 奇数次为 偶数次为
按照上面的合并方式合并完,最后检查一下是否存在某一行或某一列,奇数次和偶数次在同一个连通块内的情况
# ✅
const int N = 1010;
char s[N][N];
char t[N][N];
int nod[N * 4], sz1[N * 4], sz2[N * 4];
inline int find (int x) {return x == nod[x] ? x : nod[x] = find(nod[x]);}
inline void merge (int x, int y) {
x = find(x); y = find(y);
if (x != y) {
nod[x] = y;
sz1[y] += sz1[x];
sz2[y] += sz2[x];
}
}
int main () {
int cass; scanf("%d", &cass); while (cass --) {
int n; scanf("%d", &n);
for (int i = 1; i <= n * 4; i ++) {
nod[i] = i;
if (i <= 2 * n) sz1[i] = 1, sz2[i] = 0;
else sz2[i] = 1, sz1[i] = 0;
}
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i ++) scanf("%s", s[i] + 1);
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i ++) scanf("%s", t[i] + 1);
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i ++) {
for (int j = 1; j <= n; j ++) {
if (s[i][j] == t[i][j]) {
merge(i, j + 2 * n);
merge(i + n, j + 3 * n);
} else {
merge(i + n, j + 2 * n);
merge(i, j + 3 * n);
}
}
}
bool flag = true;
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i ++) {
if (find(i) == find(i + n)) flag = false;
if (find(i + 2 * n) == find(i + 3 * n)) flag = false;
}
if (flag) puts("YES");
else puts("NO");
}
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
# CodeForces1594D_TheNumberOfImposters
# 🔗
# 💡
首先要从人物关系中下手
如果一个人说另一个人是船员,那么两个要么都是船员要么都不是
如果一个人说另一个人是冒牌,那么两个人中必定只有一个是冒牌
我们要求得最大的冒牌数量,可以使用带权并查集
就是两个人一定同一阵营merge( x, y ), merge ( x + n, y + n )
一定不是同一阵营 merge ( x, y + n ), merge ( x + n, y )
在特判的时候,如果一个人自己和自己不是同一阵营,就输出-1
否则在遇到每个阵营的祖先的时候,从它直接代表的两个阵营中选出一个最大的即 max(siz[Find(x)], siz[Find(x + n)])
# ✅
#include <iostream>
#include <map>
#include <vector>
#include <cstring>
#include <algorithm>
#define ll long long
using namespace std;
const int mod = 1e9 + 7;
inline ll ksm ( ll a, ll b ) {
ll res = 1;
while ( b ) {
if ( b & 1 ) res = res * a % mod;
a = a * a % mod;
b >>= 1;
}
return res;
}
inline void Solve() {
ll a, b; cin >> a >> b;
ll res = 0;
while ( b > 0 ) {
ll bas = 0, sum = 0;
while ( sum + (1ll << bas) < b ) {
sum += (1ll << bas);
bas ++;
}
res = (res + ksm(a, bas)) % mod;
b -= (1ll << bas);
}
cout << res << endl;
}
int main () {
ios::sync_with_stdio(false);
#ifndef ONLINE_JUDGE
freopen("in.in", "r", stdin);
freopen("out.out", "w", stdout);
#endif
int cass; cin >> cass; while ( cass -- ) {
Solve();
}
return 0;
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
# CodeForces1691E_NumberOfGroups
# 🔗
# 💡
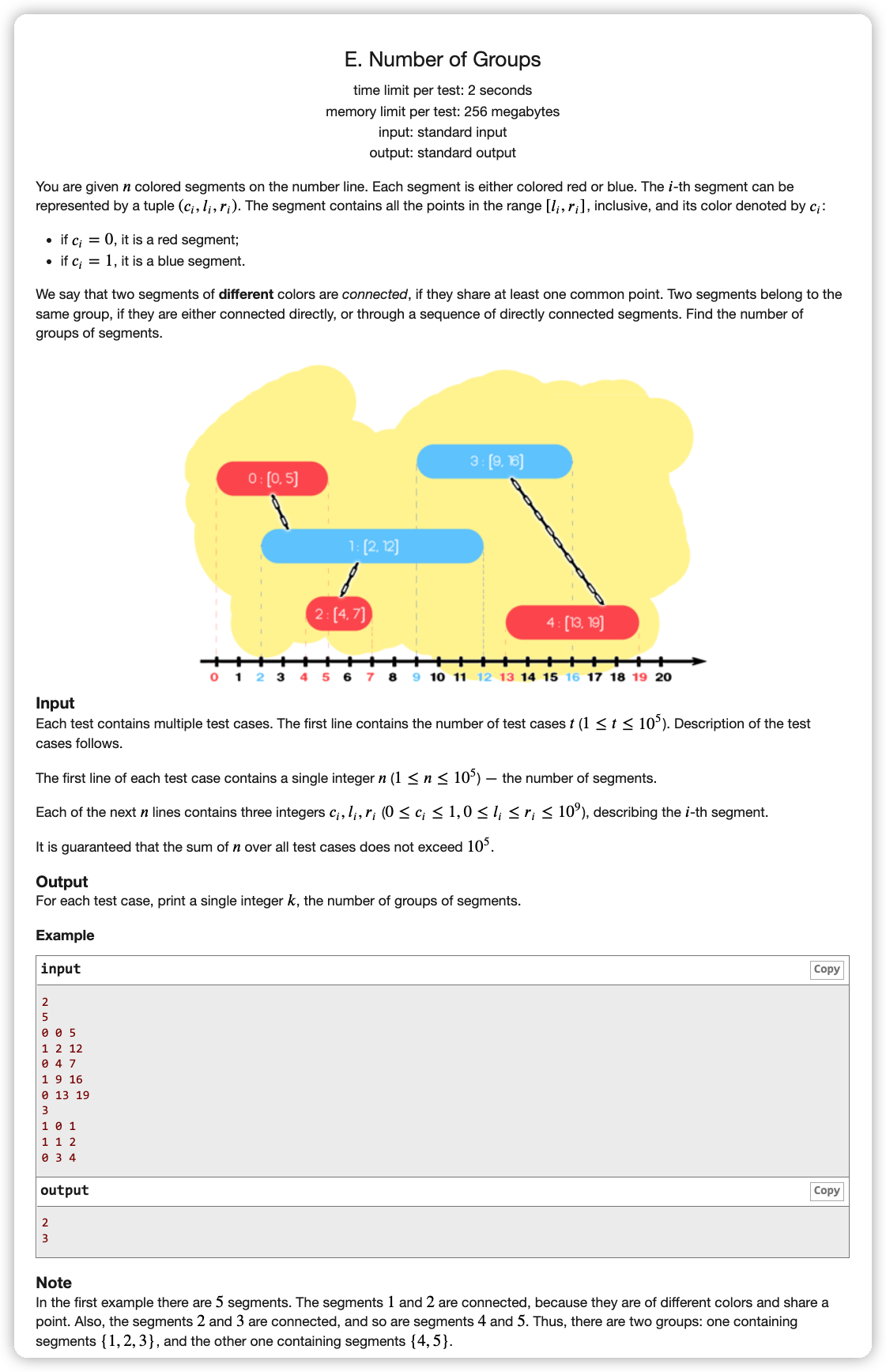
其实考虑一下有一个很明显的事情,如果每个蓝色连接自己后面第一个满足条件的红色,红色连接自己后面第一个满足条件的蓝色,那么就可以正确连接
所以我们对每一个颜色集按第一关键字 升序,第二关键字 降序后
看红色连接范围在红色 后面的蓝色
先对蓝色 升序存储,这样保证每一个蓝色 都保留的是最小的蓝色 ,且蓝色 越小,蓝色 也越小
对于一个红色,我们找到第一个满足蓝色 超过红色 的点,如果该蓝色点的 不大于该红色 ,说明满足条件,可以连接
然后反过来也一样操作
# ✅
const int N = 1e5 + 10;
int nod[N];
inline void Init (int n) { iota(nod, nod + n, 0); }
inline int Find (int x) { return x == nod[x] ? x : nod[x] = Find(nod[x]); }
inline void Merge (int x, int y) {
x = Find(x);
y = Find(y);
if (x == y) return;
nod[x] = y;
}
inline void Solve () {
int n; cin >> n;
vector<int> l(n), r(n), c(n);
vector<int> p[2];
for (int i = 0; i < n; i ++) {
cin >> c[i] >> l[i] >> r[i];
p[c[i]].push_back(i);
}
Init(n);
for (int i = 0; i < 2; i ++) {
sort(p[i].begin(), p[i].end(), [&](int a, int b) {
if (l[a] != l[b]) return l[a] < l[b];
return r[a] > r[b];
});
}
function<void(void)> Link = [&]() {
vector<int> a;
for (int i : p[0]) {
if (a.empty() || r[i] > r[a.back()])
a.push_back(i);
}
for (int i : p[1]) {
auto id = partition_point(a.begin(), a.end(), [&](int j) {
return r[j] < l[i];
});
if (id == a.end() || l[*id] > r[i]) continue;
Merge(*id, i);
}
};
Link();
swap(p[0], p[1]);
Link();
int res = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < n; i ++) res += Find(i) == i;
printf("%d\n", res);
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
# HDUOJ2844_食物链
# 🔗
http://acm.hdu.edu.cn/showproblem.php?pid=2844
# 💡
分析到题中有三种集合关系
我们在得到谁吃谁的时候无法对两者进行合并
所以可以对a的被吃、b的吃、a的吃、b的吃进行合并
即两种权值以n为边界开成两维
# ✅
#pragma region
#pragma GCC optimize(3,"Ofast","inline")
#include <algorithm>
#include <iostream>
#include <cstring>
#include <string>
#include <vector>
#include <cstdio>
#include <stack>
#include <queue>
#include <cmath>
#include <map>
#include <set>
#define G 10.0
#define LNF 1e18
#define eps 1e-6
#define PI acos(-1.0)
#define ll long long
#define INF 0x7FFFFFFF
#define Regal exit(0)
#define Chivas int main()
#define pb(x) push_back(x)
#define SP system("pause")
#define Max(a,b) ((a)>(b)?(a):(b))
#define Min(a,b) ((a)<(b)?(a):(b))
#define IOS ios::sync_with_stdio(false)
#define mm(a, b) memset(a, b, sizeof(a))
#define each_cass(cass) for (cin>>cass; cass; cass--)
#define test(a) cout << "---------" << a << "---------" << '\n'
using namespace std;
#pragma endregion
//全局变量
#pragma region
const int maxn = 155000;
int nod[maxn];
int n, k;
int cnt = 0;
#pragma endregion
//主体------------------------------------------------------------
inline int find(int x){
return x == nod[x]? x:nod[x]=find(nod[x]);
}
inline void merge(int x, int y){
int fx = find(x);
int fy = find(y);
if(fx != fy){
nod[fx] = fy;
}
}
inline void init(){
for(int i = 0; i < maxn; i ++){
nod[i] = i;
}
}
Chivas{
IOS;
cin >> n >> k;
init();
for(int i = 0; i < k; i ++){
int id, x, y;
cin >> id >> x >> y;
if(x > n || y > n || x <= 0 || y <= 0){
++cnt;
continue;
}
int fx = find(x);
int fy = find(y);
if(id == 1){
if(find(x) == find(y + n) || find(x) == find(y + 2 * n)) ++cnt;
else merge(x, y), merge(x + n, y + n), merge(x + 2 * n, y + 2 * n);
}else{
if(x == y){
cnt ++;
continue;
}
if(find(x) == find(y) || find(x) == find(y + 2 * n)) ++cnt;
else merge(x, y + n), merge(x + n, y + 2 * n), merge(x + 2 * n, y);
}
}
cout << cnt << endl;
Regal;
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
# POJ1703_FindThem,CatchThem
# 🔗
http://poj.org/problem?id=1703
# 💡
与食物链一样 并查集不仅用在正面对象 也可以对背后的对象建立并查集 所以关键是在分析都对什么建立并查集
本题让建立两个集合(两个不同的帮派) 故可以对每个帮派的反派也建立 来维护相反派之间的关系 因为有时候得到某种关系的时候,无法进行两者合并,只能对a的反派和b合并,b的反派和a合并
# ✅
#pragma region
#pragma GCC optimize(3,"Ofast","inline")
#include <algorithm>
#include <iostream>
#include <cstring>
#include <string>
#include <vector>
#include <cstdio>
#include <stack>
#include <queue>
#include <cmath>
#include <map>
#include <set>
#define G 10.0
#define LNF 1e18
#define eps 1e-6
#define PI acos(-1.0)
#define ll long long
#define INF 0x7FFFFFFF
#define Regal exit(0)
#define Chivas int main()
#define pb(x) push_back(x)
#define SP system("pause")
#define Max(a,b) ((a)>(b)?(a):(b))
#define Min(a,b) ((a)<(b)?(a):(b))
#define IOS ios::sync_with_stdio(false)
#define mm(a, b) memset(a, b, sizeof(a))
#define each_cass(cass) for (cin>>cass; cass; cass--)
#define test(a) cout << "---------" << a << "---------" << '\n'
using namespace std;
#pragma endregion
//全局变量
#pragma region
const int maxn = 2e5 + 10;
int nod[maxn];
int n, m;
#pragma endregion
//主体----------------------------------------------------------------------------------
inline void Init(){
for(int i = 0; i <= n * 2; i ++) nod[i] = i;
}
inline int find(int x){
return x == nod[x] ? x : nod[x] = find(nod[x]);
}
inline void merge(int x, int y){
int fx = find(x);
int fy = find(y);
if(fx != fy) nod[fx] = fy;
}
inline void solve(){
scanf("%d%d", &n, &m);
Init();
for(int i = 0; i < m; i ++){
char op;
int a, b;
getchar();
scanf("%c%d%d", &op, &a, &b);
if(op == 'A'){
int fa = find(a);
int fb = find(b);
int fa_n = find(a + n);
int fb_n = find(b + n);
if(fa_n == fb_n || fa == fb)
cout << "In the same gang." << endl;
else if(fa_n == fb || fa == fb_n)
cout << "In different gangs." << endl;
else
cout << "Not sure yet." << endl;
}else{
merge(a + n, b);
merge(b + n, a);
}
}
}
Chivas{
IOS;
int cass;
scanf("%d", &cass);
while(cass--){
solve();
}
Regal;
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
# POJ1988_BuildingBlock
# 🔗
http://poj.org/problem?id=1988
# 💡
一个平平无奇的带权并查集
首先我们需要固定出三个信息:
1.x属于以y为底的堆,nod[x] = y
2.以x为底的堆有y个块,pile[x] = y
3.x块底下有y个块,down[x] = y
在每一次向下找堆底的块的时候,我们需要在逆序中回溯出这个堆中每个块底下有几个块
在每一次 x 向 y 合并的时候,我们都应该更新一下 x 下面的块数量、y这个堆的总块数、x属于的堆编号
# ✅
/*
________ _ ________ _
/ ______| | | | __ | | |
/ / | | | |__| | | |
| | | |___ _ _ _ ___ _ _____ | ___| ______ _____ ___ _ | |
| | | __ \ |_| | | | | | _\| | | ____| | |\ \ | __ | | _ | | _\| | | |
| | | | \ | _ | | | | | | \ | | \___ | | \ \ | |_/ _| | |_| | | | \ | | |
\ \______ | | | | | | \ |_| / | |_/ | ___/ | | | \ \ | /_ \__ | | |_/ | | |
Author : \________| |_| |_| |_| \___/ |___/|_| |_____| _________|__| \__\ |______| | | |___/|_| |_|
____| |
\_____/
*/
//#include <unordered_map>
#include <algorithm>
#include <iostream>
#include <cstring>
#include <utility>
#include <string>
#include <vector>
#include <cstdio>
#include <stack>
#include <queue>
#include <cmath>
#include <map>
#include <set>
#define G 10.0
#define LNF 1e18
#define EPS 1e-6
#define PI acos(-1.0)
#define INF 0x7FFFFFFF
#define ll long long
#define ull unsigned long long
#define LOWBIT(x) ((x) & (-x))
#define LOWBD(a, x) lower_bound(a.begin(), a.end(), x) - a.begin()
#define UPPBD(a, x) upper_bound(a.begin(), a.end(), x) - a.begin()
#define TEST(a) cout << "---------" << a << "---------" << endl
#define CHIVAS_ int main()
#define _REGAL exit(0)
#define SP system("pause")
#define IOS ios::sync_with_stdio(false)
//#define map unordered_map
#define PB(x) push_back(x)
#define ALL(a) a.begin(),a.end()
#define MEM(a, b) memset(a, b, sizeof(a))
#define EACH_CASE(cass) for (cass = inputInt(); cass; cass--)
#define LS l, mid, rt << 1
#define RS mid + 1, r, rt << 1 | 1
#define GETMID (l + r) >> 1
using namespace std;
template<typename T> inline T MAX(T a, T b){return a > b? a : b;}
template<typename T> inline T MIN(T a, T b){return a > b? b : a;}
template<typename T> inline void SWAP(T &a, T &b){T tp = a; a = b; b = tp;}
template<typename T> inline T GCD(T a, T b){return b > 0? GCD(b, a % b) : a;}
template<typename T> inline void ADD_TO_VEC_int(T &n, vector<T> &vec){vec.clear(); cin >> n; for(int i = 0; i < n; i ++){T x; cin >> x, vec.PB(x);}}
template<typename T> inline pair<T, T> MaxInVector_ll(vector<T> vec){T MaxVal = -LNF, MaxId = 0;for(int i = 0; i < (int)vec.size(); i ++) if(MaxVal <vec[i]) MaxVal = vec[i], MaxId = i; return {MaxVal, MaxId};}
template<typename T> inline pair<T, T> MinInVector_ll(vector<T> vec){T MinVal = LNF, MinId = 0;for(int i = 0; i < (int)vec.size(); i ++) if(MinVal > vec[i])MinVal = vec[i], MinId = i; return {MinVal, MinId};}
template<typename T> inline pair<T, T> MaxInVector_int(vector<T> vec){T MaxVal = -INF, MaxId = 0;for(int i = 0; i < (int)vec.size(); i ++) if(MaxVal <vec[i]) MaxVal = vec[i], MaxId = i; return {MaxVal, MaxId};}
template<typename T> inline pair<T, T> MinInVector_int(vector<T> vec){T MinVal = INF, MinId = 0;for(int i = 0; i < (int)vec.size(); i ++) if(MinVal > vec[i])MinVal = vec[i], MinId = i; return {MinVal, MinId};}
template<typename T> inline pair<map<T, T>, vector<T> > DIV(T n){T nn = n;map<T, T> cnt;vector<T> div;for(ll i = 2; i * i <= nn; i ++){while(n % i == 0){if(!cnt[i]) div.push_back(i);cnt[i] ++;n /= i;}}if(n != 1){if(!cnt[n]) div.push_back(n);cnt[n] ++;n /= n;}return {cnt, div};}
template<typename T> vector<T>& operator-- (vector<T> &v){for (auto& i : v) --i; return v;}
template<typename T> vector<T>& operator++ (vector<T> &v){for (auto& i : v) ++i; return v;}
template<typename T> istream& operator>>(istream& is, vector<T> &v){for (auto& i : v) is >> i; return is;}
template<typename T> ostream& operator<<(ostream& os, vector<T> v){for (auto& i : v) os << i << ' '; return os;}
inline int inputInt(){int X=0; bool flag=1; char ch=getchar();while(ch<'0'||ch>'9') {if(ch=='-') flag=0; ch=getchar();}while(ch>='0'&&ch<='9') {X=(X<<1)+(X<<3)+ch-'0'; ch=getchar();}if(flag) return X;return ~(X-1);}
inline void outInt(int X){if(X<0) {putchar('-'); X=~(X-1);}int s[20],top=0;while(X) {s[++top]=X%10; X/=10;}if(!top) s[++top]=0;while(top) putchar(s[top--]+'0');}
inline ll inputLL(){ll X=0; bool flag=1; char ch=getchar();while(ch<'0'||ch>'9') {if(ch=='-') flag=0; ch=getchar();}while(ch>='0'&&ch<='9') {X=(X<<1)+(X<<3)+ch-'0'; ch=getchar();}if(flag) return X;return ~(X-1); }
inline void outLL(ll X){if(X<0) {putchar('-'); X=~(X-1);}ll s[20],top=0;while(X) {s[++top]=X%10; X/=10;}if(!top) s[++top]=0;while(top) putchar(s[top--]+'0');}
const int N = 3e4 + 10;
int pile[N], down[N], nod[N];
int Q;
inline void Init ( ) { for ( int i = 0; i < N; i ++ ) nod[i] = i, down[i] = 0, pile[i] = 1; }
inline int Find ( int x ) {
int fx = nod[x];
if ( fx != x ) {
nod[x] = Find(nod[x]); // 正常的搜祖先
down[x] += down[fx]; // 用父亲回溯出儿子的下块数
}return nod[x];
}
inline void Merge ( int x, int y ) {
int fx = Find(x);
int fy = Find(y);
if ( fx != fy ) {
nod[fx] = fy; // fx 整体编号改变
down[fx] = pile[fy]; // fx 下面的块数多了 fy 这个堆的块数
pile[fy] += pile[fx]; // fy 这个堆的块数多了 fx 这个堆的块数
}
}
CHIVAS_{Init();
Q = inputInt();
while ( Q -- ) {
char op; scanf("%c", &op);
if ( op == 'C' ) {
int id = inputInt();
int k = Find(id); // 不能少,要更新一下当前块的down值
outInt(down[id]); puts("");
} else {
int a = inputInt(), b = inputInt();
Merge(a, b);
}
}
_REGAL;
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
99
100
101
102
103
104
105
106
107
108
109
110
111
112
113
114
115
116