二分
#
# 洛谷P1462_通往奥格瑞玛的道路
# 🔗
# 💡
二分答案,check() 可以通过删点来解决
在不走 的情况下,即提前标记 ,看看最短路是多少
和血量 比较一下
# ✅
const int N = 1e4 + 10;
const int M = 1e5 + 10;
int n, m; ll b;
ll f[N];
bool vis[N];
ll dis[N];
struct Edge {
int nxt, to;
ll val;
} edge[M];
int head[N], cnt;
inline void add_Edge ( int from, int to, ll val ) {
edge[++cnt] = { head[from], to, val };
head[from] = cnt;
}
struct node { int id; ll dis; inline friend bool operator < ( node a, node b ) { return a.dis > b.dis; } };
inline bool Check ( ll x ) {
for ( int i = 1; i <= n; i ++ ) {
if ( f[i] <= x ) vis[i] = false;
else vis[i] = true;
dis[i] = 1e18;
}
priority_queue<node> pque;
pque.push({1, 0});
dis[1] = 0;
while ( !pque.empty() ) {
node cur = pque.top(); pque.pop();
if ( vis[cur.id] ) continue; vis[cur.id] = true;
for ( int i = head[cur.id]; i; i = edge[i].nxt ) {
int to = edge[i].to;
if ( dis[to] > dis[cur.id] + edge[i].val && !vis[to] ) {
dis[to] = dis[cur.id] + edge[i].val;
pque.push({to, dis[to]});
}
}
}
return dis[n] < b;
}
int main () {
scanf("%d%d%lld", &n, &m, &b);
for ( int i = 1; i <= n; i ++ ) scanf("%lld", &f[i]);
for ( int i = 1; i <= m; i ++ ) {
int x, y; ll z; scanf("%d%d%lld", &x, &y, &z);
add_Edge(x, y, z);
add_Edge(y, x, z);
}
ll l = 0, r = 1000000005;
if ( Check(r) == false ) {
puts("AFK");
return 0;
}
ll res = r;
while ( l <= r ) {
int mid = (l + r) >> 1;
if ( Check(mid) ) res = mid, r = mid - 1;
else l = mid + 1;
}
printf("%lld\n", res);
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
# 洛谷P1663_山
# 🔗
# 💡
思考什么样的点才可以被所有地方看见
在所有山坡直线上方的点
那么我们对于一个 ,可以求出它与所有山坡的交点
利用交点我们可以得到对于每个山坡,它能被看见的话, 可在的区间
利用二分答案,每一个 check() 是:对于所有 可以被看到的区间是否有交集
# ✅
struct node {
double k, b;
} l[5010];
pair<double, double> p[5010];
int n;
inline bool check ( double y ) {
double L = -1e10, R = 1e10;
for ( int i = 0; i < n - 1; i ++ ) {
if ( l[i].k == 0 ) {
if ( l[i].b > y ) return false;
} else {
double x0 = (y - l[i].b) / l[i].k, y0 = y;
if ( l[i].k < 0 ) L = max(L, x0);
else R = min(R, x0);
}
}
return L <= R;
}
int main () {
cin >> n;
for ( int i = 0; i < n; i ++ ) {
cin >> p[i].first >> p[i].second;
if ( i ) {
l[i - 1].k = (p[i].second - p[i - 1].second) / (p[i].first - p[i - 1].first);
l[i - 1].b = p[i].second - l[i - 1].k * p[i].first;
}
}
double l = 0, r = 1e10;
while ( r - l > 1e-6 ) {
double mid = (l + r) / 2;
if ( check(mid) ) r = mid;
else l = mid;
}
printf("%.3f\n", l);
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
# 洛谷P1704_寻找最优美做题曲线
# 🔗
# 💡
既然 是必须出现在 中的
那么我们可以找到 中一定不会出现在 中的,删去
即对于 或 的都不行
一看数据范围用二分法算
每次遇见 后都一定会进行 push_back()
# ✅
const int N = 5e5 + 10;
int n, k;
int p[N], c[N];
bool del[N];
int main () {
ios::sync_with_stdio(false);
cin >> n >> k;
for ( int i = 1; i <= k; i ++ ) cin >> p[i];
for ( int i = 1; i <= n; i ++ ) cin >> c[i];
sort ( p + 1, p + 1 + k );
for ( int i = 2; i <= k; i ++ ) {
if ( c[p[i]] <= c[p[i - 1]] ) {
cout << "impossible" << endl;
return 0;
}
}
for ( int j = 1; j < p[1]; j ++ ) if ( c[j] >= c[p[1]] ) del[j] = true;
for ( int j = p[k] + 1; j <= n; j ++ ) if ( c[j] <= c[p[k]] ) del[j] = true;
for ( int i = 2; i <= k; i ++ ) {
for ( int j = p[i - 1] + 1; j < p[i]; j ++ ) {
if ( c[j] <= c[p[i - 1]] || c[j] >= c[p[i]] )
del[j] = true;
}
}
vector<int> vec;
for ( int i = 1; i <= n; i ++ ) {
if ( del[i] ) continue;
if ( vec.empty() || vec.back() < c[i] ) vec.push_back(c[i]);
else vec[lower_bound(vec.begin(), vec.end(), c[i]) - vec.begin()] = c[i];
}
cout << vec.size() << endl;
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
# 洛谷P1768_天路
# 🔗
# 💡
带环的图很难求最长环
可以想一想能不能判断一个数是否为答案
考虑若 是最后的结果
那么必然所有的环均满足
这样权值大小就很明显了,在最大值中找到最小的也是二分答案的标志
使用密度二分,每次对边权重新赋值
如果具有环 那么说明还没有到最大值
否则的话可能比最大值要大
那么就是判断是否有负环,如果有的话就说名具有环满足上面的不等式,这个便是 check()
要注意可能会有不连通的情况,我们可以建立超级源点连接所有的边
这里 BFS 版 会寄, DFS 版勉强过
# ✅
const int N = 7010;
const int M = 40010;
struct Edge {
int nxt, to;
int v, p;
double val;
} edge[M];
int head[N], cnt;
inline void add_Edge ( int from, int to, int v, int p ) {
edge[++cnt] = { head[from], to, v, p };
head[from] = cnt;
}
int n, m;
bool vis[N];
double dis[N];
inline bool has_Neg ( int x ) {
vis[x] = true;
for ( int i = head[x]; i; i = edge[i].nxt ) {
int to = edge[i].to;
if ( dis[to] > dis[x] + edge[i].val ) {
dis[to] = dis[x] + edge[i].val;
if ( vis[to] ) return true;
if ( has_Neg(to) ) return true;
}
}
vis[x] = false;
return false;
}
int main () {
scanf("%d%d", &n, &m);
for ( int i = 0; i < m; i ++ ) {
int a, b, c, d; scanf("%d%d%d%d", &a, &b, &c, &d);
add_Edge(a, b, c, d);
}
for ( int i = 1; i <= n; i ++ ) add_Edge(0, i, 0, 0);
double l = 0, r = 7000000;
while ( r - l > 1e-6 ) {
double mid = (l + r) / 2;
for ( int i = 1; i <= cnt; i ++ ) edge[i].val = mid * edge[i].p - edge[i].v;
for ( int i = 0; i <= n; i ++ ) vis[i] = 0, dis[i] = 100000000;
dis[0] = 0;
has_Neg(0) ? l = mid : r = mid;
}
if ( l == 0 ) {
puts("-1");
return 0;
}
printf("%.1f\n", l);
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
# 洛谷P1800_software
# 🔗
# 💡
两个限制,即模块和模块的完成数要达到
但是没有对应的价值,那么我们可以令一个模块的完成数作为价值,一个作为限制
那么开
表示前 个人完成 个模块下最多能完成多少个模块
由于时间固定出每个物品的价值(完成物品体积个模块后又能完成多少个模块),那么就是枚举时间,枚举物品,枚举背包容积,再枚举物品容积
这是一个 的复杂度
但是考虑一下随着时间增大, 肯定是单调递增的,那么时间使用二分答案判断 是否
# ✅
const int N = 110;
const int M = 110;
int n, m;
int a[N], b[N];
int dp[N][M];
inline bool Check ( int tim ) {
memset(dp, -0x3f3f3f3f, sizeof dp);
dp[0][0] = 0;
for ( int i = 1; i <= n; i ++ ) {
for ( int j = 0; j <= m; j ++ ) { // 一共做了 j 个模块1
for ( int k = 0; k <= j; k ++ ) { // 第 i 个人做 k 个模块1
int time_else = tim - k * a[i];
if ( time_else >= 0 )
dp[i][j] = max(dp[i][j], dp[i - 1][j - k] + time_else / b[i]);
}
}
}
return dp[n][m] >= m;
}
int main () {
ios::sync_with_stdio(false);
cin >> n >> m;
for ( int i = 1; i <= n; i ++ ) cin >> a[i] >> b[i];
int l = 1, r = 100000;
while ( l <= r ) {
int mid = (l + r) >> 1;
if ( Check(mid) ) r = mid - 1;
else l = mid + 1;
}
cout << l << endl;
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
# 洛谷P1948_TelephoneLinesS
# 🔗
# 💡
以最大的那一条边做价值,经典二分答案的套路了
check(x) 表示路径上是否可以走不超过 条边权 的边,这些边可以免费
在此我们希望路径上大于等于 的越少越好,那就以 做权值,只有 和 来跑最短路
最终 则是从 到 最少有几个边权 的边
如果这个数量 了说明我们还可以继续往 小了找,否则要放松范围往 了找
最后二分出来的结果就是答案
# ✅
const int N = 1003;
const int M = 20004;
struct Edge {
int nxt, to, val;
} edge[M];
int head[N], cnt;
inline void add_Edge (int from, int to, int val) {
edge[++cnt] = {head[from], to, val};
head[from] = cnt;
}
int dis[N];// 1->i最少有多少个 长度>x的边
int vis[N];
int n, p, k;
struct node {
int id, val;
inline friend bool operator < (node a, node b) {
return a.val > b.val;
}
};
inline bool check (int x) {
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i ++) dis[i] = 0x3f3f3f3f, vis[i] = 0;
dis[1] = 0;
priority_queue<node> pque;
pque.push({1, 0});
while (!pque.empty()) {
int u = pque.top().id; pque.pop();
if (vis[u]) continue; vis[u] = 1;
for (int i = head[u]; i; i = edge[i].nxt) {
int v = edge[i].to;
int d = edge[i].val >= x;
if (dis[v] > dis[u] + d) {
dis[v] = dis[u] + d;
pque.push({v, dis[v]});
}
}
}
return dis[n] <= k;
}
int main () {
ios::sync_with_stdio(false);
cin.tie(nullptr);
cin >> n >> p >> k;
for (int i = 0; i < p; i ++) {
int u, v, w; cin >> u >> v >> w;
add_Edge(u, v, w);
add_Edge(v, u, w);
}
int l = 0, r = 1000000, res = 1000001;
while (l <= r) {
int mid = (l + r) >> 1;
if (check(mid)) res = mid, r = mid - 1;
else l = mid + 1;
}
if (res == 0) res = 1;
else if (res == 1000001) res = 0;
cout << res - 1 << endl;
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
# 洛谷P2323_公路修建问题
# 🔗
# 💡
因为答案是一个数值且要最小,所以具有单调性
且具有很多限制,如果给定一个数值我们可以很好地得出是否可以完成指标( 个 ,还要完成可以构建生成树
那么我们利用这个限制,去二分答案求解,check() 可以通过删边来解决
每次用 去 先扫一遍尽可能去把 的道路都建上
满足了 个边了再去看看生成树可不可以
# ✅
const int N = 2e4 + 10;
int n, k, m;
namespace UnionSet {
int nod[N];
inline void Init () { for ( int i = 0; i <= n; i ++ ) nod[i] = i; }
inline int Find ( int x ) { return x == nod[x] ? x : Find(nod[x]); }
inline void Merge ( int x, int y ) { int fx = Find(x), fy = Find(y); if ( fx != fy ) nod[fx] = fy; }
inline bool is_Similar ( int x, int y ) { int fx = Find(x), fy = Find(y); return fx == fy; }
} using namespace UnionSet;
struct Edge {
int a, b, c1, c2;
} e[N];
inline bool Check ( int x ) {
Init();
int cntk = 0, cnt = 0;
for ( int i = 0; i < m; i ++ ) {
if ( e[i].c1 <= x ) {
if ( !is_Similar(e[i].a, e[i].b) )
Merge(e[i].a, e[i].b),
cntk ++,
cnt ++;
}
if ( cnt == n - 1 ) {
return cntk >= k;
}
}
if ( cntk < k ) return false;
for ( int i = 0; i < m; i ++ ) {
if ( e[i].c2 <= x ) {
if ( !is_Similar(e[i].a, e[i].b) )
Merge(e[i].a, e[i].b),
cnt ++;
}
if ( cnt == n - 1 ) break;
}
return cnt == n - 1;
}
int main () {
scanf("%d%d%d", &n, &k, &m);
for ( int i = 0; i < m; i ++ ) scanf("%d%d%d%d", &e[i].a, &e[i].b, &e[i].c1, &e[i].c2);
int l = 1, r = 30000;
int res = 30000;
while ( l <= r ) {
int mid = (l + r) >> 1;
if ( Check(mid) ) res = mid, r = mid - 1;
else l = mid + 1;
}
printf("%d\n", res);
Init();
int cnt = 0, cntk = 0;
for ( int i = 0; i < m; i ++ ) {
if ( e[i].c1 <= res ) {
if ( !is_Similar(e[i].a, e[i].b) )
Merge(e[i].a, e[i].b),
cntk ++,
cnt ++,
printf("%d 1\n", i + 1);
}
if ( cnt == n - 1 ) return 0;
}
for ( int i = 0; i < m; i ++ ) {
if ( e[i].c2 <= res ) {
if ( !is_Similar(e[i].a, e[i].b) )
Merge(e[i].a, e[i].b),
cnt ++,
printf("%d 2\n", i + 1);
}
if ( cnt == n - 1 ) return 0;
}
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
# 洛谷P2754_家园 / 星际转移问题
# 🔗
# 💡
如果就是正常平面上画一个图,会发现出现绕环的情况,也就是对于一条航母路线,是一个环,这样就会导致环上两个点同时接收流量的情况出现,而正常来看是有时间存在的
既然存在时间,那就多加一条时间线,而对于相同的节点,在不同时刻是存在不同的状态,它们不是一个点
故一个时间开 个节点( 个空间站和地月球),那么就在 时刻, 航母可以用 与 相连,容量就是该航母容量
而且相邻时刻下,同一个节点的人是可以留在这个点的,就对每一个时刻的每一个节点向下一个时刻的该节点传递一个 的容量
那么为了研究 到 时间,能运走多少人,开 个时刻进行上面的操作,然后就需要源点向每一个时刻的地球都挂 个人,然后让每一时刻的月球连向汇点容量为 , 时间内能运走的人数就是总流量
这只是能判断出来这么长时间能运多少,这是一个判定条件,且时间越长能运的越多
故开二分
# ✅
const int N = 15, M = 25, K = 55;
struct Edge {
int nxt, to, flow;
} edge[N * K * N * N + 10];
int head[N * K * N + 10], cnt;
inline void add_Edge (int from, int to, int flow) {
edge[++cnt] = {head[from], to, flow};
head[from] = cnt;
edge[++cnt] = {head[to], from, 0};
head[to] = cnt;
}
inline void init_Edge () {
memset(head, 0, sizeof head);
cnt = 1;
}
int deep[N * K * N + 10], aim;
inline bool bfs (int S, int T) {
aim = T;
memset(deep, 0, sizeof deep);
deep[S] = 1; queue<int> que;
que.push(S);
while (!que.empty()) {
int u = que.front(); que.pop();
for (int i = head[u]; i; i = edge[i].nxt) {
int v = edge[i].to;
if (edge[i].flow && !deep[v]) {
deep[v] = deep[u] + 1;
que.push(v);
}
}
}
return deep[T];
}
inline int dfs (int u, int fl) {
if (u == aim) return fl;
int f = 0;
for (int i = head[u]; i && fl; i = edge[i].nxt) {
int v = edge[i].to;
if (deep[v] == deep[u] + 1 && edge[i].flow) {
int x = dfs(v, min(fl, edge[i].flow));
edge[i].flow -= x;
edge[i ^ 1].flow += x;
fl -= x;
f += x;
}
}
if (!f) deep[u] = -2;
return f;
}
inline int dicnic (int S, int T) {
int ret = 0;
while (bfs(S, T)) ret += dfs(S, 0x3f3f3f3f);
return ret;
}
vector<int> path[M];
int h[M], sz[M];
int n, m, k;
int S, T;
int mat[N * K][N];
inline bool Check (int x) {
init_Edge();
for (int i = 0; i + 1 < x; i ++) {
for (int j = 1; j <= m; j ++) {
int u = path[j][i % sz[j]];
int v = path[j][(i + 1) % sz[j]];
add_Edge(mat[i][u], mat[i + 1][v], h[j]);
}
for (int j = 0; j <= n + 1; j ++)
add_Edge(mat[i][j], mat[i + 1][j], 0x3f3f3f3f);
}
for (int i = 0; i < x; i ++)
add_Edge(S, mat[i][0], 0x3f3f3f3f),
add_Edge(mat[i][n + 1], T, 0x3f3f3f3f);
int mxf = dicnic(S, T);
return mxf >= k;
}
int main () {
for (int i = 0; i < N * K; i ++) for (int j = 0; j < N; j ++) mat[i][j] = i * N + j;
S = N * K * N;
T = S + 1;
scanf("%d%d%d", &n, &m, &k);
for (int i = 1; i <= m; i ++) {
scanf("%d%d", &h[i], &sz[i]);
for (int j = 1; j <= sz[i]; j ++) {
int x; scanf("%d", &x);
path[i].push_back(x == -1 ? n + 1 : x);
}
}
int l = 1, r = N * K - 1, res = 0x3f3f3f3f;
while (l <= r) {
int mid = (l + r) >> 1;
if (Check(mid)) res = mid, r = mid - 1;
else l = mid + 1;
}
printf("%d\n", res == 0x3f3f3f3f ? 0 : res - 1);
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
99
100
101
102
# 洛谷P5546_公共串
# 🔗
# 💡
初始可以想一个高复杂度的
这个数据量看来似乎可以将所有的子串全部枚举出来了
存储的时候如果存储所有子串空间不够,考虑压缩为 数值存储
可以直接用 将 设置为 值,将 设置为二进制表示在哪个字符串中出现过
第 个串的所有子串全部与上 最后扫描所有子串看看是否够 ,够的话代表在所有字符串中均出现过,维护最大值
这样分析一下复杂度 有点大了,优化一下
求最长公共子串应该要注意到这个“最”字,可以看一下是否存在单调性
可以发现,如果 为公共子串,那么 也为公共子串
这就证明检查公共子串的长度是否存在是存在 单调性的
于是直接二分答案即可,复杂度为 的
# ✅
const int N = 2e3 + 10;
const ll mod1 = 2000000011;
const ll mod2 = 3000000019;
const int HASH1 = 20023;
const int HASH2 = 20011;
ll h1[N], h2[N];
ll sum1[10][N], sum2[10][N];
inline ll query1 (int l, int r, int op) {
return ((sum1[op][r] - sum1[op][l - 1] * h1[r - l + 1] % mod1) % mod1 + mod1) % mod1;
}
inline ll query2 (int l, int r, int op) {
return ((sum2[op][r] - sum2[op][l - 1] * h2[r - l + 1] % mod2) % mod2 + mod2) % mod2;
}
inline pair<ll, ll> query (int l, int r, int op) {
return {query1(l, r, op), query2(l, r, op)};
}
int n;
int len[10];
inline bool Check (int x) {
map<pair<ll, ll>, int> mp;
for (int i = 0; i < n; i ++) {
for (int j = 1; j + x - 1 <= len[i]; j ++) {
mp[query(j, j + x - 1, i)] |= 1 << i;
if (mp[query(j, j + x - 1, i)] == (1 << n) - 1) return true;
}
}
return false;
}
char str[10][N];
int main () {
h1[0] = h2[0] = 1;
for (int i = 1; i < N; i ++) h1[i] = h1[i - 1] * HASH1 % mod1, h2[i] = h2[i - 1] * HASH2 % mod2;
cin >> n;
for (int i = 0; i < n; i ++) {
cin >> (str[i] + 1);
len[i] = strlen(str[i] + 1);
for (int j = 1; j <= len[i]; j ++) {
sum1[i][j] = (sum1[i][j - 1] * HASH1 % mod1 + str[i][j]) % mod1;
sum2[i][j] = (sum2[i][j - 1] * HASH2 % mod2 + str[i][j]) % mod2;
}
}
int l = 1, r = 2000, res = 0;
while (l <= r) {
int mid = (l + r) >> 1;
if (Check(mid)) res = mid, l = mid + 1;
else r = mid - 1;
}
cout << res << endl;
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
# 洛谷P5657_格雷码
# 🔗
# 💡
一道二分观察的好题
(感觉没有涉及到位运算的思想鸭(逃
因为每一次都是将整个序列的长度*2
是一个以 2 为基数按规律构造的序列
那么可以想 log(n) 怎么操作
好好观察一下,将当前固定出的序列分半(记为这是第x次分半
可以看出,在x位上,原段的两半呈现一半为1一半为0,如果上一步是选择右边的一半,那么左1右0,否则左0右1
根据这个规律,我们就可以二分地写出来了
# ✅
int main () {
ios::sync_with_stdio(false);
ll n; cin >> n;
ll k; cin >> k;
ll l = 0, r = (1ll << n) - 1;
bool where; //false: lft, true: rgt
while ( n -- ) {
ll mid = (l + r) >> 1;
if ( k <= mid ) cout << 0 + where, r = mid, where = false;
else cout << 1 - where, l = mid + 1, where = true;
}
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
# 牛客2022寒假算法基础集训营5A_疫苗小孩
# 🔗
# 💡
统计字符串中为 的位置 后
我们枚举每个起始点
对 去找离 最近的左右两点,满足的统计一下
然后对该左右两点分别去找最近的 的左右两点,满足的统计一下
即:
# ✅
ll k, w, q;
inline ll calc ( ll a, ll b ) { // 计算 a->b 的提升值
return w - llabs(b - a - k) * q;
}
int main () {
ios::sync_with_stdio(false);
ll n; string s; cin >> n >> s;
cin >> k >> w >> q;
vector<ll> ps;
for ( int i = 0; i < s.size(); i ++ ) {
if ( s[i] == '0' ) ps.push_back(i);
}
ll res = 0;
for ( int i = 0; i < ps.size(); i ++ ) {
ll pos02 = lower_bound(ps.begin(), ps.end(), ps[i] + k) - ps.begin();
ll pos01 = pos02 - 1;
if ( pos02 != ps.size() && pos02 > i ) res = max(res, calc(ps[i], ps[pos02]));
if ( pos01 != ps.size() && pos01 > i ) res = max(res, calc(ps[i], ps[pos01]));
if ( pos02 != ps.size() && pos02 > i ) {
ll disi02 = calc(ps[i], ps[pos02]);
ll pos022 = lower_bound(ps.begin(), ps.end(), ps[pos02] + k) - ps.begin();
ll pos021 = pos022 - 1;
if ( pos022 != ps.size() && pos022 > pos02 ) res = max(res, disi02 + calc(ps[pos02], ps[pos022]));
if ( pos021 != ps.size() && pos021 > pos02 ) res = max(res, disi02 + calc(ps[pos02], ps[pos021]));
}
if ( pos01 != ps.size() && pos01 > i ) {
ll disi01 = calc(ps[i], ps[pos01]);
ll pos012 = lower_bound(ps.begin(), ps.end(), ps[pos01] + k) - ps.begin();
ll pos011 = pos012 - 1;
if ( pos012 != ps.size() && pos012 > pos01 ) res = max(res, disi01 + calc(ps[pos01], ps[pos012]));
if ( pos011 != ps.size() && pos011 > pos01 ) res = max(res, disi01 + calc(ps[pos01], ps[pos011]));
}
}
cout << res << endl;
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
# ABC236E_AverageAndMedian
# 🔗
# 💡
二分求平均数是一个经典的密度二分
一个位置可以选或者不选,但是不能有两个相邻的不选
这个我们可以感觉到 就可以推出来
平均数
问题在于: 在不同选中数量下,一个数对平均数的贡献是不同的
但是我们求总值是很好求的
这个就奠定了我们可以给出一个平均数 ave 来判断能否获得比这个平均数更大的值
每一个数的贡献就变成了 x-ave
只要最终贡献大于 0 ,我们就可以说能造出来
通过这个编写一个 check ,过程中采用 的解法去递推,判断最终结果即可
中位数
有了上一个问题做支撑
我们也可以想到这个可以尝试用二分去解决
根上一个不同的是,我们在设置期望中位数 mid 后,每一个数的贡献不同了
思考中位数的命名性质,我们只要求出 “比 mid 大的数的个数” 减去 “比 mid 小的数的个数” 的差
如果这个差大于 ,那么就说明我们可以造出比它更高的中位数
两个 check 搭建完毕,可以二分了
# ✅
const int N = 1e5 + 10;
int n;
int a[N];
double f[2][N]; // 0:不选i,1:选i
inline bool Check1 ( double ave ) {
for ( int i = 1; i <= n; i ++ ) {
f[1][i] = max(f[1][i - 1] + 1.0 * a[i] - ave, f[0][i - 1] + 1.0 * a[i] - ave);
f[0][i] = f[1][i - 1];
}
return max(f[1][n], f[0][n]) > 0;
}
inline void Solve1 () {
double l = 0, r = 1e9;
while ( l - r < -1e-6 ) {
double mid = (l + r) / 2;
if ( Check1(mid) ) l = mid;
else r = mid;
}
printf("%.4f\n", l);
}
double g[2][N]; // 0:不选i,1:选i
inline bool Check2 ( int mid ) {
for ( int i = 1; i <= n; i ++ ) {
g[1][i] = max(g[1][i - 1] + (a[i] >= mid ? 1 : -1), g[0][i - 1] + (a[i] >= mid ? 1 : -1) );
g[0][i] = g[1][i - 1];
}
return max(g[1][n], g[0][n]) > 0;
}
inline void Solve2 () {
int l = 0, r = 1e9;
int res = 0;
while ( l <= r ) {
int mid = (l + r) / 2;
if ( Check2(mid) ) l = mid + 1, res = mid;
else r = mid - 1;
}
printf("%d\n", res);
}
int main () {
scanf("%d", &n);
for ( int i = 1; i <= n; i ++ ) scanf("%d", &a[i]);
Solve1();
Solve2();
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
# AcWing2694_最长公共子序列
# 🔗
# 💡
LCS是个动态规划问题,但我们可以用DP的思想贪过去
因为a中每个数只出现过一次,所以在这道题里面,我们可以将问题转化为一个LIS问题
首先设置一个数组id[]用来存入a数组里面的每个出现的数的下标
然后将b数组转化为b'数组,即b'[i] = id[b[i]]用来表示:b数组中当前数在a数组中对应的下标
那么要想b中的某个序列在a中也是其中的序列
就需要我们得到的这个b'中的某个子序列,在a中出现过就行了,同时要保证在a中的下标是顺序的
所以问题可以转化为求b'数组的最长上升子序列
具体LIS问题求法可以看 -> 这里 (opens new window)
我们发现这个数据范围是的,所以我们采用贪心+二分优化,时间复杂度O(nlogn)
# ✅
const int N = 1e6 + 10;
int id[N], n;
vector<int> vec;
int main(){
read(n);
for(int i = 1, x; i <= n; i ++) read(x), id[x] = i;
for(int i = 1, x; i <= n; i ++){ read(x);
if(!id[x]) continue;//注意:如果没出现过那就不要加进去了
if(vec.empty() || vec.back() < id[x]) vec.push_back(id[x]);
else vec[lower_bound(vec.begin(), vec.end(), id[x]) - vec.begin()] = id[x];
}write(vec.size());
return 0;
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
# CCPC2017哈尔滨站L_ColorATree
# 🔗
# 💡
操作是子树最少选 个
操作是非子树最少选 个,想办法把 移植成 的格式,那么就是子树最多选 个,这样就是一个区间的向上递归满足的问题
我们在判断一个 是否可行时,将其进行区间嵌套 到 也就是根节点,看看 的范围内是否存在 ,如果存在说明可行
且可以看出来黑点从少到多的可行判断是存在单调性的,所以对 二分即可
# ✅
const int N = 1e5 + 10;
const int M = N << 1;
struct Edge {
int nxt, to;
} edge[M];
int head[N], cnt;
inline void add_Edge (int from, int to) {
edge[++cnt] = {head[from], to};
head[from] = cnt;
}
int sz[N];
inline void dfs_Pre (int u, int fa) {
sz[u] = 1;
for (int i = head[u]; i; i = edge[i].nxt) {
int v = edge[i].to;
if (v == fa) continue;
dfs_Pre(v, u);
sz[u] += sz[v];
}
}
int n, m1, m2;
pair<int, int> A[N], B[N];
pair<int, int> limit[N];
inline pair<int, int> intersect (pair<int, int> a, pair<int, int> b) {
return {max(a.first, b.first), min(a.second, b.second)};
}
inline void dfs (int u, int fa) {
pair<int, int> limu = {0, 1};
for (int i = head[u]; i; i = edge[i].nxt) {
int v = edge[i].to;
if (v == fa) continue;
dfs(v, u);
limu.first += limit[v].first;
limu.second += limit[v].second;
}
limit[u] = intersect(limit[u], limu);
}
inline bool check (int x) {
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i ++) limit[i] = {0, sz[i]};
for (int i = 1; i <= m1; i ++) limit[A[i].first].first = max(limit[A[i].first].first, A[i].second);
for (int i = 1; i <= m2; i ++) limit[B[i].first].second = min(limit[B[i].first].second, x - B[i].second);
dfs(1, 0);
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i ++) if (limit[i].first > limit[i].second) return false;
if (limit[1].first <= x && x <= limit[1].second) return true;
return false;
}
inline void Solve () {
scanf("%d", &n);
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i ++) head[i] = 0; cnt = 0;
for (int i = 1; i < n; i ++) {
int u, v; scanf("%d%d", &u, &v);
add_Edge(u, v);
add_Edge(v, u);
}
dfs_Pre(1, 0); bool flag = true;
scanf("%d", &m1);
for (int i = 1; i <= m1; i ++) {
scanf("%d%d", &A[i].first, &A[i].second);
if (A[i].second > sz[A[i].first]) flag = false;
}
scanf("%d", &m2);
for (int i = 1; i <= m2; i ++) {
scanf("%d%d", &B[i].first, &B[i].second);
if (B[i].second > n - sz[B[i].first]) flag = false;
}
if (!flag) {
puts("-1");
return;
}
int l = 0, r = n, res = n;
while (l <= r) {
int mid = (l + r) >> 1;
if (check(mid)) res = mid, r = mid - 1;
else l = mid + 1;
}
printf("%d\n", res);
}
int main () {
int cas; scanf("%d", &cas); while (cas --) {
Solve();
}
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
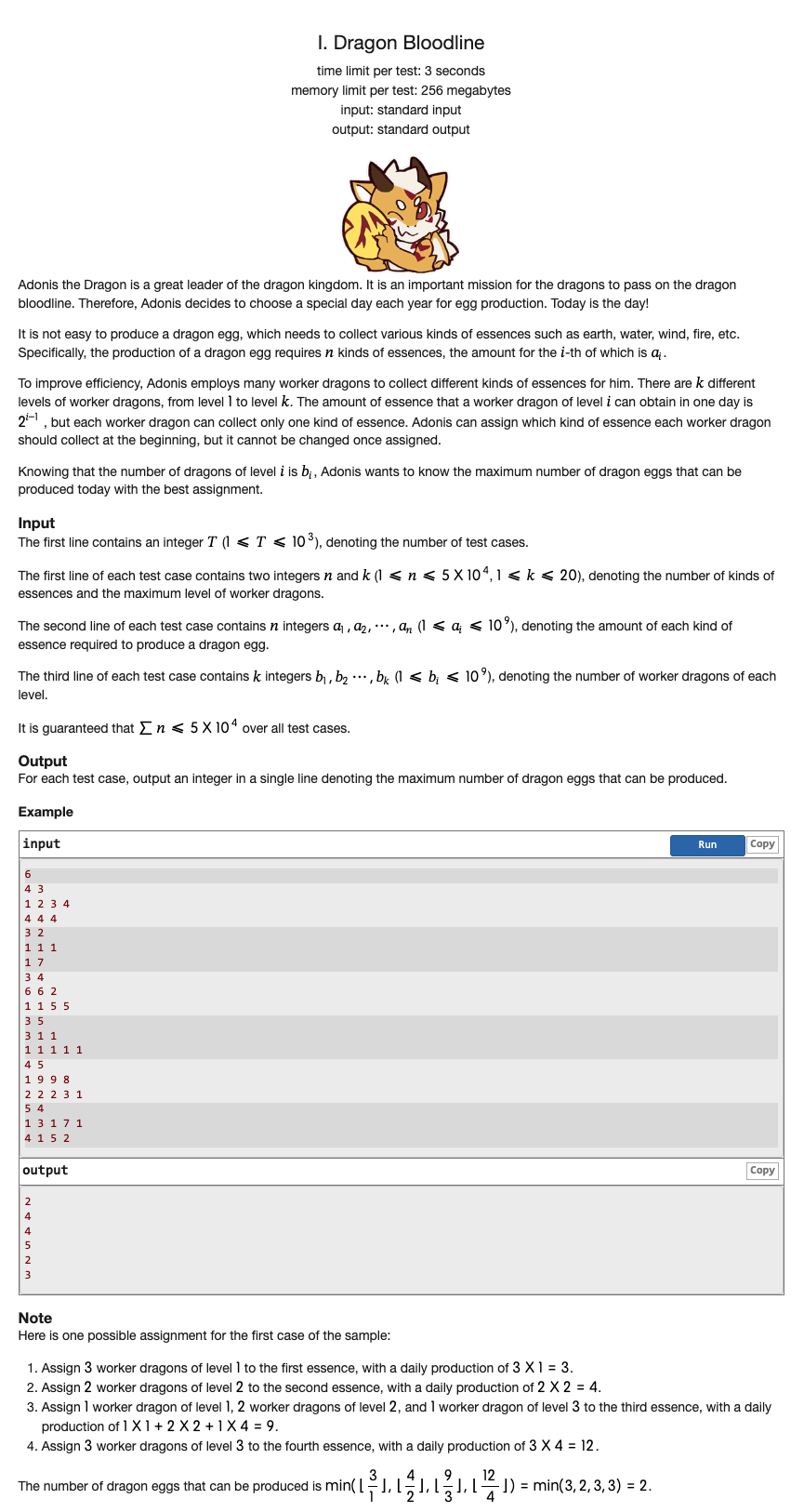
# CCPC2022威海站I_DragonBloodline
# 🔗
# 💡
由于我们很难求得最多能满足多少套食物,但是我们可以判定是否可以满足 套食物即材料 用 个
这个判定是会随着 存在单调性的,故使用二分答案
在 里面分配时,从效率高的龙开始往效率低的龙枚举, 效率的龙首先分给所有 的材料 个,当然数量总和不能超过龙数,如果最后还有剩余的,分给最多的几个材料一个材料一份
到最后判断一下是否所有材料都被给占满了即可
# ✅
const int N = 5e5 + 10;
int n, k;
__int128_t a[N], b[N], tb[N], c[N];
inline bool check (__int128_t x) {
for (int i = 0; i < k; i ++) b[i] = tb[i];
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i ++) c[i] = x * a[i];
for (int i = k - 1; i >= 0; i --) {
for (int j = 1; j <= n; j ++) {
if (c[j] <= 0) continue;
__int128_t cos = min(b[i], c[j] / (1 << i));
b[i] -= cos;
c[j] -= cos * (1 << i);
}
if (n < b[i]) nth_element(c + 1, c + 1 + n, c + 1 + n, [&](int e, int f){return e > f;});
else nth_element(c + 1, c + 1 + b[i], c + 1 + n, [&](int e, int f){return e > f;});
for (int j = 1; j <= b[i] && j <= n; j ++) {
c[j] -= 1 << i;
}
}
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i ++) if (c[i] > 0) return false;
return true;
}
inline void Solve () {
scanf("%d%d", &n, &k);
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i ++) {
int x; scanf("%d", &x);
a[i] = x;
}
for (int i = 0; i < k; i ++) {
int x; scanf("%d", &x);
tb[i] = x;
}
ll l = 0, r = 2e15, res = 0;
while (l <= r) {
ll mid = (l + r) >> 1;
if (check(mid)) res = mid, l = mid + 1;
else r = mid - 1;
}
printf("%lld\n", res);
}
int main () {
int cass; scanf("%d", &cass); while (cass --) {
Solve ();
}
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
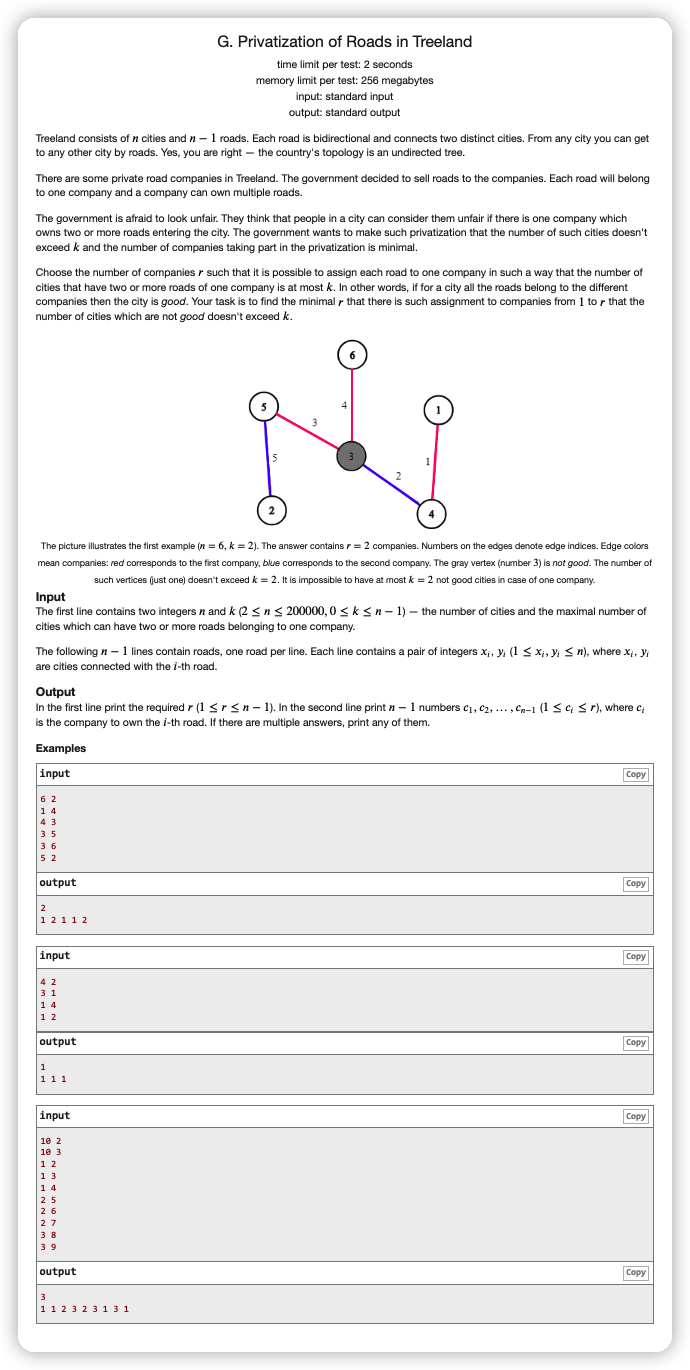
# CodeForces1141G_PrivatizationOfRoadsInTreeland
# 🔗
# 💡
首先根据鸽巢原理,如果一个点接了 条边,我们有 个公司,当 时,这个点必会被两个相同公司的边连接。
那么我们判断最少需要用多少个公司就有方法了,由于每个点的 是固定的也就是 ,我们最多坏点个数也是确定的,且公司越多坏点越少,单调性也有了,那么可以直接二分出来。
对于 check(mid) 的时候,我们去看有多少个点的度数 也就是有多少个坏点,如果有超过 个坏点,那么就是 false ,否则是 true
那么染色的方式就比较多了,思考一下省事点就是 ,一个点连接向儿子的边的公司,在与连接父亲的边的公司不同的情况下尽量不重复地去选即可
# ✅
const int N = 2e5 + 10;
const int M = N << 1;
struct Edge {
int nxt, to, id;
} edge[M];
int head[N], cnt;
inline void add_Edge (int from, int to, int id) {
edge[++cnt] = {head[from], to, id};
head[from] = cnt;
}
int du[N];
int n, m;
int res, col[M];
inline bool Check (int val) {
int num = 0;
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i ++) num += du[i] > val; // 坏点就 +1
return num <= m;
}
inline void col_Dfs (int u, int fa) {
int colidx = 0;
int colgrand; for (int i = head[u]; i; i = edge[i].nxt) if (edge[i].to == fa && fa != -1) colgrand = col[edge[i].id];
for (int i = head[u]; i; i = edge[i].nxt) {
int v = edge[i].to; if (v == fa) continue;
if (colidx == colgrand) colidx = (colidx + 1) % res; // 与连接父亲的边的公司不同
col[edge[i].id] = colidx;
col_Dfs(v, u);
colidx = (colidx + 1) % res;
}
}
int main () {
scanf("%d%d", &n, &m);
for (int i = 1; i < n; i ++) {
int u, v; scanf("%d%d", &u, &v);
add_Edge(u, v, i);
add_Edge(v, u, i);
du[u] ++, du[v] ++;
}
int l = 1, r = n - 1; res = r;
while (l <= r) {
int mid = (l + r) >> 1;
if (Check(mid)) res = mid, r = mid - 1;
else l = mid + 1;
}
col_Dfs(1, -1);
printf("%d\n", res);
for (int i = 1; i < n; i ++) printf("%d ", col[i] + 1);
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
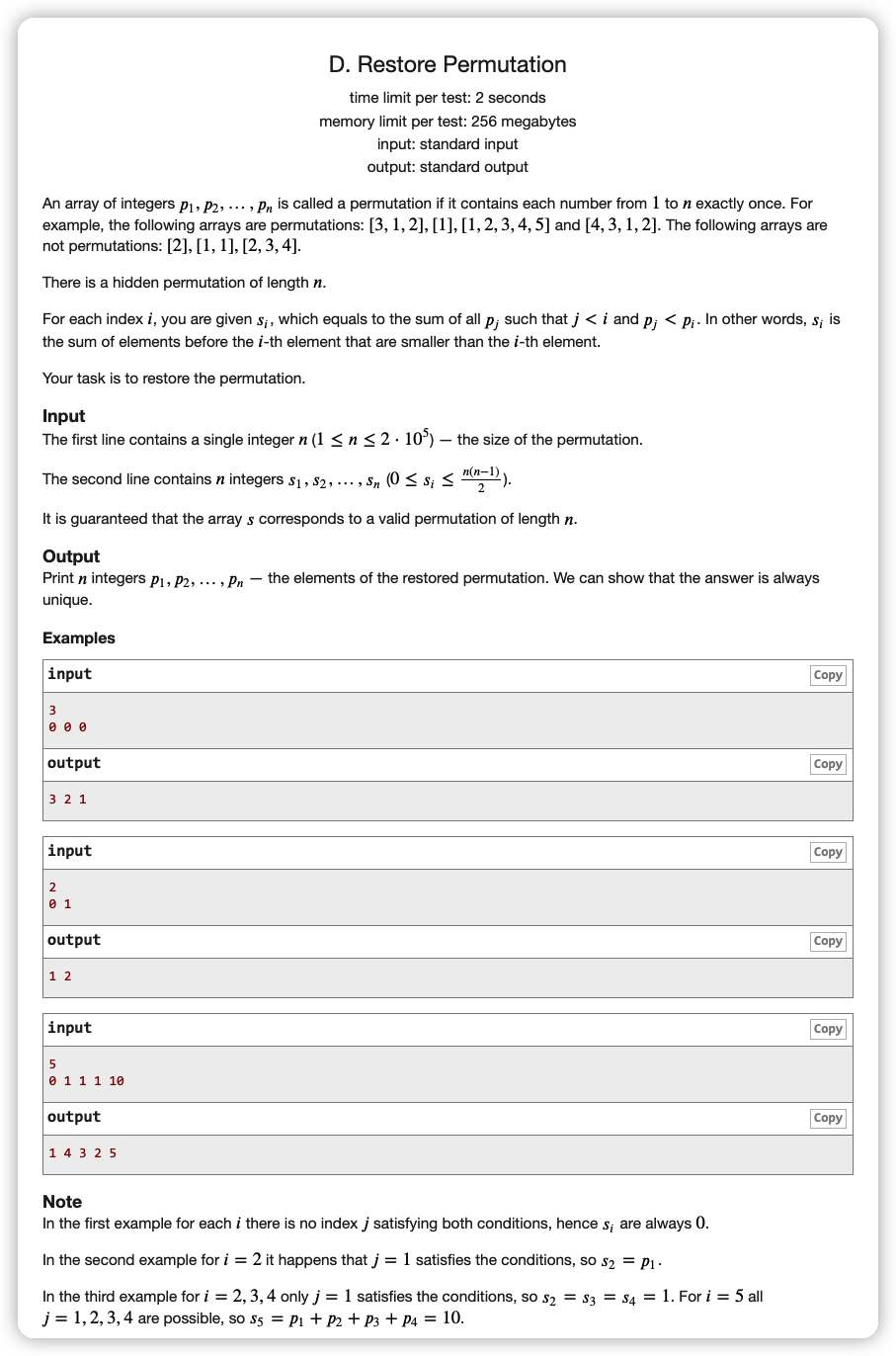
# CodeForces1208D_RestorePermutation
# 🔗
# 💡
拿到题肯定先是正着看,发现正着看了话也就是能确定 连续的相同的位置,它们对应的排列数是单调递减的。还有就是第一个非 的位置是前面 的部分位置上的数的累加和。别的没什么性质了,思路断了,考虑倒着看。
首先对于第三个样例,最后一个位置 ,这个位置一定是 。然后倒数第二个位置 ,这个位置可以选 ,由于如果选了 了话这里 还要加一个 ,因为 在前面,所以说明是选前缀 的数 ,这里 是指除掉后面确定的数后 剩余的数的前缀和。
这样就很明确了,我们有一个数组 ,其中如果 被后面的位置确定了那么就是 ,如果没有那么 ,然后 是 的前缀和
我们倒着枚举 ,在 中二分出来 且 的位置 ,然后将 设置为 并且更新
这里这两个更新操作如果暴力操作都会很费时间,可以使用线段树或树状数组进行更新,查询也是。
# ✅
const ll N = 5e5 + 10;
ll t[N];
inline ll lowbit (ll x) { return x & -x; }
inline void update (ll id, ll c) {
while (id < N) t[id] += c, id += lowbit(id);
}
inline ll query (ll id) {
ll res = 0;
while (id > 0) res += t[id], id -= lowbit(id);
return res;
}
ll n, a[N], p[N];
int main () {
ios::sync_with_stdio(false);
cin.tie(nullptr);
cin >> n;
for (ll i = 1; i <= n; i ++) cin >> a[i], update(i, i);
for (ll i = n; i >= 1; i --) {
ll l = 1, r = n, res = n;
while (l <= r) {
ll mid = (l + r) >> 1;
ll qm = query(mid - 1);
if (query(mid) - qm == 0) { // 注意如果 mid 不存在,那么要根据 sum 直接调整区间
if (qm > a[i]) {
r = mid - 1;
} else {
l = mid + 1;
}
} else { // 如果存在, qm=a[i]时说明找到了便可直接 break
if (qm > a[i]) r = mid - 1;
else if (qm == a[i]) { res = mid; break; }
else l = mid + 1;
}
}
p[i] = res;
update(res, -res);
}
for (ll i = 1; i <= n; i ++) cout << p[i] << " ";
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
# CodeForces1358D_TheBestVacation
# 🔗
# 💡
首先能分析出来的信息是,左端点一定存在于某一个块的某一个位置上,右端点也能通过左端点快速求出来。
那么我们可以枚举每一个块,看看左端点在这个块内的哪个位置可以让答案最大。
当左端点从一个块的位置 往右移动一个位置,右端点也要移动一个位置,其价值变化为 ,这里 都是块内位置
那么把加减情况列出来:
思考一下就能看出来在加减上存在单调性,因为如果出现 ,那么 将会再也追不上 ,那么一定是先加后减(当然也可能不加),所以我们可以二分 求出来最后一个加的数减的数的位置
这样也就是我们在这个块内答案的峰值
然后维护一下每一个块我们求出来 所得的 calc(L,R) 的最大值即可
# ✅
# define int ll // 雾
int n, m;
int d[200005];
int sum[200005];
int val[200005];
// pair<int, int> 第first个块的第second个
inline int toint (pair<int, int> x) { // 将二维位置换成一维
return sum[x.first - 1] + x.second;
}
inline pair<int, int> topair (int x) { // 将一维位置换成二维
pair<int, int> res;
res.first = lower_bound(sum + 1, sum + 1 + n, x) - sum; // 找出第一个大于等于 x 的块
res.second = x - sum[res.first - 1];
return res;
}
inline pair<int, int> get_r (pair<int, int> l) { // 对于二维的 l,用区间长度 m 求出二维的 r
int intr = toint(l) + m - 1;
if (intr > sum[n]) intr -= sum[n]; // 注意这是一个环, r 有可能会绕到前面
return topair(intr);
}
inline int calc (pair<int, int> L, pair<int, int> R) { // 计算二维下 l->r 的值
if (R.first == L.first) {
return (L.second + R.second) * (R.second - L.second + 1) / 2;
} else if (R.first > L.first) {
int mid = val[R.first - 1] - val[L.first];
int l = (L.second + d[L.first]) * (d[L.first] - L.second + 1) / 2;
int r = (1 + R.second) * R.second / 2;
return l + mid + r;
} else {
int mid = (val[n] - val[L.first]) + (val[R.first - 1]);
int l = (L.second + d[L.first]) * (d[L.first] - L.second + 1) / 2;
int r = (1 + R.second) * R.second / 2;
return l + mid + r;
}
}
signed main () {
ios::sync_with_stdio(false);
cin.tie(nullptr);
cin >> n >> m;
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i ++)
cin >> d[i],
sum[i] = sum[i - 1] + d[i],
val[i] = val[i - 1] + d[i] * (d[i] + 1) / 2;
int RES = 0;
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i ++) {
int l = 1, r = d[i], res = 1;
while (l <= r) {
int mid = (l + r) >> 1;
if (get_r({i, mid}).second < mid) r = mid - 1;
else l = mid + 1, res = mid;
}
RES = max(RES, calc({i, res}, get_r({i, res})));
}
cout << RES << endl;
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
# CodeForces1486D_MaxMedian
# 🔗
# 💡
套路地看一眼是二分中位数,我们用分数规划对其进行重新赋值
为 ,其余为 ,做前缀和 sum
这样的话我们评判一个区间能否比中位数大就仅看
套路出来这一点之后,我们就可以维护一个前缀的最小值,但是这个前缀必须是要在 之前的
维护出来后每次对 和 进行比较,如果出现 的情况就以为着 成功
# ✅
const int N = 2e5 + 10;
int n, k;
int a[N];
int b[N];
inline bool Check ( int x ) {
set<int> vis;
bool flag = false;
for ( int i = 1; i <= n; i ++ ) {
if ( i - k >= 0 ) vis.insert(b[i - k]);
if ( a[i] < x ) b[i] = b[i - 1] - 1;
else b[i] = b[i - 1] + 1;
if ( vis.size() && *vis.begin() < b[i] ) flag = true;
}
return flag;
}
int main () {
cin.tie(0)->sync_with_stdio(0);
cin.exceptions(cin.failbit);
cin >> n >> k;
for ( int i = 1; i <= n; i ++ ) cin >> a[i];
int l = 1, r = 200005, res = l;
while ( l <= r ) {
int mid = (l + r) >> 1;
if ( Check(mid) ) l = mid + 1, res = mid;
else r = mid - 1;
}
cout << res << endl;
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
# CodeForces1490G_OldFloppyDrive
# 🔗
# 💡
画一个图来辅助分析一下
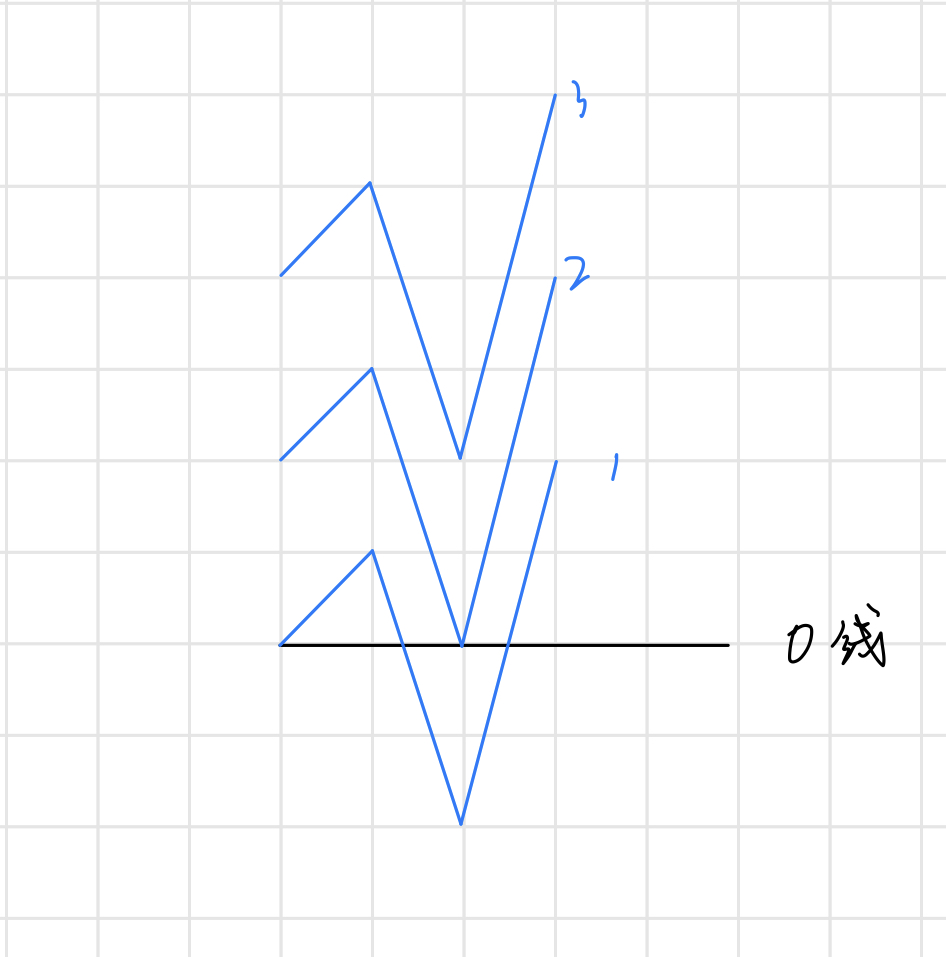
图中蓝线为每一轮的走势
如果 了话,这个线是一点点向上平移的
如果设置一个前缀和 ,那么如果第 轮 的最大值 大于等于我们查询的值了话,这一轮就一定是可以满足情况的
对于查询
是哪一轮可以做到,我们把上面的公式 变化一下直接做除法就可以 求得
问题在于是在这一轮中哪一个位置可以做到,我们可以求一个前缀和 的前缀 ,这个前缀 是具有单调性的,我们既然要求第一个 的位置,可以直接二分
不过要注意提前特判一下达不到的情况
# ✅
const int N = 2e5 + 10;
int n, m;
ll a[N], sum[N], mxsum[N];
ll mx;
inline void Solve () {
cin >> n >> m; mx = -1e18;
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i ++)
cin >> a[i],
sum[i] = sum[i - 1] + a[i],
mx = max(mx, sum[i]),
mxsum[i] = max(mxsum[i - 1], sum[i]);
while (m --) {
ll ned; cin >> ned;
if (mx < ned && sum[n] <= 0) { // 要往上走但每做一轮都会往下跑
cout << "-1 ";
continue;
} else if (ned <= mx) { // 就在第一轮
int l = 1, r = n, res = n;
while (l <= r) {
int mid = (l + r) >> 1;
if (mxsum[mid] >= ned) res = mid, r = mid - 1;
else l = mid + 1;
}
cout << res - 1 << " ";
} else {
ll ret_t = (ned - mx) / sum[n] + ((ned - mx) % sum[n] != 0); // 看看要做几轮
int l = 1, r = n, res = n;
while (l <= r) {
int mid = (l + r) >> 1;
if (mxsum[mid] + ret_t * sum[n] >= ned) res = mid, r = mid - 1;
else l = mid + 1;
}
cout << ret_t * n + res - 1 << " ";
}
} cout << endl;
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
# CodeForces1512D_CorruptedArray
# 🔗
# 💡
在b排列中我们想舍弃一个数,然后将排列的前n个数的和等于第n+1个数,我们只需要求出整个b排列的sum,然后去寻找sum减去哪个数再/2可以在其中找到(而且不能是当前减去的那个数),删去的那个数为x,找到的那个数为b[n+1]
# ✅
void solve()
{
vector<ll> b;//b排列
ll n;
ll sum = 0;//排列的和
cin >> n;
for (ll i = 0; i < n + 2; i++)
{
ll x;
cin >> x;
b.push_back(x);
sum += x;
}
sort(b.begin(), b.end());//排序,方便二分
for (ll i = 0; i < b.size(); i++)
{
ll cur_sum = sum - b[i];
if (cur_sum & 1)//奇数不再操作,因为无法准确/2
continue;
cur_sum /= 2;
if (!binary_search(b.begin(), b.end(), cur_sum))//找不到的就不再操作
continue;
int con=b[i];//记录一下删掉的是哪个,下面两行有用
b.erase(b.begin() + i, b.begin() + i + 1);
if (!binary_search(b.begin(), b.end(), cur_sum))//唯一一个小坑点,可能会因为找到的数是当前的数,而当前的数又被删掉了
{
b.insert(b.begin()+i,con);//若删掉就再放回去,这次操作不能满足,continue了
continue;
}
ll id = lower_bound(b.begin(), b.end(), cur_sum) - b.begin();//寻找我们应该设为b[n+1]的数
b.erase(b.begin() + id, b.begin() + id + 1);//删掉这个数
for (ll j = 0; j < b.size(); j++)//此时我们就只有n个数了,就是a的排列
{
cout << b[j] << " ";
}
return;
}
cout << "-1" << endl;//循环完了也找不到能满足的,就"-1"
}
int main()
{
int cass;
each_cass(cass)
{
solve();
}
return 0;
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
# CodeForces1530C_Persuit
# 🔗
https://codeforces.com/contest/1530/problem/C
# 💡
一步一步向后走的话,很多模拟细节很难维护,而且走的次数会很多
我们需要在 n 的后面找到一个满足条件的数
而且要尽可能小
这种大范围找数的题型可以用二分
写个check函数判断一下就可以开始二分了
# ✅
/*
________ _ ________ _
/ ______| | | | __ | | |
/ / | | | |__| | | |
| | | |___ _ _ _ ___ _ _____ | ___| ______ _____ ___ _ | |
| | | __ \ |_| | | | | | _\| | | ____| | |\ \ | __ | | _ | | _\| | | |
| | | | \ | _ | | | | | | \ | | \___ | | \ \ | |_/ _| | |_| | | | \ | | |
\ \______ | | | | | | \ |_| / | |_/ | ___/ | | | \ \ | /_ \__ | | |_/ | | |
Author : \________| |_| |_| |_| \___/ |___/|_| |_____| _________|__| \__\ |______| | | |___/|_| |_|
____| |
\_____/
*/
#include <unordered_map>
#include <algorithm>
#include <iostream>
#include <cstring>
#include <utility>
#include <string>
#include <vector>
#include <cstdio>
#include <stack>
#include <queue>
#include <cmath>
#include <map>
#include <set>
#define G 10.0
#define LNF 1e18
#define EPS 1e-6
#define PI acos(-1.0)
#define INF 0x7FFFFFFF
#define ll long long
#define ull unsigned long long
#define LOWBIT(x) ((x) & (-x))
#define LOWBD(a, x) lower_bound(a.begin(), a.end(), x) - a.begin()
#define UPPBD(a, x) upper_bound(a.begin(), a.end(), x) - a.begin()
#define TEST(a) cout << "---------" << a << "---------" << '\n'
#define CHIVAS_ int main()
#define _REGAL exit(0)
#define SP system("pause")
#define IOS ios::sync_with_stdio(false)
//#define map unordered_map
#define _int(a) int a; cin >> a
#define _ll(a) ll a; cin >> a
#define _char(a) char a; cin >> a
#define _string(a) string a; cin >> a
#define _vectorInt(a, n) vector<int>a(n); cin >> a
#define _vectorLL(a, b) vector<ll>a(n); cin >> a
#define PB(x) push_back(x)
#define ALL(a) a.begin(),a.end()
#define MEM(a, b) memset(a, b, sizeof(a))
#define EACH_CASE(cass) for (cass = inputInt(); cass; cass--)
#define LS l, mid, rt << 1
#define RS mid + 1, r, rt << 1 | 1
#define GETMID (l + r) >> 1
using namespace std;
template<typename T> inline T MAX(T a, T b){return a > b? a : b;}
template<typename T> inline T MIN(T a, T b){return a > b? b : a;}
template<typename T> inline void SWAP(T &a, T &b){T tp = a; a = b; b = tp;}
template<typename T> inline T GCD(T a, T b){return b > 0? GCD(b, a % b) : a;}
template<typename T> inline void ADD_TO_VEC_int(T &n, vector<T> &vec){vec.clear(); cin >> n; for(int i = 0; i < n; i ++){T x; cin >> x, vec.PB(x);}}
template<typename T> inline pair<T, T> MaxInVector_ll(vector<T> vec){T MaxVal = -LNF, MaxId = 0;for(int i = 0; i < (int)vec.size(); i ++) if(MaxVal < vec[i]) MaxVal = vec[i], MaxId = i; return {MaxVal, MaxId};}
template<typename T> inline pair<T, T> MinInVector_ll(vector<T> vec){T MinVal = LNF, MinId = 0;for(int i = 0; i < (int)vec.size(); i ++) if(MinVal > vec[i]) MinVal = vec[i], MinId = i; return {MinVal, MinId};}
template<typename T> inline pair<T, T> MaxInVector_int(vector<T> vec){T MaxVal = -INF, MaxId = 0;for(int i = 0; i < (int)vec.size(); i ++) if(MaxVal < vec[i]) MaxVal = vec[i], MaxId = i; return {MaxVal, MaxId};}
template<typename T> inline pair<T, T> MinInVector_int(vector<T> vec){T MinVal = INF, MinId = 0;for(int i = 0; i < (int)vec.size(); i ++) if(MinVal > vec[i]) MinVal = vec[i], MinId = i; return {MinVal, MinId};}
template<typename T> inline pair<map<T, T>, vector<T> > DIV(T n){T nn = n;map<T, T> cnt;vector<T> div;for(ll i = 2; i * i <= nn; i ++){while(n % i == 0){if(!cnt[i]) div.push_back(i);cnt[i] ++;n /= i;}}if(n != 1){if(!cnt[n]) div.push_back(n);cnt[n] ++;n /= n;}return {cnt, div};}
template<typename T> vector<T>& operator-- (vector<T> &v){for (auto& i : v) --i; return v;}
template<typename T> vector<T>& operator++ (vector<T> &v){for (auto& i : v) ++i; return v;}
template<typename T> istream& operator>>(istream& is, vector<T> &v){for (auto& i : v) is >> i; return is;}
template<typename T> ostream& operator<<(ostream& os, vector<T> v){for (auto& i : v) os << i << ' '; return os;}
inline int inputInt(){int X=0; bool flag=1; char ch=getchar();while(ch<'0'||ch>'9') {if(ch=='-') flag=0; ch=getchar();}while(ch>='0'&&ch<='9') {X=(X<<1)+(X<<3)+ch-'0'; ch=getchar();}if(flag) return X;return ~(X-1);}
inline void outInt(int X){if(X<0) {putchar('-'); X=~(X-1);}int s[20],top=0;while(X) {s[++top]=X%10; X/=10;}if(!top) s[++top]=0;while(top) putchar(s[top--]+'0');}
inline ll inputLL(){ll X=0; bool flag=1; char ch=getchar();while(ch<'0'||ch>'9') {if(ch=='-') flag=0; ch=getchar();}while(ch>='0'&&ch<='9') {X=(X<<1)+(X<<3)+ch-'0'; ch=getchar();}if(flag) return X;return ~(X-1); }
inline void outLL(ll X){if(X<0) {putchar('-'); X=~(X-1);}ll s[20],top=0;while(X) {s[++top]=X%10; X/=10;}if(!top) s[++top]=0;while(top) putchar(s[top--]+'0');}
int n;
inline bool check(deque<int> da, deque<int> db, int x){
for(int i = n + 1; i <= x; i ++){
da.push_back(100); db.push_front(0);
}
int los = x / 4;
while(los --) da.pop_front(), db.pop_front();
int suma = 0, sumb = 0;
for(int i = 0; i < da.size(); i ++) suma += da[i], sumb += db[i];
return suma >= sumb;
}
inline void solve(){
n = inputInt();
deque<int> da, db;
for(int i = 0; i < n; i ++) da.push_back(inputInt());
for(int i = 0; i < n; i ++) db.push_back(inputInt());
sort(ALL(da)); sort(ALL(db));
int r = n * 10, l = n;
while(l <= r){
int mid = (l + r) >> 1;
if(check(da, db, mid)) r = mid - 1;
else l = mid + 1;
}cout << r - n + 1 << endl;
}
int main(){
int cass;
EACH_CASE(cass){
solve();
}
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
99
100
101
102
103
104
105
106
107
108
109
110
111
112
113
114
115
116
117
# CodeForces1611F_ATMAndStudents
# 🔗
# 💡
看到这个题首先会想一段区间会被前缀影响也会被后缀影响,那么我们可以采用区间求解的形式
由于收益的累加是从前往后的,所以我们建立一个前缀和 表示从 到 这一段的总收益为
如果我们选 这一段,因为不看前面的收益了,所以从 到 的准确收益会是
而这一段能否被选择的关键在于这一段准确收益的最小值是否低于
好了, 的区间最小值,可以开一个 表
for ( int i = 1; i <= n; i ++ ) st[i][0] = sum[i];
inline void Build () {
int k = 32 - __builtin_clz(n) - 1;
for ( int j = 1; j <= k; j ++ ) {
for ( int i = 1; i + (1 << j) - 1 <= n; i ++ ) {
st[i][j] = min ( st[i][j - 1], st[i + (1 << (j - 1))][j - 1] );
}
}
}
inline ll Query ( int l, int r ) {
int k = 32 - __builtin_clz(r - l + 1) - 1;
return min ( st[l][k], st[r - (1 << k) + 1][k] );
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
那么如何确定最多能选多长的区间呢?
由于区间长度的行于不行单调递增
那么可以采用二分区间长度,对每一个二分到的区间长度下的区间最小值(准确收益下的)逐一判断
如果不可行说明我们这个选的太长了,应该跑小的那一半,否则跑大的那一半
inline bool this_MinInLen ( int len ) {
for ( int i = 1; i + len - 1 <= n; i ++ ) {
ll cur = Query ( i, i + len - 1 );
if ( s + (cur - sum[i - 1]) >= 0 ) { // cur-sum[i-1]:准确收益
if ( len > res.second - res.first + 1 ) res = {i, i + len - 1};
return true;
}
}
return false;
}
int l = 1, r = n;
while ( l <= r ) {
int mid = ( l + r ) >> 1;
if ( this_MinInLen(mid) ) l = mid + 1;
else r = mid - 1;
}
this_MinInLen ( l );
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
时间复杂度:
# ✅
const int N = 2e5 + 10;
ll a[N], sum[N];
ll st[N][100];
int n;
ll s;
pair<int, int> res;
inline void Build () {
int k = 32 - __builtin_clz(n) - 1;
for ( int j = 1; j <= k; j ++ ) {
for ( int i = 1; i + (1 << j) - 1 <= n; i ++ ) {
st[i][j] = min ( st[i][j - 1], st[i + (1 << (j - 1))][j - 1] );
}
}
}
inline ll Query ( int l, int r ) {
int k = 32 - __builtin_clz(r - l + 1) - 1;
return min ( st[l][k], st[r - (1 << k) + 1][k] );
}
inline bool this_MinInLen ( int len ) {
for ( int i = 1; i + len - 1 <= n; i ++ ) {
ll cur = Query ( i, i + len - 1 );
if ( s + (cur - sum[i - 1]) >= 0 ) {
if ( len > res.second - res.first + 1 ) res = {i, i + len - 1};
return true;
}
}
return false;
}
inline void Solve () {
res = {0, -1};
cin >> n >> s;
for ( int i = 1; i <= n; i ++ ) {
cin >> a[i];
sum[i] = sum[i - 1] + a[i];
st[i][0] = sum[i];
}
Build ();
int l = 1, r = n;
while ( l <= r ) {
int mid = ( l + r ) >> 1;
if ( this_MinInLen(mid) ) l = mid + 1;
else r = mid - 1;
}
this_MinInLen ( l );
if ( res.first <= res.second ) cout << res.first << " " << res.second << endl;
else cout << -1 << endl;
}
int main () {
ios::sync_with_stdio(false);
int cass; cin >> cass; while ( cass -- ) {
Solve ();
}
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
# CodeForces1622C_SetOrDecrease
# 🔗
# 💡
两个操作
- 令
- 令
分析一下这两个操作,对于操作一,我们肯定是贪心地想让 ,并且是优先让最大的
对于操作二,我们肯定为了让操作一的收益更高,让最小的
我们先令一个 ,这样我们就是想让通过最少的步数让减去的值
注意到一个性质,随着操作数的增大,我们减去的值可以越来越大,具备单调性
发现两个操作对于操作总数 的增减是相反的
并且如果有 次操作一, 次操作二,就一定是先来 次操作一再来 次操作二
那么操作一没必要对一个位置上的数反复赋值,所以操作一最多有 次,最少有 次
这个我们枚举操作一的次数就可以 地求出每一种操作分配情况下,我们所能减去的最大值
既然这个非常容易,那么就二分操作次数去获得答案即可
# ✅
inline bool check ( ll x, const vector<ll> a, const ll down ) {
ll cur = 0;
for ( ll i = a.size() - 1; i >= max(1ll, (ll)a.size() - x); i -- ) cur += a[i] - a[0];
ll two = min(x, (ll)a.size() - 1);
ll one = x - two;
if ( cur + one + two * one >= down ) return true;
for ( ll i = max(1ll, (ll)a.size() - x); i < a.size(); i ++ ) {
cur -= a[i] - a[0];
two --;
one = x - two;
if ( cur + one + two * one >= down ) return true;
}
return one >= down;
}
inline void Solve () {
ll n, k; cin >> n >> k;
ll down = 0;
vector<ll> a(n); for ( ll &i : a ) cin >> i, down += i;
down -= k;
sort(a.begin(), a.end());
ll l = 0, r = 1e15, res = 1e15;
while ( l <= r ) {
ll mid = (l + r) >> 1;
if ( check(mid, a, down) ) res = mid, r = mid - 1;
else l = mid + 1;
}
cout << res << endl;
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
# CodeForces1623C_BalancedStoneHeaps
# 🔗
# 💡
既然想让每一个都比答案 大,那我们分配时肯定是贪心地让后面的在不低于 的情况下尽可能向前分配
我们令 为第 个位置上获取的值,后面的向前分配我们就可以倒着走,显然由于题上让从前往后走,那么我们前面的不能利用后面给的,但是可以考虑自己能往前分配多少
在 的限制下,肯定是 越大越难得
所以我们可以二分答案进行求解
# ✅
inline bool check ( int x, const vector<ll> a ) {
vector<ll> b(a.size());
vector<ll> aa = a;
for ( int i = aa.size() - 1; i >= 2; i -- ) {
if ( aa[i] + b[i] - x < 0 ) return false;
ll giv = min(aa[i] + b[i] - x, aa[i]) / 3;
aa[i] -= giv * 3;
b[i - 1] += giv;
b[i - 2] += giv * 2;
}
for ( int i = 0; i < aa.size(); i ++ ) {
if ( aa[i] + b[i] < x ) return false;
}
return true;
}
inline void Solve () {
int n; cin >> n;
vector<ll> a(n); for ( auto &i : a ) cin >> i;
int l = 0, r = 1000000000;
int res = 0;
while ( l <= r ) {
int mid = (l + r) >> 1;
if ( check(mid, a) ) l = mid + 1, res = mid;
else r = mid - 1;
}
cout << res << endl;
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
# CodeForces1632D_NewYearConcert
# 🔗
# 💡
思索一下,如果我们对一个从 开始的前缀可以发现存在这样 的,那么我们可以在 的位置加一个很大的质数从而隔断 到 的位置
这样我们后面的任意一个位置到达 都会变成 ,我们要从 之后进行判断即可
所以隔断后我们在后面枚举 时只需要判断 是否 即是否存在
注意一下单调性,对于固定的右端点,区间越长 不会越来越大,同时区间长度越来越大,他们两个呈相遇状
那么我们找这个满足 就可以采用二分左端点的形式
- 如果 说明我们枚举的太长了,应该让左端点往右走
- 如果 就说明要往左走
- 如果 就说明找到了,存在这样的位置,我们对 进行隔断然后让答案 即可
注意中间存在区间查询 的操作,可以使用 表预处理
# ✅
const int N = 2e5 + 10;
ll st[N][25];
ll a[N];
ll n;
inline ll gcd ( ll a, ll b ) { return b ? gcd(b, a % b) : a; }
inline void Build(){ // 构建ST
for ( int i = 1; i <= n; i ++ ) st[i][0] = a[i];
ll k = 32 - __builtin_clz(n) - 1;
for (ll j = 1; j <= k; j ++) {
for (ll i = 1; i + (1 << j) - 1 <= n; i ++) {
st[i][j] = gcd(st[i][j - 1],st[i + (1 << (j - 1))][j - 1]);
}
}
}
ll Query(ll l, ll r){ // 查询
ll k = 32 - __builtin_clz(r - l + 1) - 1;
return gcd(st[l][k], st[r - (1 << k) + 1][k]);
}
inline int check ( ll p, ll i ) {
ll qry = Query(p, i);
if ( qry < i - p + 1 ) return -1;
else if ( qry == i - p + 1 ) return 0;
return 1;
}
inline void Solve () {
cin >> n;
for ( int i = 1; i <= n; i ++ ) cin >> a[i];
Build();
int l = 1, res = 0; // 隔断后面的第一个位置,答案
for ( int i = 1; i <= n; i ++ ) {
int R = i;
int L = l;
bool flg = 0;
while ( L <= R ) {
int mid = (L + R) >> 1;
if ( check(mid, i) == 0) {
flg = true;
break;
}
if ( check(mid, i) == 1 ) R = mid - 1;
else L = mid + 1;
}
if ( flg ) {
l = i + 1;
res ++;
}
cout << res << " ";
}
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
# HDU2022多校(3)B_BossRush
# 🔗
# 💡
在限制条件下找最值,注意到随着值的变大,限制是从满足不了到满足的,这是一个单调性,考虑二分。
选取一个值 ,找到最优的填技能的方式
注意到 ,用状态表示,对于同一种选择技能的状态,花费的时间 是固定的,即里面所有 的 总和对 取 。那么我下一步选择第 个技能能放出来的伤害也能得知,即 ,这个可以前缀和预处理出来。
既然我们要伤害最大,那么用 存储状态 的伤害,在每一次选取新技能的时候维护 即可
最后看最大伤害是否满足限制(大于等于 )是对于选定值 的单调性,依次进行二分答案。
# ✅
int n;
ll H;
int t[20], len[20];
ll d[20][100005];
ll sum[20][100005];
ll alt[1000006];
ll dp[1000006];
inline bool check (int T) {
for (int S = 0; S < (1 << n); S ++) dp[S] = -1;
dp[0] = 0;
ll res = 0;
for (int S = 0; S < (1 << n); S ++) {
if (dp[S] < 0) continue;
if (dp[S] >= H) return 1;
int cT = T - alt[S];
if (cT <= 0) continue;
for (int i = 0; i < n; i ++) {
if (S >> i & 1) continue;
dp[S | (1 << i)] = max(dp[S | (1 << i)], dp[S] + sum[i][min(len[i], cT)]);
res = max(res, dp[S | (1 << i)]);
}
}
return res >= H;
}
inline void Solve () {
memset(alt, 0, sizeof alt);
cin >> n >> H;
for (int i = 0; i < n; i ++) {
cin >> t[i] >> len[i];
for (int j = 1; j <= len[i]; j ++) {
cin >> d[i][j];
sum[i][j] = sum[i][j - 1] + d[i][j];
}
}
for (int S = 0; S < (1 << n); S ++) {
for (int i = 0; i < n; i ++) {
if (S >> i & 1) alt[S] += t[i];
}
}
int l = 0, r = 1e9, res = 1e9;
while (l <= r) {
int mid = (l + r) >> 1;
if (check(mid)) res = mid - 1, r = mid - 1;
else l = mid + 1;
}
cout << (res == 1e9 ? -1 : res) << endl;
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
# ICPC2020上海站D_Walker
# 🔗
# 💡
给定一条路,两个人的位置,两个人的速度,怎么样最快走完这条路
如果考虑左左,左右,右左,右右这样会很麻烦,要根据速度还要考虑相遇点
相遇最好,每个人都能做出贡献
那么我们根据相遇入手
首先要考虑一个人走完全程的情况
然后是相遇点
1.相遇完不扭头
2.相遇完扭头
相遇完不扭头很好计算,就直接对向走到头即可
相遇完扭头我们可以二分一下 p1,p2 中间的相遇点
对每个相遇点我们求一下两个人全部走完自己路程的最小用时
其实有了相遇点这个就会很好求,就是每个人已经固定了要走的 l 和 r 了,在 l,r 内走需要 (min(p-l,r-p)+(r-l))/v
所以在这里我们不需要考虑一个人左走还是右走,程序会用 min 判断
我们二分一百次之后的中点就已经很确定了,每次维护一下花费时间的最小值即可
# ✅
inline double LRTime ( double l, double r, double v, double p ) {
return (min(p - l, r - p) + (r - l)) / v;
}
inline void Solve () {
double n, p1, v1, p2, v2;
cin >> n >> p1 >> v1 >> p2 >> v2;
if ( p1 > p2 ) swap(p1, p2), swap(v1, v2);
double res = min(LRTime(0, n, v1, p1), LRTime(0, n, v2, p2));
res = min(res, max((n - p1) / v1, p2 / v2));
double l = p1, r = p2;
for ( int i = 0; i < 100; i ++ ) {
double mid = (l + r) / 2;
double res1 = LRTime(0, mid, v1, p1);
double res2 = LRTime(mid, n, v2, p2);
res = min(res, max(res1, res2));
if ( res1 > res2 ) r = mid;
else l = mid;
}
printf("%.10f\n", res);
}
int main () {
ios::sync_with_stdio(false);
ll cass; cin >> cass; while ( cass -- ) {
Solve();
}
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
# ICPC2021台湾省赛E_EatCoin
# 🔗
# 💡
首先我们化简一下问题
第 天算法会消耗 ,获得
也就是若算法可以执行,那么将获得
若开始前有 ,执行 天后会成为
我们要让这个值
同时要保证 ,不然就继续不了算法了,(左侧如果开始上升那么就可以保证了
我们求 可以用求自然数幂和 (opens new window)的方式进行拉格朗日插值,这里 不大,所以就是常数复杂度
我们求 可以使用第二个限制进行二分
求 可以使用第一个进行二分
数很大,开java的BigInteger
# ✅
public class Main{
static int N = 100;
static BigInteger zero = BigInteger.ZERO;
static BigInteger one = BigInteger.ONE;
static BigInteger two = BigInteger.valueOf(2);
static BigInteger six = BigInteger.valueOf(6);
static BigInteger ten = BigInteger.TEN;
static BigInteger five = BigInteger.valueOf(5);
static BigInteger ksm ( BigInteger a, BigInteger b ) {
BigInteger res = one;
while ( b.compareTo(zero) == 1 ) {
if ( b.mod(two).compareTo(one) == 0 ) {
res = res.multiply(a);
} a = a.multiply(a);
b = b.divide(two);
} return res;
}
static BigInteger[] fac = new BigInteger[N];
static BigInteger[] pre = new BigInteger[N];
static BigInteger[] suf = new BigInteger[N];
static BigInteger pownk ( BigInteger n, int k ) {
BigInteger y = zero, up = zero, down = zero, res = zero;
fac[0] = pre[0] = suf[k + 3] = one;
for ( int i = 1; i <= k + 2; i ++ ) {
pre[i] = pre[i - 1].multiply(n.subtract(BigInteger.valueOf(i)));
fac[i] = fac[i - 1].multiply(BigInteger.valueOf(i));
}
for ( int i = k + 2; i >= 1; i -- ) {
suf[i] = suf[i + 1].multiply(n.subtract(BigInteger.valueOf(i)));
}
for ( int i = 1; i <= k + 2; i ++ ) {
y = y.add(ksm(BigInteger.valueOf(i), BigInteger.valueOf(k)));
up = pre[i - 1].multiply(suf[i + 1]);
down = fac[i - 1].multiply(fac[k + 2 - i]).multiply(((k - i) & 1) > 0 ? zero.subtract(one) : one);
res = res.add(y.multiply(up).divide(down));
}
return res;
}
static BigInteger q, p;
static BigInteger x, y;
static boolean check ( BigInteger j ) {
BigInteger a = x.subtract(p.multiply(j)).add(q.multiply(pownk(j, 5)));
BigInteger b = ksm(ten, BigInteger.valueOf(99));
if ( a.compareTo(b) >= 0 ) return true;
return false;
}
static boolean chk_x ( BigInteger xx ) {
boolean flg = false;
for ( Long i = Long.valueOf(0);; i ++ ) {
if ( xx.subtract(p.multiply(BigInteger.valueOf(i))).add(q.multiply(pownk(BigInteger.valueOf(i), 5))).compareTo(p) == -1 ) break;
if ( i > Long.valueOf(0) && xx.subtract(p.multiply(BigInteger.valueOf(i))).add(q.multiply(pownk(BigInteger.valueOf(i), 5))).compareTo(xx.subtract(p.multiply(BigInteger.valueOf(i - 1))).add(q.multiply(pownk(BigInteger.valueOf(i - 1), 5)))) == 1 ) { flg = true; break;}
}
return flg;
}
public static void main (String[] args) {
Scanner input = new Scanner(System.in);
p = input.nextBigInteger();
q = input.nextBigInteger();
x = p;
y = zero;
BigInteger l = zero, r = ksm(ten, BigInteger.valueOf(20));
while ( l.compareTo(r) == -1 ) {
BigInteger mid = l.add(r).divide(two);
if ( chk_x(mid) ) r = mid;
else l = mid.add(one);
}
x = l;
l = zero; r = ksm(ten, BigInteger.valueOf(30));
while ( l.compareTo(r) == -1 ) {
BigInteger mid = l.add(r).divide(two);
if ( check(mid) ) r = mid;
else l = mid.add(one);
}
y = l;
System.out.println(x + "\n" + y);
}
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
# NCD2019A_HasanTheLazyJudge
# 🔗
# 💡
答案问我们在满足一定条件下的结果,要最优的
可以使用二分答案
我们对结果 进行二分,思考这个答案如何进行
首先,这两条线的长度都至少为
我们设横线为 竖线为 ,每条线都有 ,即端点、垂直坐标,我们枚举竖线,满足的情况应为 且 ,这个集合 是包含在集合 中的,我们首先要满足 才能找
我们可以把这两个情况用两种方式同步求
对于 ,可以发现这三者有偏序关系,所以排序就可以解决
我们存入每个横线的 和 以及竖线的 ,将它们进行排序后进行遍历,如果当前遍历到的是横线的 ,就把这个横线的 存入,如果是 就把这个横线的 弹出,这个可以用一个 multiset 来维护
如果遍历到的是 的 ,就是子集的求法
已知所有存在 multiset 中的 都是满足第一个集合的情况,我们在其中进行二分出满足 这个子集的最左端,如果这个点也能满足 那么就说明可能存在比这个答案更大的情况,我们就 成功了
# ✅
onst int N = 1e5 + 10;
struct node {
int a, b, pos;
inline friend bool operator < ( node a, node b ) {
if ( a.a != b.a ) return a.a < b.a;
return a.b < b.b;
}
} p[N], q[N];
int n, m;
inline bool Check ( int len ) {
vector<node> vec;
for ( int i = 0; i < n; i ++ ) {
if ( p[i].b - p[i].a >= 2 * len )
vec.push_back({p[i].a + len, 1, p[i].pos}), // 优先满足区间的左端点
vec.push_back({p[i].b - len, 3, p[i].pos}); // 最后满足区间的右端点
}
for ( int i = 0; i < m; i ++ ) {
if ( q[i].b - q[i].a >= 2 * len )
vec.push_back({q[i].pos, 2, i}); // 我们要尽可能在两个端点中间看看有没有 q[i].pos
}
sort ( vec.begin(), vec.end() );
multiset<int> mst;
for ( auto i : vec ) {
if ( i.b == 1 ) mst.insert(i.pos);
else if ( i.b == 3 ) mst.erase(mst.find(i.pos));
else {
auto id = mst.lower_bound(q[i.pos].a + len); // 找子集合的区间左端点
if ( id == mst.end() ) continue; // 找不到
if ( *id <= q[i.pos].b - len ) return true; // 这个也能满足子集合的区间右端点
}
}
return false;
}
inline void Solve () {
cin >> n >> m;
for ( int i = 0, x, y, z; i < n; i ++ ) cin >> x >> y >> z, p[i] = {min(x, y), max(x, y), z};
for ( int i = 0, x, y, z; i < m; i ++ ) cin >> x >> y >> z, q[i] = {min(x, y), max(x, y), z};
int l = 0, r = 5e4;
int res = 0;
while ( l <= r ) {
int mid = (l + r) >> 1;
if ( Check(mid) ) l = mid + 1, res = mid;
else r = mid - 1;
}
cout << res << endl;
}
int main () {
ios::sync_with_stdio(false);
int cass; cin >> cass; while ( cass -- ) {
Solve ();
}
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
# POJ3579_Median
# 🔗
http://poj.org/problem?id=3579
# 💡
一个比较妙的二分题
首先我们获得差值的中位数
而差值之间又无太大的关系
所以我们利用中位数的性质
在个数上做文章
而本题中个数上操作的方法就是:二分找出所处差值在中间的元素
check函数:枚举的差值,用a[i]-x然后upperbound遍历出比他小的数的个数和总差值数目(n*(n-1)/2)的关系
然后在这层关系上二分缩l和r即可
# ✅
/*
________ _ ________ _
/ ______| | | | __ | | |
/ / | | | |__| | | |
| | | |___ _ _ _ ___ _ _____ | ___| ______ _____ ___ _ | |
| | | __ \ |_| | | | | | _\| | | ____| | |\ \ | __ | | _ | | _\| | | |
| | | | \ | _ | | | | | | \ | | \___ | | \ \ | |_/ _| | |_| | | | \ | | |
\ \______ | | | | | | \ |_| / | |_/ | ___/ | | | \ \ | /_ \__ | | |_/ | | |
Author : \________| |_| |_| |_| \___/ |___/|_| |_____| _________|__| \__\ |______| | | |___/|_| |_|
____| |
\_____/
*/
//#include <unordered_map>
#include <algorithm>
#include <iostream>
#include <cstring>
#include <utility>
#include <string>
#include <vector>
#include <cstdio>
#include <stack>
#include <queue>
#include <cmath>
#include <map>
#include <set>
#define G 10.0
#define LNF 1e18
#define EPS 1e-6
#define PI acos(-1.0)
#define INF 0x7FFFFFFF
#define ll long long
#define ull unsigned long long
#define LOWBIT(x) ((x) & (-x))
#define LOWBD(a, x) lower_bound(a.begin(), a.end(), x) - a.begin()
#define UPPBD(a, x) upper_bound(a.begin(), a.end(), x) - a.begin()
#define TEST(a) cout << "---------" << a << "---------" << '<br>'
#define CHIVAS_ int main()
#define _REGAL exit(0)
#define SP system("pause")
#define IOS ios::sync_with_stdio(false)
//#define map unordered_map
#define PB(x) push_back(x)
#define ALL(a) a.begin(),a.end()
#define MEM(a, b) memset(a, b, sizeof(a))
#define EACH_CASE(cass) for (cass = inputInt(); cass; cass--)
#define LS l, mid, rt << 1
#define RS mid + 1, r, rt << 1 | 1
#define GETMID (l + r) >> 1
using namespace std;
/*
template<typename T> inline T MAX(T a, T b){return a > b? a : b;}
template<typename T> inline T MIN(T a, T b){return a > b? b : a;}
template<typename T> inline void SWAP(T &a, T &b){T tp = a; a = b; b = tp;}
template<typename T> inline T GCD(T a, T b){return b > 0? GCD(b, a % b) : a;}
template<typename T> inline void ADD_TO_VEC_int(T &n, vector<T> &vec){vec.clear(); cin >> n; for(int i = 0; i < n; i ++){T x; cin >> x, vec.PB(x);}}
template<typename T> inline pair<T, T> MaxInVector_ll(vector<T> vec){T MaxVal = -LNF, MaxId = 0;for(int i = 0; i < (int)vec.size(); i ++) if(MaxVal <vec[i]) MaxVal = vec[i], MaxId = i; return {MaxVal, MaxId};}
template<typename T> inline pair<T, T> MinInVector_ll(vector<T> vec){T MinVal = LNF, MinId = 0;for(int i = 0; i < (int)vec.size(); i ++) if(MinVal > vec[i])MinVal = vec[i], MinId = i; return {MinVal, MinId};}
template<typename T> inline pair<T, T> MaxInVector_int(vector<T> vec){T MaxVal = -INF, MaxId = 0;for(int i = 0; i < (int)vec.size(); i ++) if(MaxVal <vec[i]) MaxVal = vec[i], MaxId = i; return {MaxVal, MaxId};}
template<typename T> inline pair<T, T> MinInVector_int(vector<T> vec){T MinVal = INF, MinId = 0;for(int i = 0; i < (int)vec.size(); i ++) if(MinVal > vec[i])MinVal = vec[i], MinId = i; return {MinVal, MinId};}
template<typename T> inline pair<map<T, T>, vector<T> > DIV(T n){T nn = n;map<T, T> cnt;vector<T> div;for(ll i = 2; i * i <= nn; i ++){while(n % i == 0){if(!cnt[i]) div.push_back(i);cnt[i] ++;n /= i;}}if(n != 1){if(!cnt[n]) div.push_back(n);cnt[n] ++;n /= n;}return {cnt, div};}
template<typename T> vector<T>& operator-- (vector<T> &v){for (auto& i : v) --i; return v;}
template<typename T> vector<T>& operator++ (vector<T> &v){for (auto& i : v) ++i; return v;}
template<typename T> istream& operator>>(istream& is, vector<T> &v){for (auto& i : v) is >> i; return is;}
template<typename T> ostream& operator<<(ostream& os, vector<T> v){for (auto& i : v) os << i << ' '; return os;}
*/inline int inputInt(){int X=0; bool flag=1; char ch=getchar();while(ch<'0'||ch>'9') {if(ch=='-') flag=0; ch=getchar();}while(ch>='0'&&ch<='9') {X=(X<<1)+(X<<3)+ch-'0'; ch=getchar();}if(flag) return X;return ~(X-1);}
inline void outInt(int X){if(X<0) {putchar('-'); X=~(X-1);}int s[20],top=0;while(X) {s[++top]=X%10; X/=10;}if(!top) s[++top]=0;while(top) putchar(s[top--]+'0');}
inline ll inputLL(){ll X=0; bool flag=1; char ch=getchar();while(ch<'0'||ch>'9') {if(ch=='-') flag=0; ch=getchar();}while(ch>='0'&&ch<='9') {X=(X<<1)+(X<<3)+ch-'0'; ch=getchar();}if(flag) return X;return ~(X-1); }
inline void outLL(ll X){if(X<0) {putchar('-'); X=~(X-1);}ll s[20],top=0;while(X) {s[++top]=X%10; X/=10;}if(!top) s[++top]=0;while(top) putchar(s[top--]+'0');}
const int N = 1e5 + 10;
ll a[N], n, npr;
inline int check ( ll x ) {
ll cnt = 0;
for ( ll i = 1; i <= n; i ++ ) {
cnt += upper_bound( a + 1, a + 1 + n, a[i] - x) - (a + 1);
}
return cnt < npr / 2 + 1;
}
inline void solve(){
for ( int i = 1; i <= n; i ++ ) a[i] = inputLL(); sort(a + 1, a + 1 + n);
int l = 0, r = a[n] - a[1];
while ( l <= r ) {
ll mid = (l + r) >> 1;
if ( check (mid) ) r = mid - 1;
else l = mid + 1;
}
outInt(r); puts("");
}
CHIVAS_{
while ( scanf("%lld", &n) == 1 ) {
npr = (n - 1) * n / 2;
solve();
}
_REGAL;
};
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
99
100
101
102
103
104
105
106
107
108
109