BFS
#
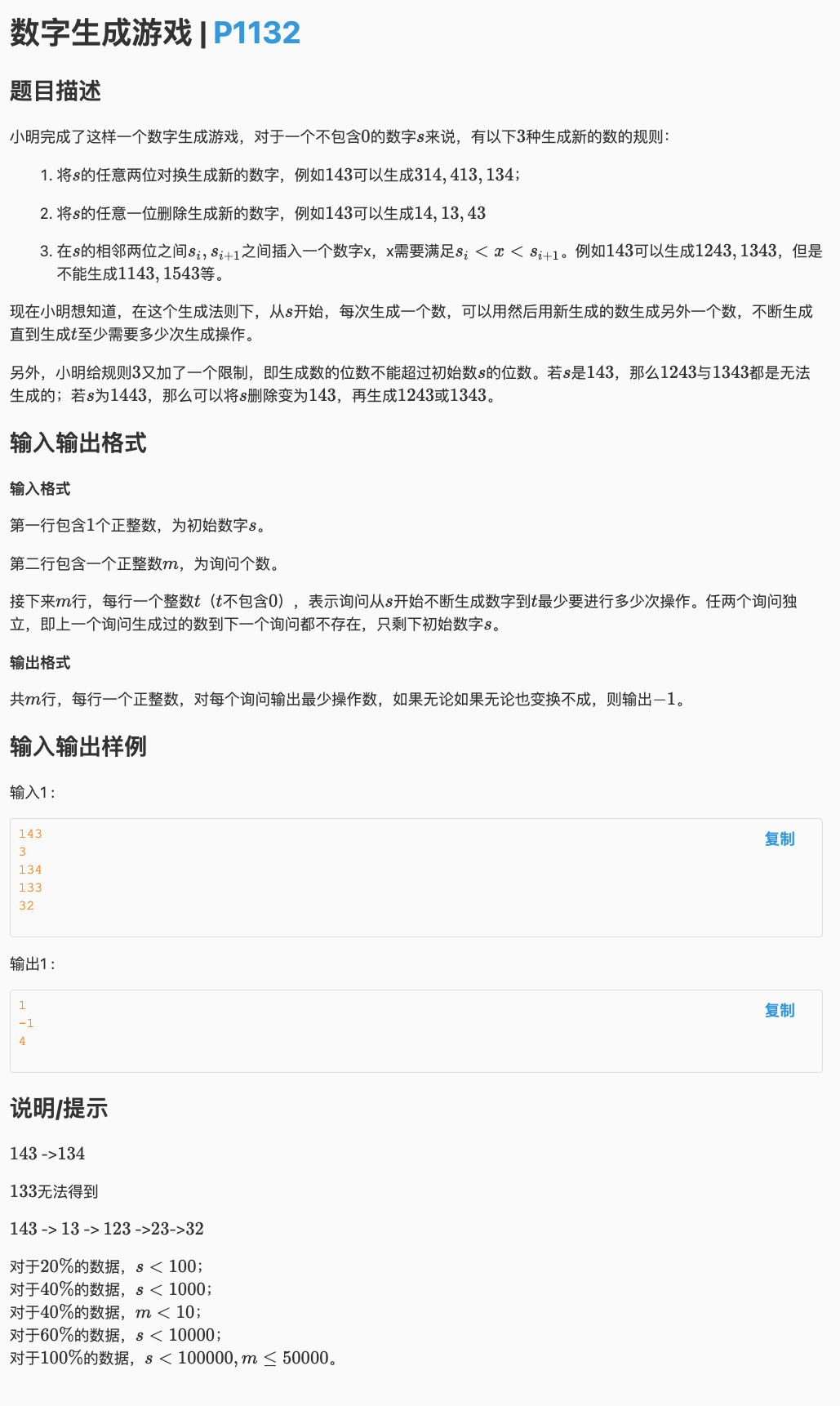
# 洛谷P1132_数字生成游戏
# 🔗
# 💡
一看 ,最多 位,那时间最多也就 ,直接暴力搜然后标记
我们发现如果一个串可以更快得到,那么它之后的所有转移出来的串都应该被更新,所以我们用
对给定的串,把它能变成的所有串都标记下来并存一下要变的次数
如果这个串搜过了就continue掉
要注意的是:
交换要够两个数字
插入要够两个数字
删除要够一个数字
这样的话,到最后我们查数的时候看看这个数有没有被标记即可
标记的话输出记录的次数,否则
# ✅
map<string, int> vis, res;
string wanna;
string s;
struct node {
string s;
int num;
};
inline void bfs () {
queue<node> que; que.push({s, 0});
while ( que.size() ) {
node nd = que.front(); que.pop();
string x = nd.s;
if ( vis[x] ) continue; vis[x] = 1;
res[x] = nd.num;
// 1.
if ( x.size() )
for ( int i = 0; i < x.size(); i ++ )
for ( int j = i + 1; j < x.size(); j ++ )
swap ( x[i], x[j] ),
que.push({x, nd.num + 1}),
swap ( x[i], x[j] );
// 2.
if ( x.size() )
for ( int i = 0; i < x.size(); i ++ ) {
string tmp; tmp += x[i];
x.erase(i, 1);
que.push({x, nd.num + 1});
x.insert(i, tmp);
}
//3.
if ( x.size() > 1 && x.size () + 1 <= s.size() )
for ( int i = 0; i < x.size() - 1; i ++ ) {
for ( char c = x[i] + 1; c <= x[i + 1] - 1; c ++ ) {
string tmp; tmp += c;
x.insert(i + 1, tmp);
que.push({x, nd.num + 1});
x.erase(i + 1, 1);
}
}
}
}
int main () {
ios::sync_with_stdio(false);
cin >> s;
bfs ();
int m; cin >> m;
while ( m -- ) {
cin >> wanna;
if ( !res.count(wanna) ) cout << "-1" << endl;
else cout << res[wanna] << endl;
}
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
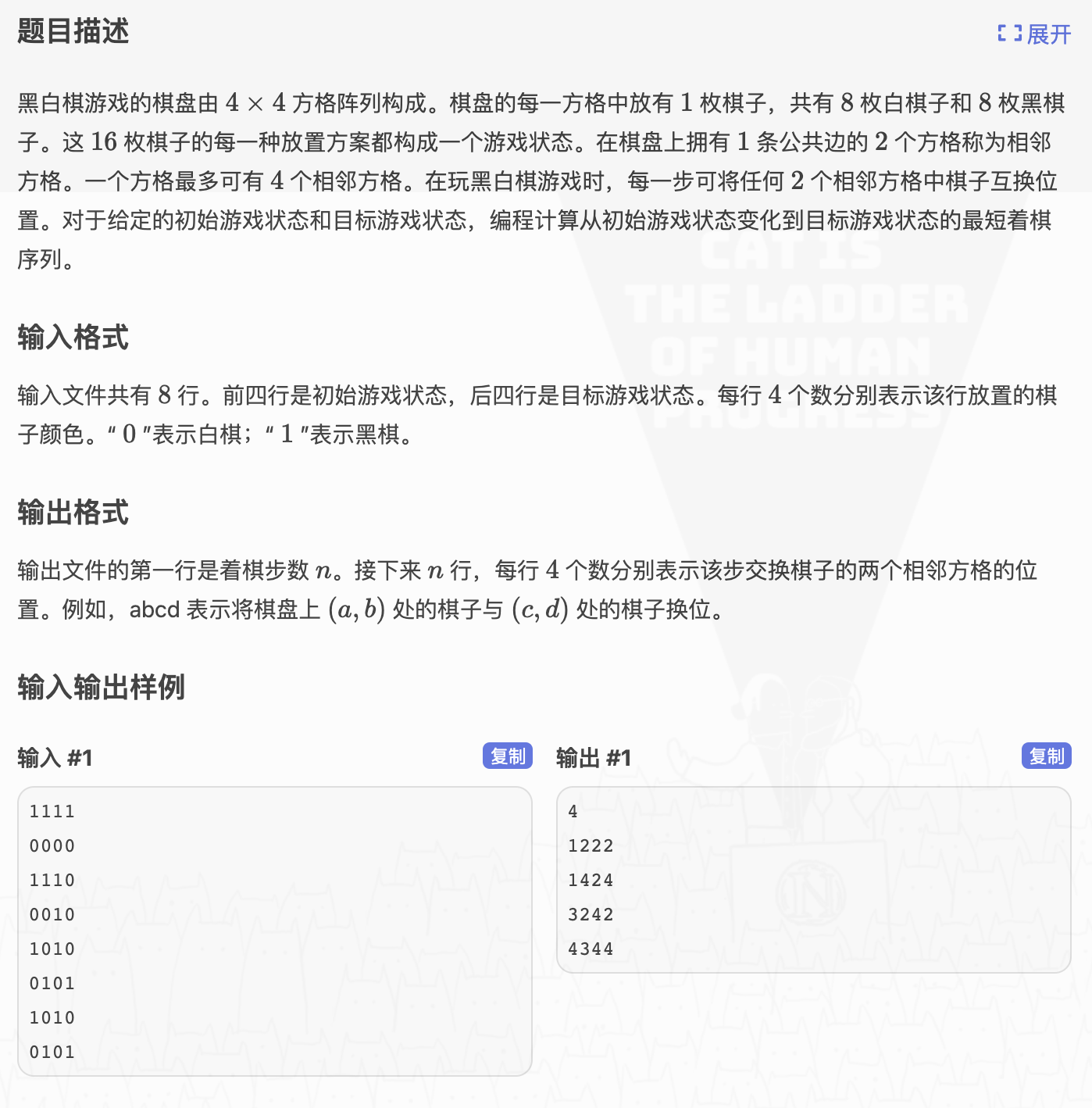
# 洛谷P1225_黑白棋
# 🔗
# 💡
首先要体会到一件事情,总步数不会超过 256 (感性一下
这个肯定是要用 BFS 的
硬着头皮直线搜太伤了
每一步的矩阵判断也很伤
但是矩阵不大,我们完全可以压成一行数,用这个数判相不相等就很好
对于换位,我们枚举1到16为这行数的第几位,对这些数拆分成矩阵坐标
从而可以得出相邻的坐标,要换的相邻坐标也可以变成数位
inline pair<int, int> NumToPos ( int x ) {
return {(x - 1) / 4 + 1, (x - 1) % 4 + 1};
}
inline int PosToNum ( int x, int y ) {
return (x - 1) * 4 + y;
}
2
3
4
5
6
交换这两个数位即可
inline ll new_Swap ( ll x, int i, int j ) {
ll a = x % ksm(10, i) / ksm(10, i - 1);
ll b = x % ksm(10, j) / ksm(10, j - 1);
if ( a != b ) {
if ( a ) x -= ksm(10, i - 1), x += ksm(10, j - 1);
else x -= ksm(10, j - 1), x += ksm(10, i - 1);
}
return x;
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
然后对每一个数存一个记录不重复搜索别的也就是普通的BFS了
# ✅
const int mxstp = 256;
const int N = 4;
struct pth {
int a, b, c, d;
};
struct node {
ll val;
int stp;
vector<pth> p;
} tmp, tgt;
inline ll ksm ( ll a, ll b ) { ll res = 1; while ( b > 0 ) { if ( b & 1 ) res = res * a; a = a * a; b >>= 1; } return res; }
inline ll new_Swap ( ll x, int i, int j ) {
ll a = x % ksm(10, i) / ksm(10, i - 1);
ll b = x % ksm(10, j) / ksm(10, j - 1);
if ( a != b ) {
if ( a ) x -= ksm(10, i - 1), x += ksm(10, j - 1);
else x -= ksm(10, j - 1), x += ksm(10, i - 1);
}
return x;
}
inline pair<int, int> NumToPos ( int x ) {
return {(x - 1) / 4 + 1, (x - 1) % 4 + 1};
}
inline int PosToNum ( int x, int y ) {
return (x - 1) * 4 + y;
}
int dx[4] = {0, 0, 1, -1};
int dy[4] = {1, -1, 0, 0};
map<ll, bool> vis;
inline void BFS () {
queue<node> que;
que.push(tmp);
while ( que.size() ) {
node cur = que.front(); que.pop();
if ( cur.val == tgt.val ) {
cout << cur.stp << endl;
for ( int i = 0; i < cur.p.size(); i ++ ) cout << cur.p[i].a << cur.p[i].b << cur.p[i].c << cur.p[i].d << endl;
cout << endl;
exit(0);
}
if ( vis[cur.val] || cur.stp > 256 ) continue; vis[cur.val] = 1;
for ( int np = 1; np <= 16; np ++ ) {
int x = NumToPos(np).first, y = NumToPos(np).second;
for ( int i = 0; i < 4; i ++ ) {
int nxtx = x + dx[i], nxty = y + dy[i];
if ( nxtx >= 1 && nxtx <= 4 && nxty >= 1 && nxty <= 4 ) {
int num = PosToNum(nxtx, nxty);
cur.p.push_back({x, y, nxtx, nxty});
cur.stp ++;
cur.val = new_Swap ( cur.val, np, num );
que.push(cur);
cur.val = new_Swap ( cur.val, np, num );
cur.stp --;
cur.p.pop_back();
}
}
}
}
}
int main () {
ios::sync_with_stdio(false);
string s1, s2;
for ( int i = 0; i < 4; i ++ ) {
string ss; cin >> ss;
s1 += ss;
}
for ( int i = 0; i < 4; i ++ ) {
string ss; cin >> ss;
s2 += ss;
}
reverse(s1.begin(), s1.end());
reverse(s2.begin(), s2.end());
tmp.val = stoll ( s1 );
tgt.val = stoll ( s2 );
BFS();
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
# ABC224_D8PuzzleOnGraph
# 🔗
# 💡
首先图上点个数只有9个,那么就模拟搜一下
每次可以交换空位置和它相邻的节点
那么按这种方式搜,记录状态保证不会重复搜索,看看能不能生成一个123456789
最多也就9!次
DFS太深了扛不下,使用BFS
# ✅
int n;
struct Egde {
int nxt, to;
} edge[100];
int head[100], cnt;
map<string, int> num;
queue<string> que;
inline void add_Edge ( int from, int to ) {
edge[ ++ cnt ] = { head[from], to };
head[from] = cnt;
}
int main () {
ios::sync_with_stdio(false);
for ( int i = 0; i < 100; i ++ ) head[i] = -1;
cin >> n;
for ( int i = 0, x, y; i < n; i ++ ) {
cin >> x >> y; x --, y --;
add_Edge ( x, y );
add_Edge ( y, x );
}
string s = "999999999";
for ( int i = 1, x; i <= 8; i ++ )
cin >> x, x --,
s[x] = i + '0';
que.push(s);
num[s] = 0;
while ( que.size() ) {
s = que.front(); que.pop();
if ( s == "123456789" ) break;
int x; for ( int i = 0; i < 9; i ++ ) if ( s[i] == '9' ) x = i;
for ( int i = head[x]; ~i; i = edge[i].nxt ) {
int to = edge[i].to;
string t = s;
swap ( t[x], t[to] );
if ( !num[t] )
que.push(t),
num[t] = num[s] + 1;
}
}
if ( !num.count("123456789") ) cout << "-1" << endl;
else cout << num["123456789"] << endl;
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
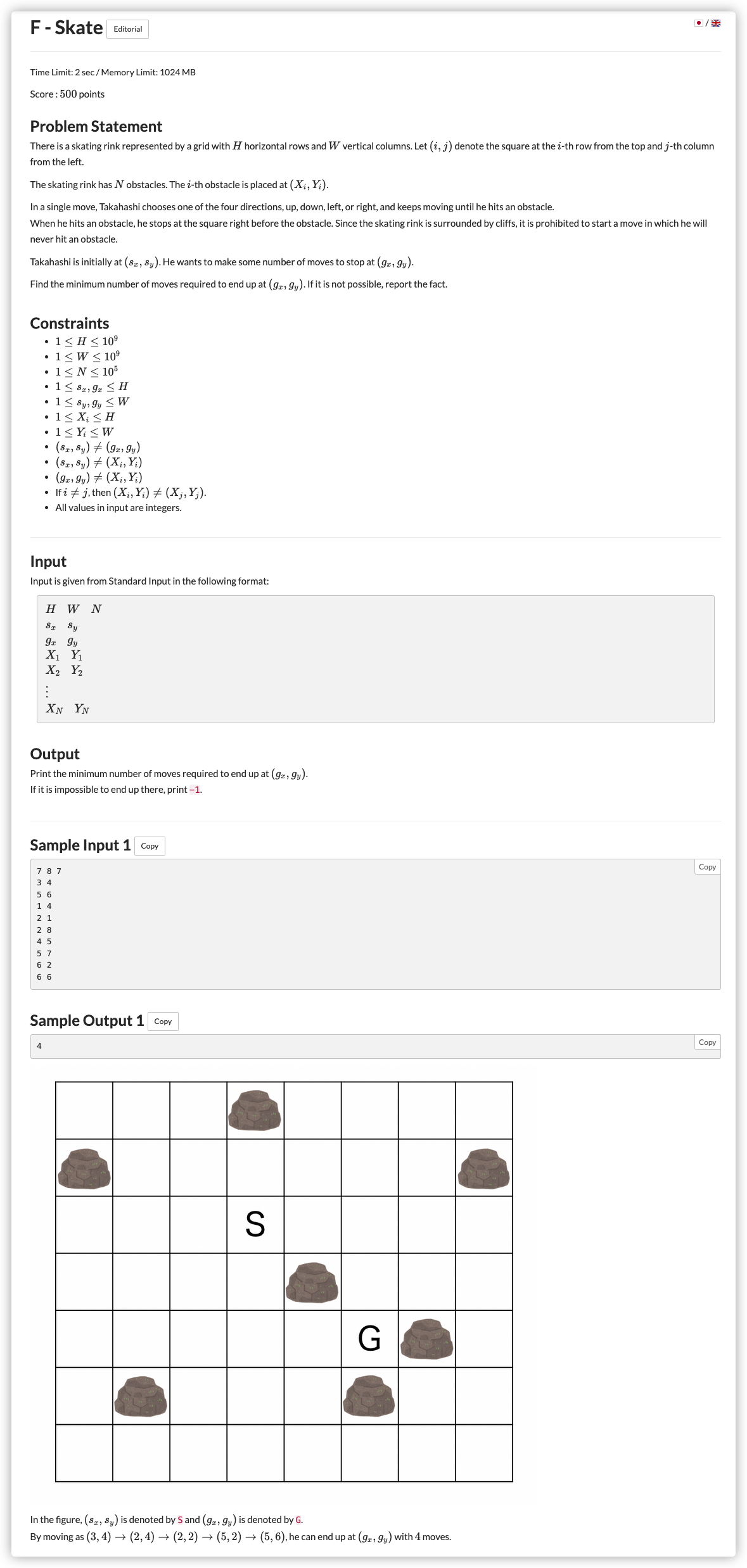
# ABC241F_Skate
# 🔗
# 💡
分析一波,有 个石头,那么能让我们停下来的也就是石头的四个方向,我们只会停在 个点
不多,开始搜索
大概思索一下搜索的流程
记录:set<pair<int, int> > vis 即可实现
队列:queue<tuple<int, int, int> > que ,前两个是坐标,后面是步数
那么就该看怎么走了
往四个方向走一个一个点走显然不现实,那么我们存两个
vector<int> X[i]第 列所有石头所在的行vector<int> Y[i]第 行所有石头所在的列
下标有 个,如果我们直接存会炸
既然停在哪能往哪走都是固定的且坐标没有价值,那么将坐标离散化
注意这里离散化 如果只是存入 那么会导致本不相邻的两个石头合在一起
所以我们一次要存入
离散化之后我们将每个石头存入 X[].push_back() 和 Y[].push_back()
然后我们就继续我们的走法(当前在 处
- 向上走,用
lower_boundX[y]锁定出来第 列行数第一个比当前 小的石头位置,存入那个石头下面的第一个位置的坐标,如果没有则不存 - 向下走,用
lower_boundX[y]锁定出来第 列行数第一个比当前 大的石头位置,存入那个石头上面的第一个位置的坐标,如果没有则不存 - 向右走,用
lower_boundY[x]锁定出来第 行列数第一个比当前 小的石头位置,存入那个石头右侧的第一个位置的坐标,如果没有则不存 - 向右走,用
lower_boundY[x]锁定出来第 行列数第一个比当前 大的石头位置,存入那个石头左侧的第一个位置的坐标,如果没有则不存
直到当前位置等于离散化后的重点即可输出步数
# ✅
int h, w, n;
set<pair<int, int> > vis;
pair<int, int> a[100005];
vector<int> x, y;
pair<int, int> s, g;
vector<int> X[400005], Y[400005];
struct node { pair<int, int> pr; int dep; };
inline void BFS () {
queue<node> que;
que.push({s, 0});
while ( que.size() ) {
node cur = que.front(); que.pop();
if ( vis.count(cur.pr) ) continue; vis.insert(cur.pr);
if ( cur.pr == g ) {
cout << cur.dep << endl;
return;
}
auto i = lower_bound(X[cur.pr.second].begin(), X[cur.pr.second].end(), cur.pr.first);
i = upper_bound(X[cur.pr.second].begin(), X[cur.pr.second].end(), cur.pr.first);
if ( i != X[cur.pr.second].end() ) que.push({{*i - 1, cur.pr.second}, cur.dep + 1});
if ( i != X[cur.pr.second].begin() ) i --, que.push({{*i + 1, cur.pr.second}, cur.dep + 1});
i = upper_bound(Y[cur.pr.first].begin(), Y[cur.pr.first].end(), cur.pr.second);
if ( i != Y[cur.pr.first].end() ) que.push({{cur.pr.first, *i - 1}, cur.dep + 1});
if ( i != Y[cur.pr.first].begin() ) i --, que.push({{cur.pr.first, *i + 1}, cur.dep + 1});
}
cout << "-1" << endl;
}
inline int get_Id ( int num, int op ) {
if ( op == 1 ) return lower_bound(x.begin(), x.end(), num) - x.begin();
else return lower_bound(y.begin(), y.end(), num) - y.begin();
}
inline void add_Num (int num, int op) {
if ( op == 1 ) {
x.push_back(num - 1);
x.push_back(num);
x.push_back(num + 1);
} else {
y.push_back(num - 1);
y.push_back(num);
y.push_back(num + 1);
}
}
int main () {
scanf("%d%d%d", &h, &w, &n);
scanf("%d%d%d%d", &s.first, &s.second, &g.first, &g.second);
add_Num(s.first, 1);
add_Num(s.second, 2);
add_Num(g.first, 1);
add_Num(g.second, 2);
for ( int i = 0; i < n; i ++ ) {
scanf("%d%d", &a[i].first, &a[i].second);
add_Num(a[i].first, 1);
add_Num(a[i].second, 2);
}
sort ( x.begin(), x.end() );
sort ( y.begin(), y.end() );
x.erase(unique(x.begin(), x.end()), x.end());
y.erase(unique(y.begin(), y.end()), y.end());
s = {get_Id(s.first, 1), get_Id(s.second, 2)};
g = {get_Id(g.first, 1), get_Id(g.second, 2)};
for ( int i = 0; i < n; i ++ ) {
X[get_Id(a[i].second, 2)].push_back(get_Id(a[i].first, 1));
Y[get_Id(a[i].first, 1)].push_back(get_Id(a[i].second, 2));
}
for ( int i = 0; i < 400005; i ++ ) {
sort ( X[i].begin(), X[i].end() );
sort ( Y[i].begin(), Y[i].end() );
}
BFS();
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
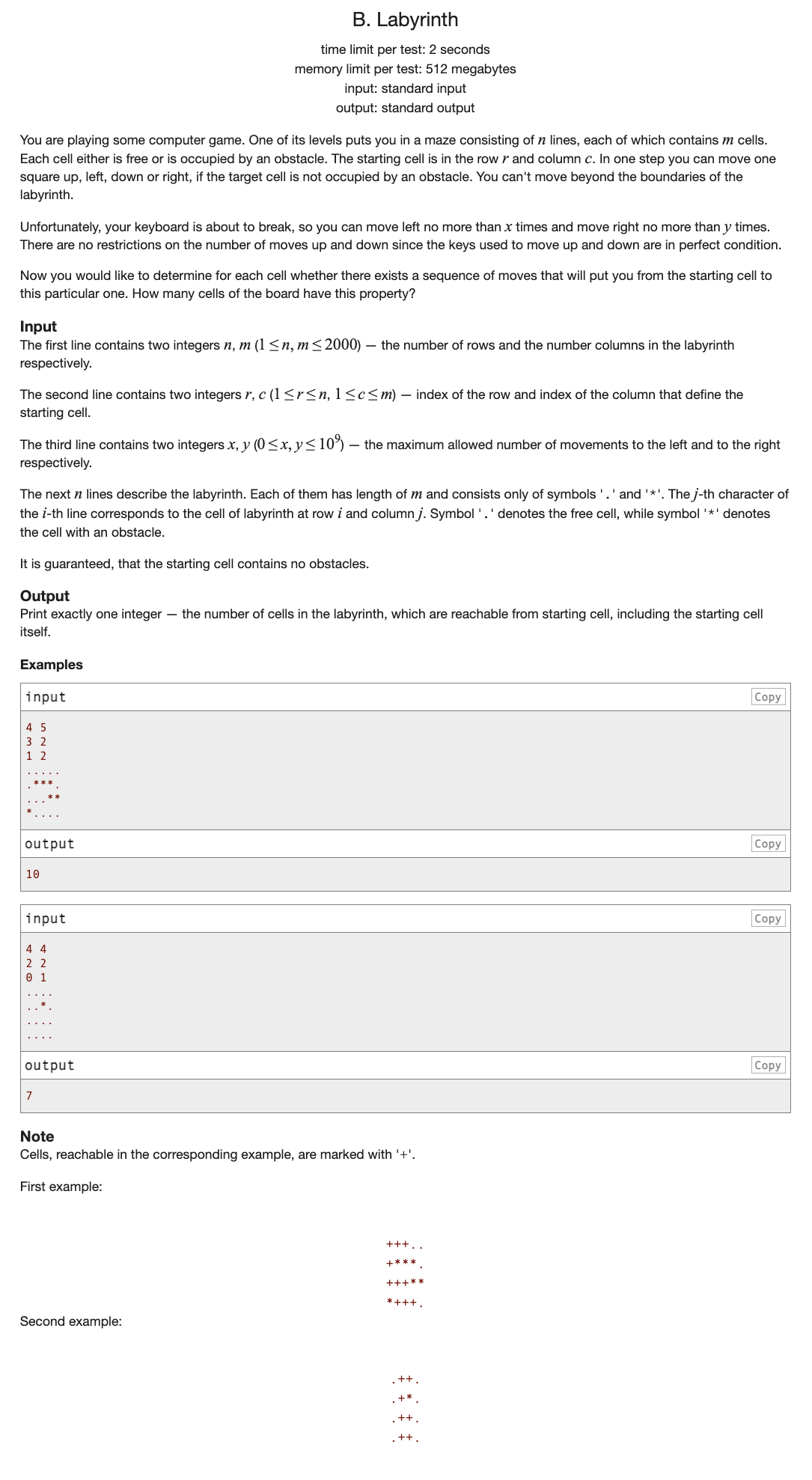
# CodeForces1063B_Labyrinth
# 🔗
# 💡
即然要记录能到达的点数
其实每个点访问一次就行了
那么主要设计好标记不重复走每一格,时间复杂度允许我们开BFS搜索遍历的
关键问题在于:如何让没怎么消耗左右走机会的访问节点优先走
没怎么消耗左右节点也就意味着尽可能上下走的节点
那就只需要对上下走优先遍历即可
DFS肯定爆栈,我们可以对BFS中遍历队列设为双端队列
我们每次优先将上下走的节点压入队首,左右走压入队尾
每次遍历时取队头即可满足优先上下走的条件了
# ✅
#include <iostream>
#include <algorithm>
#include <vector>
#include <map>
#include <queue>
#define ll long long
using namespace std;
const int mod = 1e9 + 7;
const int N = 2100;
int n, m;
int r, c;
int _l, _r;
char s[N][N];
struct node {
int x, y, nl, nr;
};
int vis[N * N * 2];
int res;
inline void BFS () {
deque<node> dq;
dq.push_back({r, c, _l, _r});
while ( dq.size() ) {
node cur = dq.front(); dq.pop_front();
if ( cur.x < 1 || cur.x > n || cur.y < 1 || cur.y > m ) continue;
if ( vis[(cur.x - 1) * m + cur.y] ) continue; vis[(cur.x - 1) * m + cur.y] = 1;
if ( s[cur.x][cur.y] == '*' ) continue;
res ++;
dq.push_front({cur.x + 1, cur.y, cur.nl, cur.nr}); // 优先上下走
dq.push_front({cur.x - 1, cur.y, cur.nl, cur.nr});
if ( cur.nl ) dq.push_back({cur.x, cur.y - 1, cur.nl - 1, cur.nr}); // 其次左右走
if ( cur.nr ) dq.push_back({cur.x, cur.y + 1, cur.nl, cur.nr - 1});
}
}
int main () {
#ifndef ONLINE_JUDGE
freopen("in.in", "r", stdin);
freopen("out.out", "w", stdout);
#endif
scanf("%d%d%d%d%d%d", &n, &m, &r, &c, &_l, &_r);
for ( int i = 1; i <= n; i ++ ) scanf("%s", s[i] + 1);
BFS();
printf("%d\n", res);
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
# CodeForces1536B_PrinzessinDerVerurteilung
# 🔗
# 💡
首先明白
如果一个个字符串按顺序向后搜索查找
我们搜到的字符串数量不会超过
这是根据容斥出来的最坏情况
这么看来可以用搜索,但是DFS是一条路径向后找,会有很多不必要搜的字符串
所以我们用BFS
# ✅
struct cmp{
bool operator ()(string a, string b){//保证两个字符串是先按长度再按字典序排序
if(a.size() != b.size()) return a.size() > b.size();
return a > b;
}
};
string in;//输入字符串
string none;//空字符串
inline void BFS(){
priority_queue<string, vector<string>, cmp> pque;
for(char i = 'a'; i <= 'z'; i ++) pque.push(none + i);//先都初始化为一个字符
while(pque.size()){
string cur = pque.top(); pque.pop();
if(in.find(cur) == in.npos){//找不到了就输出
cout << cur << endl;
return;
}
for(char i = 'a'; i <= 'z'; i ++) pque.push(cur + i);
}
}
inline void solve(){
int n; cin >> n >> in;
BFS();
}
CHIVAS_{
int cass;
EACH_CASE(cass){
solve();
}
_REGAL;
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
# CodeForces1638D_BigBrush
# 🔗
# 💡
考虑覆盖效果
发现最后一个覆盖的元素一定是四个方格全有的
倒数第二个覆盖的可以有一部分在这四个方格内,但它所染色的四个点不在这些方格内的点一定要同色才可以
接下来同理
那么可以使用倒着构造操作的方式
每次看看是否有可以涂色的且未出发的点
将它塞入操作内
然后去看它所包含的四个点是否有可以入队的
这样进行 BFS
# ✅
const int N = 1e3 + 10;
int a[N][N];
int n, m;
struct node { int x, y, val; };
int dx[4] = {0, 0, -1, 1};
int dy[4] = {1, -1, 0, 0};
bool vis[N][N];
bool ismark[N][N];
inline int check ( int x, int y ) {
if ( x <= 0 || y <= 0 || x >= n || y >= m || vis[x][y] ) return -1;
vector<pair<int, int> > vec;
if ( ismark[x][y] == 0 ) vec.push_back({x, y});
if ( ismark[x + 1][y] == 0 ) vec.push_back({x + 1, y});
if ( ismark[x][y + 1] == 0 ) vec.push_back({x, y + 1});
if ( ismark[x + 1][y + 1] == 0 ) vec.push_back({x + 1, y + 1});
if ( vec.size() == 0 ) return 1;
int clr = a[vec[0].first][vec[0].second];
for ( int i = 0; i < vec.size(); i ++ ) {
if ( clr != a[vec[i].first][vec[i].second] ) return -1;
}
return clr;
}
inline void Solve () {
scanf("%d%d", &n, &m);
for ( int i = 1; i <= n; i ++ ) for ( int j = 1; j <= m; j ++ ) scanf("%d", &a[i][j]), vis[i][j] = 0, ismark[i][j] = 0;
vector<node> res;
queue<pair<int, int> > que;
for ( int i = 1; i < n; i ++ ) {
for ( int j = 1; j < m; j ++ ) {
if ( a[i][j] == a[i + 1][j] && a[i][j] == a[i][j + 1] && a[i][j] == a[i + 1][j + 1] ) {
que.push({i, j});
}
}
}
while ( que.size() ) {
pair<int, int> cur = que.front(); que.pop();
int x = cur.first, y = cur.second;
int chk = check(x, y);
if ( chk == -1 ) continue;
res.push_back({x, y, chk});
vis[x][y] = 1;
ismark[x][y] = ismark[x + 1][y] = ismark[x][y + 1] = ismark[x + 1][y + 1] = 1;
for ( int i = 0; i < 4; i ++ ) {
int nx = x + dx[i];
int ny = y + dy[i];
que.push({nx, ny});
}
}
for ( int i = 1; i <= n; i ++ ) for ( int j = 1; j <= m; j ++ ) {
if ( !ismark[i][j] ) {
puts("-1");
return;
}
}
printf("%d\n", (int)res.size());
for ( int i = res.size() - 1; i >= 0; i -- ) printf("%d %d %d\n", res[i].x, res[i].y, res[i].val);
}
int main () {
Solve();
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
# CodeForces1651D_NearestExcludedPoints
# 🔗
# 💡
考虑一个点如果被包围住,意味着它无法直接获取答案,那么是否存在一种方式让它可以间接地获取答案
间接那么就是利用周围包围它的点,纸上模拟一下即可发现
它的最近空点一定是周围四个点中的一个点的最近空点
我们开反向 ,先把一个块内最外层的答案求出来,然后向内更新
处理方式可以使用对输入枚举周围是否存在空点,若存在的话就入队并且设置答案
向内更新的过程中对当前点扫描周围点,选择一个周围点答案中最近的设置为该点答案
赛中想了个 回溯, 到最后发现
如果用左侧点开始搜索,那么左半部分点本应该由左侧进行递推,但是按照 反向顺序这里则会由右半部分进行递推
# ✅
const int N = 2e5 + 10;
const int dx[4] = {0, 0, 1, -1};
const int dy[4] = {1, -1, 0, 0};
struct node {
int x, y;
inline friend bool operator < ( node a, node b ) {
if ( a.x != b.x ) return a.x < b.x;
return a.y < b.y;
}
inline node move ( int op ) { return {x + dx[op], y + dy[op]}; }
} a[N];
int n;
map<node, node> res;
map<node, bool> vis;
inline int dis ( node a, node b ) {
return abs(a.x - b.x) + abs(a.y - b.y);
}
int main () {
scanf("%d", &n);
queue<node> que;
for ( int i = 1; i <= n; i ++ ) {
scanf("%d%d", &a[i].x, &a[i].y);
vis[a[i]] = true;
res[a[i]] = {-10, -10};
}
for ( int i = 1; i <= n; i ++ ) {
node u = a[i];
for ( int j = 0; j < 4; j ++ ) {
node v = u.move(j);
if ( !vis[v] )
res[v] = v,
que.push(v);
}
}
while ( !que.empty() ) {
node u = que.front(); que.pop();
for ( int op = 0; op < 4; op ++ ) {
node v = u.move(op);
if ( !vis[v] ) continue;
res[v] = res[u];
vis[v] = false;
que.push(v);
}
}
for ( int i = 1; i <= n; i ++ ) printf("%d %d\n", res[a[i]].x, res[a[i]].y);
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
# ICPC2017沈阳站G_InfiniteFractionPath
# 🔗
# 💡
首先选择一些起点,这些起点的值一定是最大的,用这些起点路径进行
这些起点构成了很多条路径,目标是每次向后走一步,只保留下一步获得的值最大的路径
但是光这么做在遇到 的时候就优化不了了
不过画了图或者打了表会发现很多点的入度都很大,但出度一定只有一,所以汇聚量很大,可以做一个标记,如果第 步走到过 了,那么别的路径上第 步走到 就不往下走了。
由于 的特性步数一样的会出现在一起,所以建立一个一维数组 ,表示 的位置最后一次出现的是第几步即可
两个剪枝就能把时间优化下来了
# ✅
int vis[150004];
char mxc[150004];
int casid;
int nxt[150004];
inline void Solve () {
int n; cin >> n;
string s; cin >> s;
for (int i = 0; i <= n; i ++) vis[i] = -1, mxc[i] = '0' - 1, nxt[i] = (1ll * i * i + 1) % n;
mxc[1] = *max_element(s.begin(), s.end());
queue<pair<int, int> > que; // id,len
for (int i = 0; i < n; i ++) if (s[i] == mxc[1]) que.push({i, 1});
while (!que.empty()) {
int i = que.front().first, sz = que.front().second; que.pop();
if (s[i] < mxc[sz]) continue; // 这一个位置不是最大值
if (sz == n) continue; // 长度够了
if (vis[i] == sz) continue; vis[i] = sz; // 之前这一步访问过了
if (s[nxt[i]] < mxc[sz + 1]) continue; // 不是最大值
mxc[sz + 1] = s[nxt[i]];
que.push({nxt[i], sz + 1});
}
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i ++) cout << mxc[i]; cout << endl;
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26