博弈论
#
# 贪心
# ARC137C_DistinctNumbers
# 🔗
# 💡
乍一看确实很像尼姆博弈,但是每次只能选最大的数这个条件我们很难处理
于是思考能不能使用这个限制去求解
在双人下,先手可以看看是否可以用这个限制去卡掉次手
那么如果 变成比 小的为必败态,那么 必胜
如果 变成比 小的为必胜态,那么考虑是否可以让自己必胜,那便是强制次手走到那一步,即让
这个是需要 的
那么这个条件下先手必胜
如果不满足这个条件,那么就是每次让 ,看一下 是否为奇数即可
# ✅
inline void read_Array ( int *a, int beg, int end ) { for ( int i = beg; i <= end; i ++ ) cin >> a[i]; }
inline void print_Array ( int *a, char c, int beg, int end ) { for ( int i = beg; i <= end; i ++ ) cout << a[i] << c; }
const int N = 3e5 + 10;
int main () {
cin.tie(0)->sync_with_stdio(0);
cin.exceptions(cin.failbit);
int n; cin >> n;
int a[n + 10]; read_Array(a, 1, n);
sort ( a + 1, a + n + 1 );
if ( a[n] - a[n - 1] >= 2 ) {
cout << "Alice";
} else if ( (a[n] - (n - 1)) & 1 ) {
cout << "Alice";
} else {
cout << "Bob" << endl;
}
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
# CCPC2021湘潭省赛H_Game
# 🔗
# 💡
操作 和操作 是一类 ,因为考虑模 相同的数,如果数可以重复的话最后一定会贴在一起,而这样的话每次操作就是减
由于只有两个人,看操作次数奇偶性即可
则对于一个数,操作 次 和操作 次 是一样的,都是奇数次
于是我们先将所有数按模 分类,相同的存一下操作次数,即
那么为了不重复,对于同一类的数,最多会变成 ,所以每一类都统计变成最终态的次数,将所有类的次数累加在一起
如果总次数为奇数, 赢,否则 赢
# ✅
const int N = 2e5 + 10;
int n;
int a[N];
inline void Solve () {
vector<int> v[10];
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i ++) {
v[a[i] % 9].push_back(a[i] / 9);
}
int all_cnt = 0;
for (int i = 0, idx = 1; i < 9; i ++, idx = 0) {
sort(v[i].begin(), v[i].end());
for (int j = 0; j < v[i].size(); j ++) {
all_cnt ^= (v[i][j] - idx) & 1;
idx ++;
}
}
printf("%c\n", "AB"[all_cnt == 0]);
}
int main () {
while (scanf("%d", &n) != EOF) {
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i ++) scanf("%d", &a[i]);
Solve ();
}
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
# 棋盘
# HDU2021多校(9)2_AnotherBoardGame
# 🔗
# 💡
首先看一眼数据量,1e18,....想想都知道不能模拟和递归
首先考虑一个人游戏的进行方案(以第一个人为例
1.到达这一行最大的值
2.让第二个人可以到达的最小的值最大
由于每一个人的目的都是上面的两种,所以游戏模式将会很固定,即第一个人只会走到最小值最大的那一列,第二个人只会走到最大值最小的那一列
由于第二个人的走向会被上一步中第一个人控制,所以只用考虑最后是谁走的
那么就判断一下k的奇偶即可
首先特判1
即第一个人走到第一行中最大的位置
然后是奇数
代表第一个人走最后一步,那么他的行为将会受到第二个人的限制,即只能走到最小的行最大值
当然他也可以提前结束游戏,所以与第一个点比较一下
然后是偶数
代表第二个人走最后一步,那么他的行为将会受到第一个人的限制,即只能走到最大的最小值
当然第一个人如果看出来了情况不妙也可以提前结束游戏,所以与第一个点比较一下
# ✅
const ll N = 1e5 + 10;
ll n, m, k;
vector<vector<ll> > g; // 存图,1e5*1e5硬开内存可能会炸
ll min_maxRow, max_minCol;
int main() {
ios::sync_with_stdio(false);
ll cass; cin >> cass; while ( cass -- ) {
g.clear();
cin >> n >> m >> k;
for ( ll i = 0; i < n; i ++ ) {
vector<ll> cur;
for ( ll j = 0, x; j < m; j ++ )
cin >> x,
cur.push_back(x);
g.push_back(cur);
}
min_maxRow = 1e18, max_minCol = 0; // 最小的行最大值和最大的行最小值
for ( ll i = 0; i < n; i ++ ) {
ll maxRow = 0;
for ( ll j = 0; j < m; j ++ ) maxRow = max ( maxRow, g[i][j] );
min_maxRow = min ( min_maxRow, maxRow );
}
for ( ll j = 0; j < m; j ++ ) {
ll minCol = 1e18;
for ( ll i = 0; i < n; i ++ ) minCol = min ( minCol, g[i][j] );
max_minCol = max ( max_minCol, minCol );
}
if ( k == 1 ) { // 走第一行
ll res = 0;
for ( ll j = 0; j < m; j ++ ) res = max ( res, g[0][j] );
cout << res << endl;
} else if ( k & 1 ) {
cout << max(min_maxRow, g[0][0]) << endl;
} else {
cout << max(max_minCol, g[0][0]) << endl;
}
}
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
# 尼姆
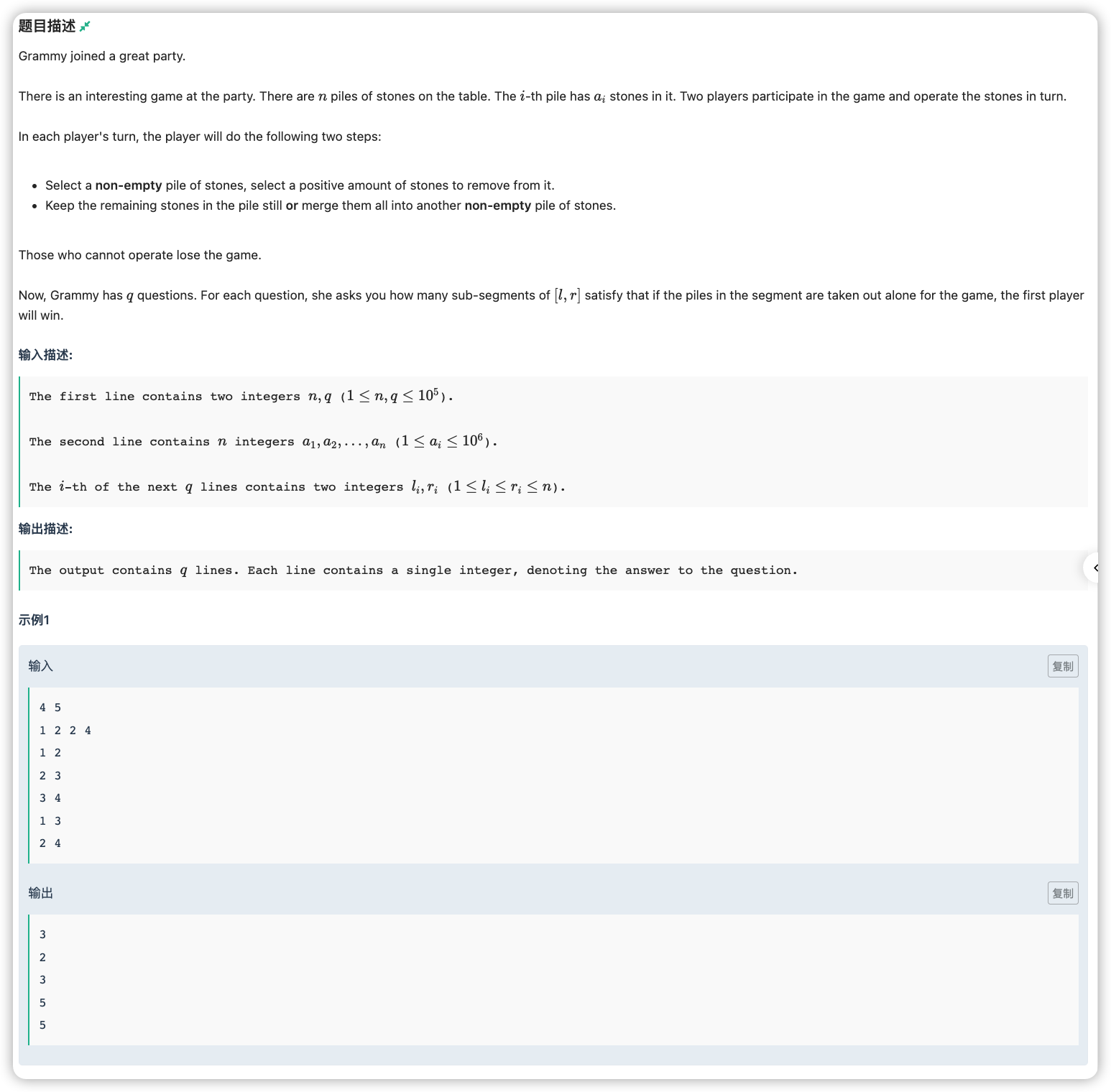
# 牛客2022多校(7)K_GreatParty
# 🔗
# 💡
一堆石子可以拿了一个丢弃剩下的,必胜。
两堆石子谁都不想拿完一堆,尼姆游戏。
三堆石子可以直接把一堆拿走部分然后剩下的去拼到另外两堆较小的那堆上来让两堆补齐,成为异或为 的尼姆必败态,所以必胜。
四堆石子和两堆一样,尼姆游戏。
...
这样规律就有了,奇数必胜,偶数尼姆。
对于查询 ,其中的奇子串全是赢,偶子段异或为 是输、别的都是赢。
统计偶子段异或为 的数量,其实就是前缀异或相同的对数。
如果异或为 的有 个,那么就产生了 对
由于区间 的异或为 ,所以位置的奇偶性相同的前缀产生的区间为偶段,故前缀异或为某个数值的个数的计数需要开两个数组。
如果一个个跑是很费时间的,发现只有查询,使用莫队进行动态操作即可。
# ✅
int sq;
inline int getpos (int x) {
return x / sq;
}
int a[100005];
int n, Q;
struct qry {
int l, r, id;
inline friend bool operator < (qry a, qry b) {
if (getpos(a.l) != getpos(b.l)) return a.l < b.l;
else {
int gp = getpos(a.l);
if (gp & 1) return a.r > b.r;
else return a.r < b.r;
}
}
} q[100005];
ll res1, res2;
ll cnt1[3000006], cnt2[3000006];
inline void add (int x, int id) {
if (id & 1) {
res1 -= cnt1[x] * (cnt1[x] - 1) / 2;
cnt1[x] ++;
res1 += cnt1[x] * (cnt1[x] - 1) / 2;
} else {
res2 -= cnt2[x] * (cnt2[x] - 1) / 2;
cnt2[x] ++;
res2 += cnt2[x] * (cnt2[x] - 1) / 2;
}
}
inline void sub (int x, int id) {
if (id & 1) {
res1 -= cnt1[x] * (cnt1[x] - 1) / 2;
cnt1[x] --;
res1 += cnt1[x] * (cnt1[x] - 1) / 2;
} else {
res2 -= cnt2[x] * (cnt2[x] - 1) / 2;
cnt2[x] --;
res2 += cnt2[x] * (cnt2[x] - 1) / 2;
}
}
ll res[100005];
int main() {
scanf("%d%d", &n, &Q);
sq = sqrt(n);
for (int i =1 ; i <= n ;i ++) {
scanf("%d", &a[i]);
a[i] --;
a[i] ^= a[i - 1];
}
for (int i = 1; i <= Q; i ++) {
scanf("%d%d", &q[i].l, &q[i].r);
q[i].l --;
q[i].id = i;
}
sort(q, q + 1 + Q);
int L = 0, R = -1;
for (int i = 1; i <= Q; i ++) {
int l = q[i].l, r = q[i].r;
while (L < l) sub(a[L], L), L ++;
while (L > l) L --, add(a[L], L);
while (R < r) R ++, add(a[R], R);
while (R > r) sub(a[R], R), R --;
ll len = q[i].r - q[i].l;
res[q[i].id] = len * (len + 1) / 2 - (res1 + res2);
}
for (int i = 1; i <= Q; i ++) {
printf("%lld\n", res[i]);
}
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
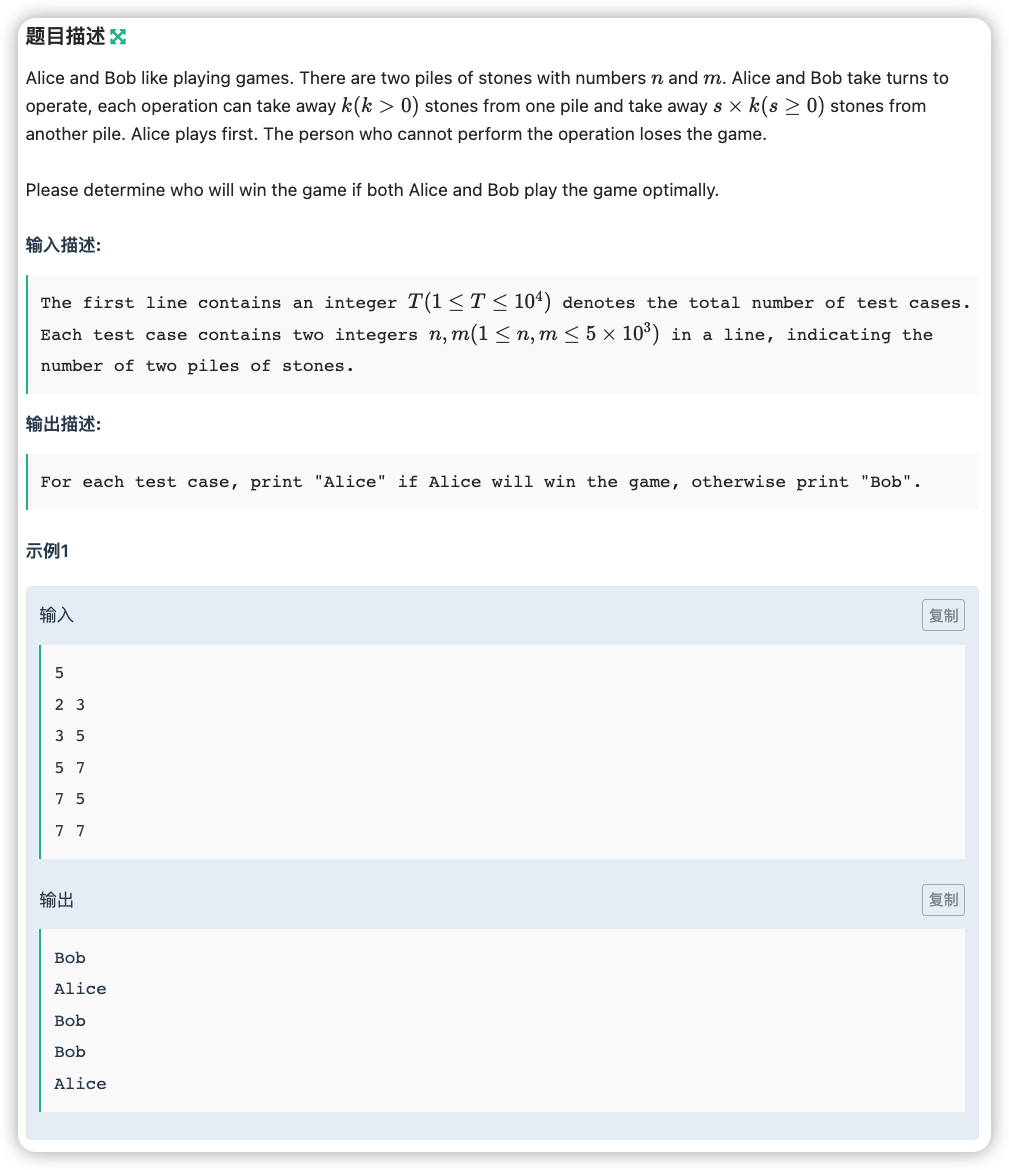
# SG转移
# 牛客2021多校(1)A_AliceAndBob
# 🔗
# 💡
这里 都是小于等于 ,且 很大,这种就是让你预处理的,而由于 的大小,确定出来是预处理二维数组然后直接 得答案的
预处理了话,首先取必败态
然后由博弈状态得到,只要状态可以往下转移出来一个必败态,那么这个状态就是必胜态
所以我们对于每一个必败态,去看谁能转移过来
即 ,或者
这种拿埃氏筛的方式转移一下,然后往大跑 就行,但是一次 可能会被卡断,即一个 都是必胜态,所以我们要外层双重循环枚举,如果 为必败态,就进入
(当然这么多次进入 肯定需要一个记忆化搜索)
# ✅
int sg[5003][5003];
inline void dfs (int x, int y) {
if (x > 5000 || y > 5000) return;
for (int d = 1; d + x <= 5000; d ++) {
for (int i = 0; i + y <= 5000; i += d) {
sg[x + d][i + y] = 0;
}
}
for (int d = 1; d + y <= 5000; d ++) {
for (int i = 0; i + x <= 5000; i += d) {
sg[x + i][y + d] = 0;
}
}
if (sg[x + 1][y]) dfs(x + 1, y);
if (sg[x][y + 1]) dfs(x, y + 1);
if (sg[x + 1][y + 1]) dfs(x + 1, y + 1);
}
inline void Solve () {
int x, y; scanf("%d%d", &x, &y);
if (sg[x][y]) puts("Bob");
else puts("Alice");
}
int main () {
for (int i = 0; i < 5003; i ++) for (int j = 0; j < 5003; j ++) sg[i][j] = 1;
for (int i = 0; i <= 5000; i ++) {
for (int j = 0; j <= 5000; j ++) {
if (sg[i][j]) dfs(i, j);
}
}
int t; scanf("%d", &t); while (t --) Solve();
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35