矩阵树定理
Chivas-Regal
#
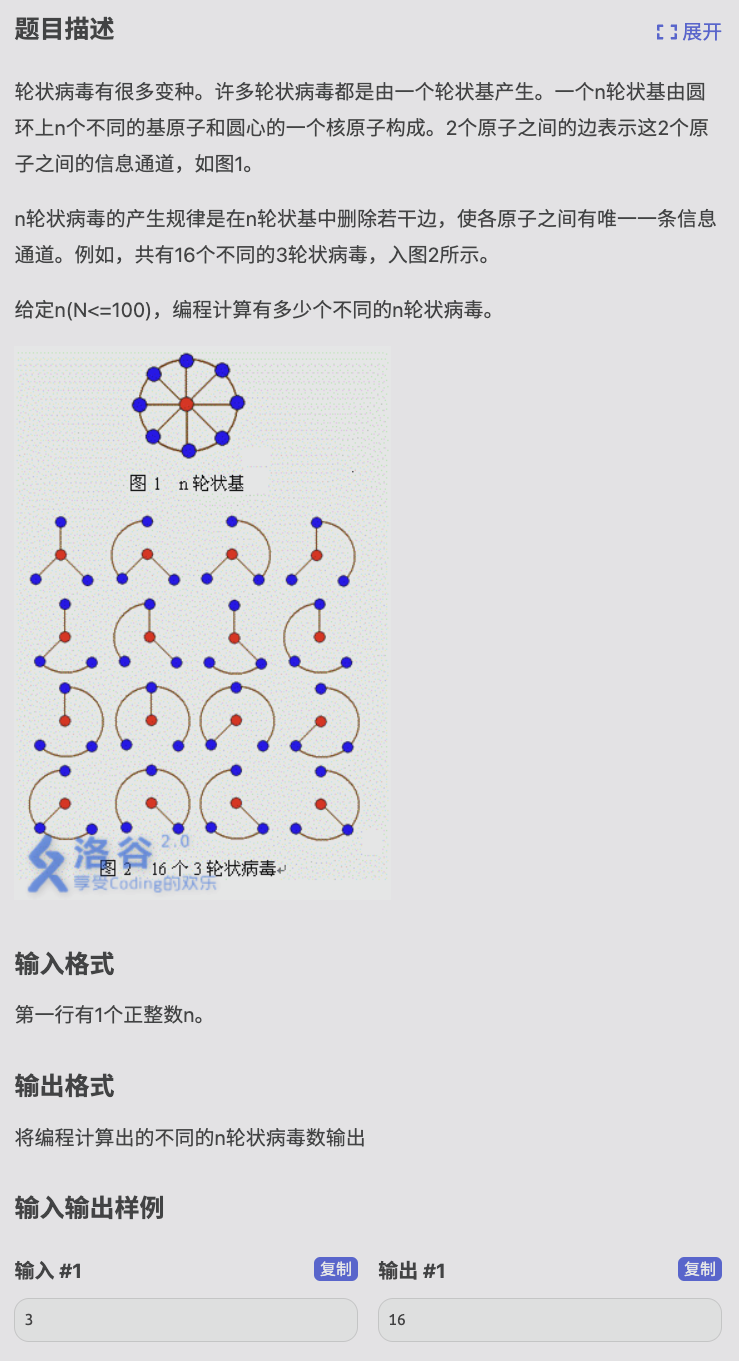
# 洛谷P2144_轮状病毒
# 🔗
# 💡
无向图统计生成树个数
设一圈是1~n号点,中心是n+1号点,就连一圈边,然后每个点还要与n+1号点相连
利用矩阵树定理构建行列式,然后高斯消元求一下行列式即可
(答案过大爆longlong,Java出击
# ✅
public class Main {
static BigInteger [][] a = new BigInteger[110][110];
static int n;
public static void add ( int x, int y ) {
a[x][y] = a[x][y].subtract(BigInteger.ONE);
a[y][x] = a[y][x].subtract(BigInteger.ONE);
a[x][x] = a[x][x].add(BigInteger.ONE);
a[y][y] = a[y][y].add(BigInteger.ONE);
}
public static BigInteger Gauss ( int n ) {
BigInteger res = BigInteger.ONE;
for ( int i = 1; i <= n; i ++ ) {
for ( int ii = i + 1; ii <= n; ii ++ ) {
while ( a[ii][i].compareTo(BigInteger.ZERO) != 0 ) {
BigInteger d = a[i][i].divide(a[ii][i]);
for ( int j = i; j <= n; j ++ ) {
a[i][j] = a[i][j].subtract(d.multiply(a[ii][j]));
BigInteger tmp = a[i][j];
a[i][j] = a[ii][j];
a[ii][j] = tmp;
}
res = BigInteger.ZERO.subtract(res);
}
}
res = res.multiply(a[i][i]);
if ( res.compareTo(BigInteger.ZERO) == 0 ) return BigInteger.ZERO;
}
return res;
}
public static void main (String[] args) {
for ( int i = 0; i < 110; i ++ ) for ( int j = 0; j < 110; j ++ ) a[i][j] = BigInteger.ZERO;
Scanner cin = new Scanner(System.in);
n = cin.nextInt();
for ( int i = 1; i <= n; i ++ ) {
add((i % n) + 1, (i + 1) % n + 1);
add((i % n) + 1, n + 1);
}
System.out.println(Gauss(n));
}
}
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
# 洛谷P4111_小Z的房间
# 🔗
# 💡
两两能到达的房间连边
求无向图生成树个数
对每一个单位重新编号,然后进行连边
可以采用每一个点如果能向右连就向右连,能向下连就向下连,可以防止重复
使用矩阵树定理建行列式
高斯消元求一下行列式sz-1阶行列式即可即可
# ✅
const int N = 15, M = 105;
const int mod = 1e9;
char s[N][N];
int id[N][N], a[M][M];
int n, m;
inline void add ( int x, int y ) {
-- a[x][y];
-- a[y][x];
++ a[x][x];
++ a[y][y];
}
inline int Gauss ( int n ) {
int res = 1;
for ( int i = 1; i <= n; i ++ ) { // 在(i, i)上进行消元
for ( int ii = i + 1; ii <= n; ii ++ ) { // 将(ii, i)变成0
while ( a[ii][i] ) {
int d = a[i][i] / a[ii][i];
for ( int j = i; j <= n; j ++ )
a[i][j] = (a[i][j] - (ll)d * a[ii][j] % mod + mod) % mod,
swap ( a[i][j], a[ii][j] );
res = -res;
}
}
res = (ll)res * a[i][i] % mod;
if ( res == 0 ) return 0;
}
return (res % mod + mod) % mod;
}
int main () {
cin >> n >> m;
for ( int i = 1; i <= n; i ++ ) cin >> (s[i] + 1);
int idx = 0;
for ( int i = 1; i <= n; i ++ ) for ( int j = 1; j <= m; j ++ ) if ( s[i][j] == '.' ) id[i][j] = ++ idx;
for ( int i = 1; i <= n; i ++ ) for ( int j = 1; j <= m; j ++ ) if ( s[i][j] == '.' ) {
if ( id[i - 1][j] ) add ( id[i][j], id[i - 1][j] );
if ( id[i][j - 1] ) add ( id[i][j], id[i][j - 1] );
}
cout << Gauss ( idx - 1 ) << endl;
return 0;
}
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
# 洛谷P4336_黑暗前的幻想乡
# 🔗
# 💡
每条公路只能给一个公司构造
如果多个公司建造这条路
那么就是我们重复考虑的地方
重复,计数,可以想到容斥原理
我们可以二进制枚举一下让哪些公司来建边
每一次的结果就是这套方案的生成树个数
然后容斥地加减,最后得到每条边一个公司建造的结果
# ✅
const ll M = 100;
const ll mod = 1e9 + 7;
ll a[M][M];
ll n, m;
inline void add ( ll x, ll y ) {
-- a[x][y];
-- a[y][x];
++ a[x][x];
++ a[y][y];
}
inline ll Gauss ( ll n ) {
ll res = 1;
for ( ll i = 1; i <= n; i ++ ) { // 在(i, i)上进行消元
for ( ll ii = i + 1; ii <= n; ii ++ ) { // 将(ii, i)变成0
while ( a[ii][i] ) {
ll d = a[i][i] / a[ii][i];
for ( ll j = i; j <= n; j ++ )
a[i][j] = (a[i][j] - (ll)d * a[ii][j] % mod + mod) % mod,
swap ( a[i][j], a[ii][j] );
res = -res;
}
}
res = (ll)res * a[i][i] % mod;
if ( res == 0 ) return 0;
}
return (res % mod + mod) % mod;
}
vector<pair<ll, ll> > vec[M];
int main () {
cin >> n;
for ( ll i = 0; i < n - 1; i ++ ) {
cin >> m;
for ( ll j = 0, x, y; j < m; j ++ ) {
cin >> x >> y;
vec[i].push_back({x, y});
}
}
ll res = 0;
for ( ll num = 0; num < (1ll << (n - 1)); num ++ ) {
for ( ll i = 0; i < M; i ++ ) for ( ll j = 0; j < M; j ++ ) a[i][j] = 0;
ll cnt = 0;
for ( ll i = 0; i < n - 1; i ++ ) {
if ( num & (1 << i) ) {
cnt ++;
for ( auto j : vec[i] ) add(j.first, j.second);
}
}
if ( (n - cnt) & 1 ) res = (res + Gauss(n - 1)) % mod;
else res = (res - Gauss( n - 1 ) + mod) % mod;
}
cout << res << endl;
return 0;
}
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
# 洛谷P4821_生成树
# 🔗
# 💡
无向图+生成树个数
对内圈每一个节点编一个号,外面的五边形多出来的三个点设一个计数器进行编号
对连的边用矩阵树定理构造行列式
然后高斯消元解行列式即可
# ✅
const int N = 105, M = 505;
const int mod = 2007;
int a[M][M];
int n, m;
inline void add ( int x, int y ) {
-- a[x][y];
-- a[y][x];
++ a[x][x];
++ a[y][y];
}
inline int Gauss ( int n ) {
int res = 1;
for ( int i = 1; i <= n; i ++ ) { // 在(i, i)上进行消元
for ( int ii = i + 1; ii <= n; ii ++ ) { // 将(ii, i)变成0
while ( a[ii][i] ) {
int d = a[i][i] / a[ii][i];
for ( int j = i; j <= n; j ++ )
a[i][j] = (a[i][j] - (ll)d * a[ii][j] % mod + mod) % mod,
swap ( a[i][j], a[ii][j] );
res = -res;
}
}
res = (ll)res * a[i][i] % mod;
if ( res == 0 ) return 0;
}
return (res % mod + mod) % mod;
}
int main () {
int cass;
for ( cin >> cass; cass; cass -- ) {
for ( int i = 0; i < M; i ++ ) for ( int j = 0; j < M; j ++ ) a[i][j] = 0;
cin >> n;
int idx = n + 1;
for ( int i = 1; i < n; i ++ ) {
add ( i, idx );
add ( idx, idx + 1 );
add ( idx + 1, idx + 2 );
add ( idx + 2, i + 1 );
add ( i, i + 1 );
idx += 3;
}
add ( n, idx );
add ( idx, idx + 1 );
add ( idx + 1, idx + 2 );
add ( idx + 2, 1 );
add ( n, 1 );
idx += 2;
cout << Gauss ( idx - 1 ) << endl;
}
return 0;
}
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55