贪心-构造
#
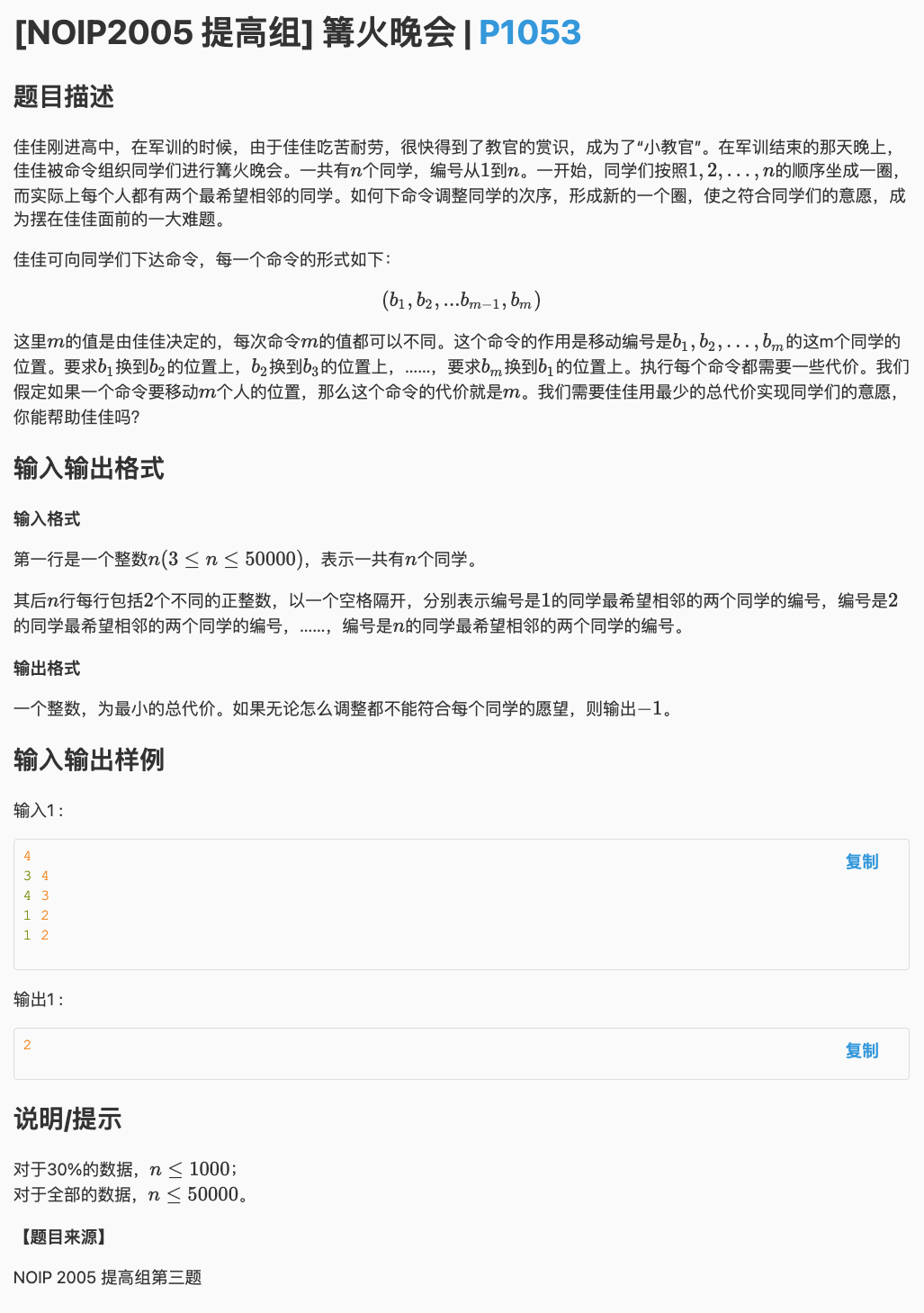
# 洛谷P1053_篝火晚会
# 🔗
# 💡
一个序列整体变动成为另一个序列的话,最大的不动量是与目标位置距离相同的点个数
首先对这个要求,我们先建立出来一条链
同时如果一个点的好朋友不把它当作好朋友,就肯定是
这个可以在建链的时候检查一下
建完之后就对这个距离统计一下数值,看看最多的是多少个点距离相同
(注意,距离有正反,因为这是个链)
然后 减掉这个数量就行了
# ✅
class P1053NOIP2005 {
private:
static const int N = 5e4 + 10;
int n;
pair<int, int> pr[N];
int newlst[N], cnt = 0;
int dir1[N] = {0}, dir2[N] = {0};
public:
inline void build () {
newlst[1] = 1; newlst[2] = pr[1].first; newlst[n] = pr[1].second;
for ( int i = 3; i < n; i ++ ) {
if ( pr[newlst[i - 1]].first == newlst[i - 2] )
newlst[i] = pr[newlst[i - 1]].second;
else if ( pr[newlst[i - 1]].second == newlst[i - 2] )
newlst[i] = pr[newlst[i - 1]].first;
}
}
inline void solve(std::istream& in, std::ostream& out) {
in >> n;
for ( int i = 1; i <= n; i ++ )
in >> pr[i].first >> pr[i].second;
for ( int i = 1; i <= n; i ++ ) {
if ((pr[pr[i].first].first != i && pr[pr[i].first].second != i) ||
(pr[pr[i].second].first != i && pr[pr[i].second].second != i)) {
out << "-1" << endl;
return;
}
}
build ();
int res = 0;
for ( int i = 1; i <= n; i ++ ) {
dir1[(newlst[i] - i + n) % n] ++;
dir2[(newlst[i] + i - 1) % n] ++;
}
for ( int i = 0; i < n; i ++ )
res = max ( res, max(dir1[i], dir2[i]) );
out << n - res << endl;
}
};
int main() {
P1053NOIP2005 solver;
std::istream& in(std::cin);
std::ostream& out(std::cout);
solver.solve(in, out);
return 0;
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
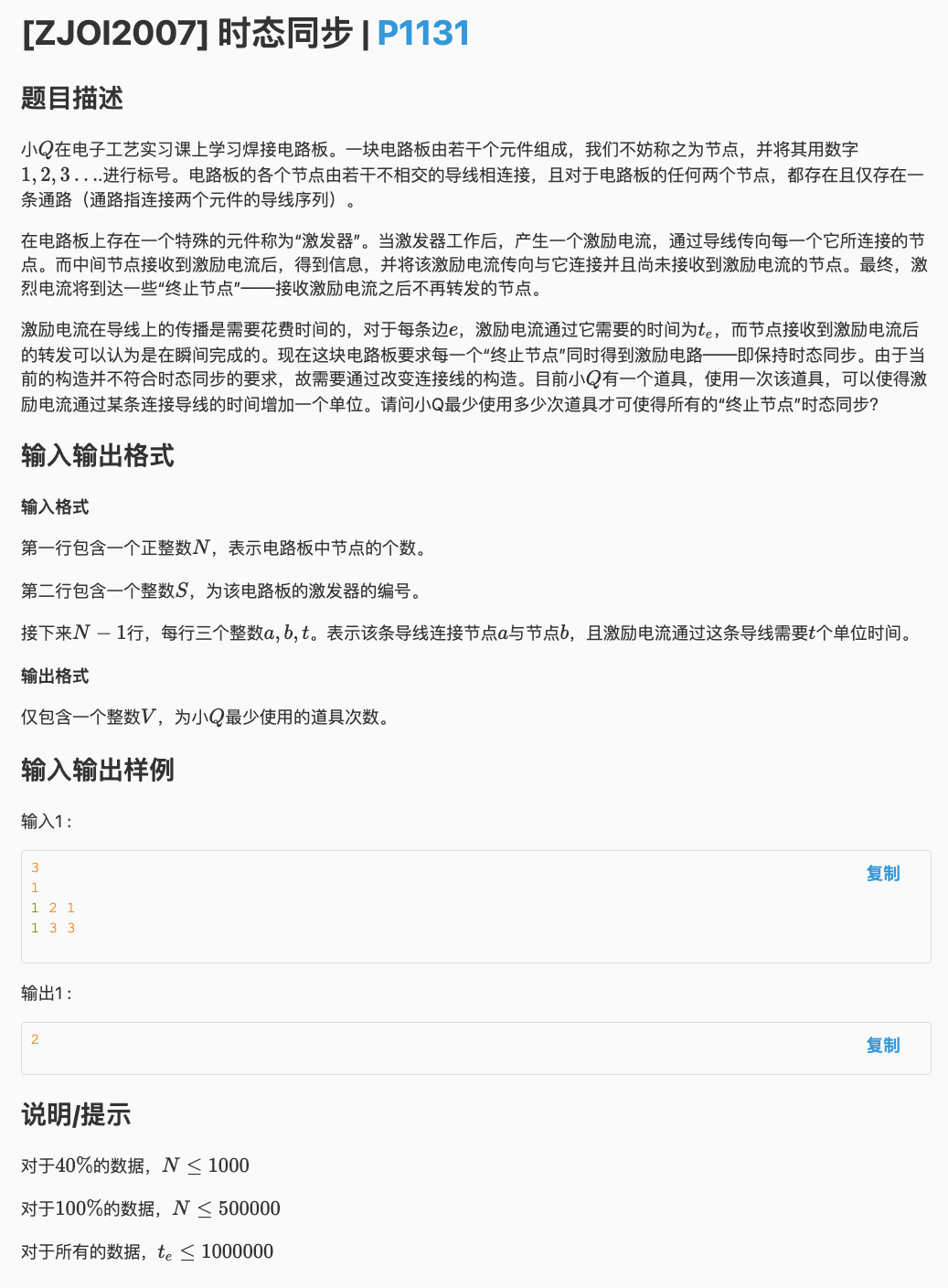
# 洛谷P1131_时态同步
# 🔗
# 💡
很灵活的题,想到这个懒标记解法感觉很妙,想了这么久果然还是wtcl
# 问题转换
简化一下任务,一个有根树
在边上改变最少的全值让根到叶子节点的距离相同
因为边权只能加不能减,那么再简化一下任务
利用差分的思想将每个叶子节点与根节点的距离 设置为这个距离与最远叶子节点距离的差值即
我们要让所有叶子节点的
# 解题思路
纸上试推一下我们不难发现:
每一个边权的增加 会让这个边权下面的子树上所有叶子节点的 同加
也就是我们转换后的 同减
而这种做法是很划算的,因为我们只需要减一次就能对很多叶子节点产生影响
但是要注意,不能减成负数了
因为减成负数了话还要在后面的过程中对很多子树的叶子节点再减些值补到一样,很不划算
所以我们的每棵子树所能减的最多的值是有一个限制的,也就是这颗子树上所有叶子节点 的最小值,这显然是可以直接预处理出来的,设为
这样看来似乎还是有些难以解决
那么就是想到了懒标记的处理方式
因为在往下推子树的时候,是子树减 ,这样的话子树的最小值也会减
因为在枚举到一个节点 的时候,要让这颗子树的最小值 减到 ,而减的时候我们孙子节点 是可以先放着不管的,那么就是让儿子节点 减去这个
节点什么时候减呢?那就是在枚举到 节点的时候,会让这个 节点下减
减得少了怎么办?毕竟 可是子树减过了,不能不算吧?诶我们懒标记累加一下减的值,在 节点减的时候给它算上不就行了
我们每次答案要加的值就是我们在每一个节点上要子树减的值
就是这样一个顺序
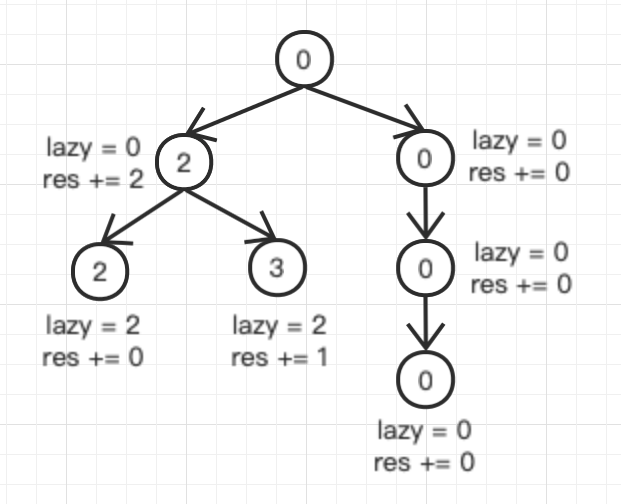
那么这一题完整的思想就出来了
# 程序框架
|----预处理叶子节点与根节点距离 数组
|----将 数组差分化
|--------求
|--------
|----预处理子树最小叶子 的 数组
|----懒标记递推
|--------每个节点的 加给
|--------儿子节点的 同减
|--------答案累加该节点的
|----输出答案
# ✅
namespace Map { // 存图
const int M = 1e6 + 10;
struct Edge {
int nxt, to;
ll val;
} edge[M];
int head[M], cnt;
inline void add_Edge ( int from, int to, ll val ) {
edge [ ++ cnt ] = { head[from], to, val };
head[from] = cnt;
}
} using namespace Map;
int n, a, b, m;
ll res, t;
namespace TreeHasRoot {
const int N = 5e5 + 10;
ll dis[N], min_val[N]; // 距离,子树最小dis
vector<int> leaves; // 叶子节点数组
inline void pre_Dis ( int x, int fath ) { // 预处理直接距离dis
int cnt = 0;
for ( int i = head[x]; i; i = edge[i].nxt ) {
int to = edge[i].to;
if ( to == fath ) continue;
dis[to] = dis[x] + edge[i].val;
pre_Dis ( to, x );
cnt ++;
}
if ( !cnt ) leaves.push_back(x); // 没有儿子,是叶子节点!
}
inline void get_dir_dis () { //将dis数组差分化
pre_Dis (m, m);
ll mx = 0;
for ( auto i : leaves ) mx = max ( mx, dis[i] );
for ( auto i : leaves ) dis[i] = mx - dis[i];
}
inline void pre_MinVal ( int x, int fath ) { // 预处理min_val数组
min_val[x] = 0x3f3f3f3f;
for ( int i = head[x]; i; i = edge[i].nxt ) {
int to = edge[i].to;
if ( to == fath ) continue;
pre_MinVal ( to, x );
min_val[x] = min ( min_val[x], min_val[to] );
}
if ( min_val[x] == 0x3f3f3f3f ) min_val[x] = dis[x]; // 是子节点!设置为本身就行了
}
inline void Solve ( int lazy, int x, int fath ) {
lazy += min_val[x]; // 递推懒标记
for ( int i = head[x]; i; i = edge[i].nxt ) {
int to = edge[i].to;
if ( to == fath ) continue;
min_val[to] -= lazy; // 儿子同减lazy
Solve ( lazy, to, x );
}
res += min_val[x]; // 答案累加这一次子树减的值
}
} using namespace TreeHasRoot;
int main () {
cin >> n >> m;
for ( int i = 0; i < n - 1; i ++ ) {
cin >> a >> b >> t;
add_Edge ( a, b, t );
add_Edge ( b, a, t );
}
get_dir_dis ();
pre_MinVal ( m, m );
for ( int i = head[m]; i; i = edge[i].nxt ) Solve ( 0, edge[i].to, m ); // 注意根节点上面没有边,没法子树减
cout << res << endl;
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
# 洛谷P1286_两数之和
# 🔗
# 💡
首先去计算我们可以得到的
a[1] = ((a[1] + a[2]) + (a[1] + a[3]) + (a[2] + a[3])) / 2 - (a[2] + a[3])
对sum[]排序一下我们很容易知道a[1]+a[2]和a[1]+a[3](就是前两个
那么a[2]+a[3]最多是sum[n],那么我们直接枚举即可
我们要求a[i],可以将a[1~(i-1)]两两构造方式都binary_search一下,如果没有找到的话说明我们枚举得到的a[1]是错的,那么直接否认这一种构造方式
找的的就erase掉
然后剩下的最小的就是a[1] + a[i],我们已知a[1],那么我们直接求得a[i]就行了
每次求完a[i]都进行上述的二分erase即可
如果删完的话说明构造正确
# ✅
const ll N = 150;
ll a[N];
vector<ll> sum, tmp;
bool flag;
ll n;
inline void Solve () {
for ( ll i = 2; i <= n; i ++ ) {
a[i] = tmp[1] - a[1];
for ( ll j = 1; j < i; j ++ ) {
if ( !binary_search ( tmp.begin(), tmp.end(), a[j] + a[i]) ) return;
tmp.erase(lower_bound(tmp.begin(), tmp.end(), a[i] + a[j]));
}
}
flag = 1;
for ( ll i = 1; i <= n; i ++ ) cout << a[i] << " "; cout << endl;
}
int main () {
ios::sync_with_stdio(false);
while ( cin >> n ) {
flag = false; sum.clear();
sum.push_back(-100005); for ( ll i = 1, x; i <= n * (n - 1) / 2; i ++ ) cin >> x, sum.push_back(x);
sort ( sum.begin(), sum.end() );
for ( int i = 3; i <= n; i ++ ) {
tmp = sum;
a[1] = (tmp[1] + tmp[2] + tmp[i]) / 2 - tmp[i];
Solve ();
if ( flag ) goto end;
}
cout << "Impossible" << endl;
end:;
}
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
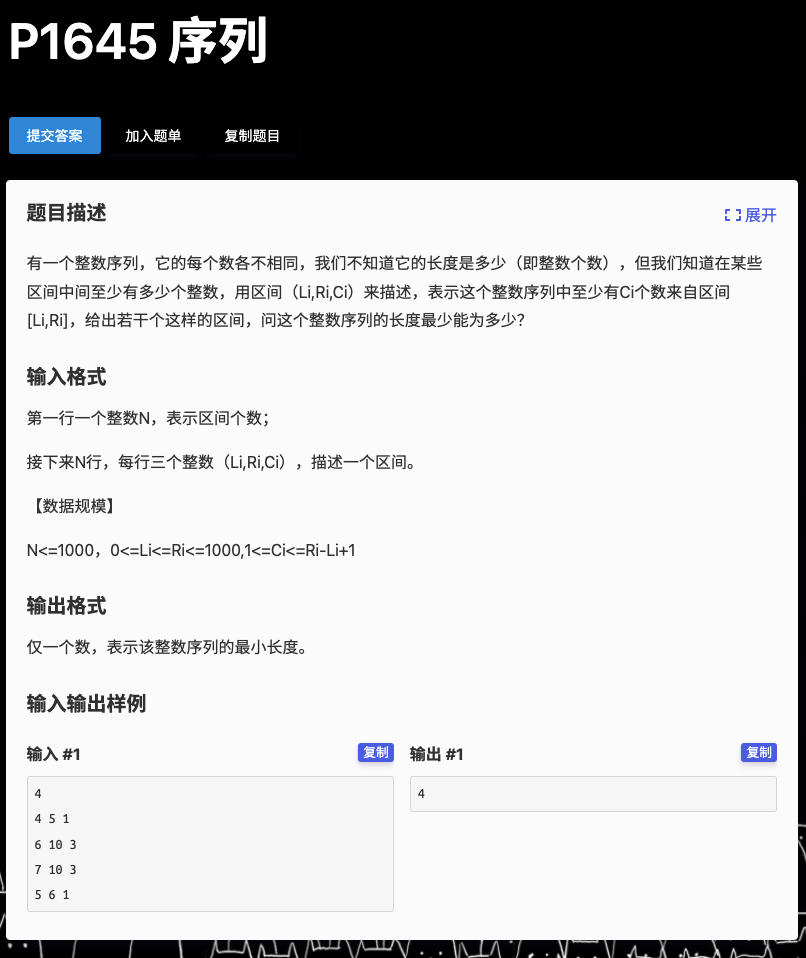
# 洛谷P1645_序列
# 🔗
# 💡
一个贪心的思想
我们对 从小到大排序,每次尽可能选择区间右边的去占位
从而保证后面的区间内部有了更多的占位,做到压缩答案序列数
# ✅
const int N = 1100;
int n;
bool vis[N];
struct node {
int l, r, c;
inline friend bool operator < ( node a, node b ) {
return a.r < b.r;
}
} nd[N];
int res = 0;
int main () {
ios::sync_with_stdio(false);
cin >> n;
for ( int i = 0; i < n; i ++ ) cin >> nd[i].l >> nd[i].r >> nd[i].c;
sort ( nd, nd + n );
for ( int i = 0; i < n; i ++ ) {
for ( int j = nd[i].l; j <= nd[i].r; j ++ ) nd[i].c -= vis[j];
for ( int j = nd[i].r; j >= nd[i].l && nd[i].c > 0; j -- ) {
if ( vis[j] ) continue;
vis[j] = 1,
nd[i].c --, res ++;
}
}
cout << res << endl;
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
# 洛谷2127_序列排序
# 🔗
# 💡
首先要知道每个点应该在哪
这个可以用离散化给出
然后对每个点和其应该在的点连线,发现这是几个环
我们可以考虑环内交换排序,肯定是用环内最小值 进行交换
当然还有一种策略,就是可以利用环外最小值 顶替这个环内最小值 进行交换
用环内最小值
进出两次
进出两次
排里面的 个数用了 次
别的数各用 次
用环外最小值
排 个数用了 次
别的数各用一次
可以看出差别在于 和 上
对于每个环我们取最小即可
# ✅
const int N = 1e5 + 10;
int n;
ll a[N]; int b[N];
ll res;
bool vis[N];
ll numrol;
ll sumrol;
ll minrol;
inline void DFS ( int x ) {
if ( vis[x] ) return; vis[x] = true;
numrol ++;
sumrol += a[x];
minrol = min(minrol, a[x]);
DFS(b[x]);
}
int main () {
ios::sync_with_stdio(false);
cin >> n;
vector<int> vec;
for ( int i = 1; i <= n; i ++ )
cin >> a[i],
vec.push_back(a[i]);
sort ( vec.begin(), vec.end() );
for ( int i = 1; i <= n; i ++ )
b[i] = lower_bound(vec.begin(), vec.end(), a[i]) - vec.begin() + 1;
for ( int i = 1; i <= n; i ++ ) {
if ( vis[i] ) continue;
numrol = 0;
sumrol = 0;
minrol = 0x3f3f3f3f;
DFS(i);
res += sumrol - minrol + min(2 * (vec[0] + minrol) + (numrol - 1) * vec[0], (numrol - 1) * minrol);
}
cout << res << endl;
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
# 洛谷P2869_GourmetGrazersG
# 🔗
# 💡
一个很显然的贪心题
但注意这里有两个关键字:价格,口感
这两个关键字同级,如果直接进行双关键字排序然后双关键字lowerbound会导致因为关键字主次之分产生的错误比较
留意一下最后要求的东西是最小价格
那么我们深究一下问题:保证口感的同时,选取价格要求范围内最小的
那么我们可以只对口感排序,从大口感奶牛开始往小口感扫
每扫一个口感,就要将这个口感以上所有的草的价格都加到一个容器内
那么这组容器对应的奶牛口感一定是满足的
那么我们只需要lowerbound出最小的满足价格要求的价格即可
# ✅
const int N = 1e5 + 10;
multiset<int> mst;
struct grass {
int p, q;
inline friend bool operator < (grass a, grass b) {
if (a.q != b.q) return a.q < b.q;
return a.p < b.p;
}
} g[N];
struct cow {
int a, b;
inline friend bool operator < (cow a, cow b) {
if (a.b != b.b) return a.b < b.b;
return a.a < b.a;
}
} c[N];
int n, m;
int main () {
cin >> n >> m;
for ( int i = 0; i < n; i ++ ) cin >> c[i].a >> c[i].b;
for ( int i = 0; i < m; i ++ ) cin >> g[i].p >> g[i].q;
sort ( g, g + m );
sort ( c, c + n );
ll res = 0;
for ( int i = n - 1, j = m - 1; i >= 0; i -- ) {
while ( j >= 0 && g[j].q >= c[i].b )
mst.insert(g[j].p),
j --;
multiset<int>::iterator it = mst.lower_bound(c[i].a);
if ( it == mst.end() ) {
cout << "-1" << endl;
return 0;
}
res += (ll)*it;
mst.erase(it);
}
cout << res << endl;
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
# 牛客2021多校(2)K_Stack
# 🔗
https://ac.nowcoder.com/acm/contest/11253/K
# 💡
一个比较纯的构造题
构造内容分为两块
1.b[i]的构造
由于b[i]是残缺的,所以我们要构造出一整个b数组
我们知道,b[i] <= b[i - 1] + 1
所以我们从b[0]向后推即可,在未知的b[i]保持是前一个+1(好求),即只有已知的b[i]才有可能删数
若b[i] > b[i - 1] + 1,则不成立
2.a[i]的构造
因为b本身就是个逆向求得的,所以求a用b的逆向
每次都是a[i]放进stack中,然后(删数)求得长度b[i]
那么我们已知某个位置的长度b[i],我们就先在stack内填上数,直到size=b[i]为止
将top还给a[i],依次求得即可
# ✅
/*
________ _ ________ _
/ ______| | | | __ | | |
/ / | | | |__| | | |
| | | |___ _ _ _ ___ _ _____ | ___| ______ _____ ___ _ | |
| | | __ \ |_| | | | | | _\| | | ____| | |\ \ | __ | | _ | | _\| | | |
| | | | \ | _ | | | | | | \ | | \___ | | \ \ | |_/ _| | |_| | | | \ | | |
\ \______ | | | | | | \ |_| / | |_/ | ___/ | | | \ \ | /_ \__ | | |_/ | | |
Author : \________| |_| |_| |_| \___/ |___/|_| |_____| _________|__| \__\ |______| | | |___/|_| |_|
____| |
\_____/
*/
#include <unordered_map>
#include <algorithm>
#include <iostream>
#include <cstring>
#include <utility>
#include <string>
#include <vector>
#include <cstdio>
#include <stack>
#include <queue>
#include <cmath>
#include <map>
#include <set>
#define G 10.0
#define LNF 1e18
#define EPS 1e-6
#define PI acos(-1.0)
#define INF 0x7FFFFFFF
#define ll long long
#define ull unsigned long long
#define LOWBIT(x) ((x) & (-x))
#define LOWBD(a, x) lower_bound(a.begin(), a.end(), x) - a.begin()
#define UPPBD(a, x) upper_bound(a.begin(), a.end(), x) - a.begin()
#define TEST(a) cout << "---------" << a << "---------" << '<br>'
#define CHIVAS_ int main()
#define _REGAL exit(0)
#define SP system("pause")
#define IOS ios::sync_with_stdio(false)
//#define map unordered_map
#define _int(a) int a; cin >> a
#define _ll(a) ll a; cin >> a
#define _char(a) char a; cin >> a
#define _string(a) string a; cin >> a
#define _vectorInt(a, n) vector<int>a(n); cin >> a
#define _vectorLL(a, b) vector<ll>a(n); cin >> a
#define PB(x) push_back(x)
#define ALL(a) a.begin(),a.end()
#define MEM(a, b) memset(a, b, sizeof(a))
#define EACH_CASE(cass) for (cass = inputInt(); cass; cass--)
#define LS l, mid, rt << 1
#define RS mid + 1, r, rt << 1 | 1
#define GETMID (l + r) >> 1
using namespace std;
template<typename T> inline T MAX(T a, T b){return a > b? a : b;}
template<typename T> inline T MIN(T a, T b){return a > b? b : a;}
template<typename T> inline void SWAP(T &a, T &b){T tp = a; a = b; b = tp;}
template<typename T> inline T GCD(T a, T b){return b > 0? GCD(b, a % b) : a;}
template<typename T> inline void ADD_TO_VEC_int(T &n, vector<T> &vec){vec.clear(); cin >> n; for(int i = 0; i < n; i ++){T x; cin >> x, vec.PB(x);}}
template<typename T> inline pair<T, T> MaxInVector_ll(vector<T> vec){T MaxVal = -LNF, MaxId = 0;for(int i = 0; i < (int)vec.size(); i ++) if(MaxVal < vec[i]) MaxVal = vec[i], MaxId = i; return {MaxVal, MaxId};}
template<typename T> inline pair<T, T> MinInVector_ll(vector<T> vec){T MinVal = LNF, MinId = 0;for(int i = 0; i < (int)vec.size(); i ++) if(MinVal > vec[i]) MinVal = vec[i], MinId = i; return {MinVal, MinId};}
template<typename T> inline pair<T, T> MaxInVector_int(vector<T> vec){T MaxVal = -INF, MaxId = 0;for(int i = 0; i < (int)vec.size(); i ++) if(MaxVal < vec[i]) MaxVal = vec[i], MaxId = i; return {MaxVal, MaxId};}
template<typename T> inline pair<T, T> MinInVector_int(vector<T> vec){T MinVal = INF, MinId = 0;for(int i = 0; i < (int)vec.size(); i ++) if(MinVal > vec[i]) MinVal = vec[i], MinId = i; return {MinVal, MinId};}
template<typename T> inline pair<map<T, T>, vector<T> > DIV(T n){T nn = n;map<T, T> cnt;vector<T> div;for(ll i = 2; i * i <= nn; i ++){while(n % i == 0){if(!cnt[i]) div.push_back(i);cnt[i] ++;n /= i;}}if(n != 1){if(!cnt[n]) div.push_back(n);cnt[n] ++;n /= n;}return {cnt, div};}
template<typename T> vector<T>& operator-- (vector<T> &v){for (auto& i : v) --i; return v;}
template<typename T> vector<T>& operator++ (vector<T> &v){for (auto& i : v) ++i; return v;}
template<typename T> istream& operator>>(istream& is, vector<T> &v){for (auto& i : v) is >> i; return is;}
template<typename T> ostream& operator<<(ostream& os, vector<T> v){for (auto& i : v) os << i << ' '; return os;}
inline int inputInt(){int X=0; bool flag=1; char ch=getchar();while(ch<'0'||ch>'9') {if(ch=='-') flag=0; ch=getchar();}while(ch>='0'&&ch<='9') {X=(X<<1)+(X<<3)+ch-'0'; ch=getchar();}if(flag) return X;return ~(X-1);}
inline void outInt(int X){if(X<0) {putchar('-'); X=~(X-1);}int s[20],top=0;while(X) {s[++top]=X%10; X/=10;}if(!top) s[++top]=0;while(top) putchar(s[top--]+'0');}
inline ll inputLL(){ll X=0; bool flag=1; char ch=getchar();while(ch<'0'||ch>'9') {if(ch=='-') flag=0; ch=getchar();}while(ch>='0'&&ch<='9') {X=(X<<1)+(X<<3)+ch-'0'; ch=getchar();}if(flag) return X;return ~(X-1); }
inline void outLL(ll X){if(X<0) {putchar('-'); X=~(X-1);}ll s[20],top=0;while(X) {s[++top]=X%10; X/=10;}if(!top) s[++top]=0;while(top) putchar(s[top--]+'0');}
const int N = 1e6 + 10;
int a[N], b[N];
CHIVAS_{
int n = inputInt(), k = inputInt();
for ( int i = 1, x; i <= k; i ++ ) x = inputInt(), b[x] = inputInt();
// 构造b
for ( int i = 1; i <= n; i ++ ) {
if ( !b[i] ) b[i] = b[i - 1] + 1;
else if ( b[i] > b[i - 1] + 1 ) {
puts ( "-1" );
return 0;
}
}
// 构造a
stack<int> stk; int cur = 0;
for ( int i = n; i >= 1; i -- ){
while(stk.size() < b[i]) stk.push ( ++ cur ); // 填数
a[i] = stk.top(), stk.pop(); // 还给a[i]
}
for ( int i = 1; i <= n; i ++ ) outInt( a[i] ), putchar(' ');
_REGAL;
};
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
99
100
101
102
103
104
105
106
107
108
109
110
# 牛客2021多校(6)I_IntervalsontheRing
# 🔗
# 💡
本体思路在于如何构造
我们知道如果一个完整区间里面少了一块区间lr,那么最后总交区间也不会有lr
那么我们输入时把区间里面的元素设置为1,在构造的时候只需要求空白区间即可
用 r -> l 成功绕过这一段区间,从而也能保证别的区间都被覆盖到
用环形双指针锁定lr即可
# ✅
/*
________ _ ________ _
/ ______| | | | __ | | |
/ / | | | |__| | | |
| | | |___ _ _ _ ___ _ _____ | ___| ______ _____ ___ _ | |
| | | __ \ |_| | | | | | _\| | | ____| | |\ \ | __ | | _ | | _\| | | |
| | | | \ | _ | | | | | | \ | | \___ | | \ \ | |_/ _| | |_| | | | \ | | |
\ \______ | | | | | | \ |_| / | |_/ | ___/ | | | \ \ | /_ \__ | | |_/ | | |
Author : \________| |_| |_| |_| \___/ |___/|_| |_____| _________|__| \__\ |______| | | |___/|_| |_|
____| |
\_____/
*/
#include <unordered_map>
#include <algorithm>
#include <iostream>
#include <cstring>
#include <utility>
#include <string>
#include <vector>
#include <cstdio>
#include <stack>
#include <queue>
#include <cmath>
#include <map>
#include <set>
#define G 10.0
#define LNF 1e18
#define EPS 1e-6
#define PI acos(-1.0)
#define INF 0x7FFFFFFF
#define ll long long
#define ull unsigned long long
#define INT __int128
#define LOWBIT(x) ((x) & (-x))
#define LOWBD(a, x) lower_bound(a.begin(), a.end(), x) - a.begin()
#define UPPBD(a, x) upper_bound(a.begin(), a.end(), x) - a.begin()
#define TEST(a) cout << "---------" << a << "---------" << endl
#define CHIVAS_ int main()
#define _REGAL exit(0)
#define SP system("pause")
#define IOS ios::sync_with_stdio(false)
//#define map unordered_map
#define pii pair<int, int>
#define pll pair<ll, ll>
#define PB(x) push_back(x)
#define ALL(a) a.begin(),a.end()
#define MEM(a, b) memset(a, b, sizeof(a))
#define EACH_CASE(cass) for (cass = inputInt(); cass; cass--)
#define LS l, mid, rt << 1
#define RS mid + 1, r, rt << 1 | 1
#define GETMID (l + r) >> 1
using namespace std;
template<typename T> inline T MAX(T a, T b){return a > b? a : b;}
template<typename T> inline T MIN(T a, T b){return a > b? b : a;}
template<typename T> inline void SWAP(T &a, T &b){T tp = a; a = b; b = tp;}
template<typename T> inline T GCD(T a, T b){return b > 0? GCD(b, a % b) : a;}
template<typename T> inline void ADD_TO_VEC_int(T &n, vector<T> &vec){vec.clear(); cin >> n; for(int i = 0; i < n; i ++){T x; cin >> x, vec.PB(x);}}
template<typename T> inline pair<T, T> MaxInVector_ll(vector<T> vec){T MaxVal = -LNF, MaxId = 0;for(int i = 0; i < (int)vec.size(); i ++) if(MaxVal < vec[i]) MaxVal = vec[i], MaxId = i; return make_pair(MaxVal, MaxId);}
template<typename T> inline pair<T, T> MinInVector_ll(vector<T> vec){T MinVal = LNF, MinId = 0;for(int i = 0; i < (int)vec.size(); i ++) if(MinVal > vec[i]) MinVal = vec[i], MinId = i; return make_pair(MinVal, MinId);}
template<typename T> inline pair<T, T> MaxInVector_int(vector<T> vec){T MaxVal = -INF, MaxId = 0;for(int i = 0; i < (int)vec.size(); i ++) if(MaxVal < vec[i]) MaxVal = vec[i], MaxId = i; return make_pair(MaxVal, MaxId);}
template<typename T> inline pair<T, T> MinInVector_int(vector<T> vec){T MinVal = INF, MinId = 0;for(int i = 0; i < (int)vec.size(); i ++) if(MinVal > vec[i]) MinVal = vec[i], MinId = i; return make_pair(MinVal, MinId);}
template<typename T> inline pair<map<T, T>, vector<T> > DIV(T n){T nn = n;map<T, T> cnt;vector<T> div;for(ll i = 2; i * i <= nn; i ++){while(n % i == 0){if(!cnt[i]) div.push_back(i);cnt[i] ++;n /= i;}}if(n != 1){if(!cnt[n]) div.push_back(n);cnt[n] ++;n /= n;}return make_pair(cnt, div);}
inline int inputInt(){int X=0; bool flag=1; char ch=getchar();while(ch<'0'||ch>'9') {if(ch=='-') flag=0; ch=getchar();}while(ch>='0'&&ch<='9') {X=(X<<1)+(X<<3)+ch-'0'; ch=getchar();}if(flag) return X;return ~(X-1);}
inline void outInt(int X){if(X<0) {putchar('-'); X=~(X-1);}int s[20],top=0;while(X) {s[++top]=X%10; X/=10;}if(!top) s[++top]=0;while(top) putchar(s[top--]+'0');}
inline ll inputLL(){ll X=0; bool flag=1; char ch=getchar();while(ch<'0'||ch>'9') {if(ch=='-') flag=0; ch=getchar();}while(ch>='0'&&ch<='9') {X=(X<<1)+(X<<3)+ch-'0'; ch=getchar();}if(flag) return X;return ~(X-1); }
inline void outLL(ll X){if(X<0) {putchar('-'); X=~(X-1);}ll s[20],top=0;while(X) {s[++top]=X%10; X/=10;}if(!top) s[++top]=0;while(top) putchar(s[top--]+'0');}
const int N = 5000;
int vis[N];
inline void solve() {
MEM(vis, 0);
int n, m; cin >> n >> m;
for ( int i = 0; i < m; i ++ ) {
int l, r; cin >> l >> r; l --, r --;
for ( int i = l;; i = (i + 1 ) % n ) {
vis[i] = 1;
if(i == r) break;
}
}
int stt;
for ( stt = 0; stt < n; stt ++ ) {
if ( vis[stt] == 0 ) break;
} // 随便固定一个stt位置(为0
if ( stt == n ) {
cout << 1 << endl << 2 << " " << 1 << endl;
return ;
}
vector<pii> res;
while( !vis[stt] ) stt = (stt + n - 1) % n; // 让stt移动到某个全1区间的末尾
int tgt = (stt + n - 1) % n; while (vis[tgt] == 1) tgt = (tgt - 1 + n) % n; tgt = (tgt + 1) % n; // 让tgt移动到与stt同全1区间的开头
// i快,j慢
for ( int i = stt, j = i; ; j = i){
j = (j + 1) % n; while( !vis[j] ) j = (j + 1) % n; // j走到下一个全1区间的开头
res.push_back(make_pair(j, i));
if ( j == tgt ) break; // 说明已经一圈了,就break掉了
while (vis[j] ) j = (j + 1) % n; // j继续往后走到下一个全0区间的开头
i = (j + n - 1) % n; // i位于下一个全1区间的末尾
}
cout << res.size() << endl;
for ( int i = 0; i < res.size(); i ++ ) {
cout << res[i].first + 1 << " " << res[i].second + 1 << endl;
}
}
CHIVAS_{IOS;
int cass;
for(cin >> cass; cass; cass --) {
solve();
}
_REGAL;
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
99
100
101
102
103
104
105
106
107
108
109
110
111
112
113
114
115
116
117
118
119
120
121
122
123
124
125
126
127
128
# 牛客2022多校(6)A_Array
# 🔗
# 💡
一个比较明显的特点:在构造出来的数组中,两个相邻的数值为 的数的间隔最多为
但直接按 去构造显然会出现冲突的情况,比如 ,这种冲突情况是极不安全的,考虑什么情况下不会出现冲突。
如果对 排一个序,只要保证后面是前面的倍数的话,如果每次挑第一个空位放 ,就不会出现冲突。
可以将 转化为小于等于 的最大 的幂,这样就保证了。
# ✅
const int N = 3e5 + 10;
int n;
struct node {
int v, id;
} a[N];
int res[N];
int main () {
ios::sync_with_stdio(false);
cin.tie(nullptr);
cin >> n;
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i ++) {
cin >> a[i].v;
int bit = 1; while (bit <= a[i].v) bit <<= 1; bit >>= 1;
a[i] = {bit, i};
}
sort(a + 1, a + 1 + n, [&](node x, node y) { return x.v < y.v; });
int m = a[n].v;
set<int> st;
for (int i = 1; i <= m; i ++) st.insert(i);
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i ++) {
for (int j = *st.begin(); j <= m; j += a[i].v) {
res[j] = a[i].id;
st.erase(j);
}
}
while (st.size()) res[*st.begin()] = 1, st.erase(*st.begin());
cout << m << endl;
for (int i = 1; i <= m; i ++) cout << res[i] << " ";
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
# 牛客2022多校(9)E_LongestIncreasingSubsequence
# 🔗
# 💡
这种构造完,让和等于某个数的可以往二进制上想,因为任何一个数都可以被转换为二进制。
如果我们对其进行分段,让每一段只有一个可以选,根据乘法原理结果将是所有段长的乘积。
那么如果 ,可以分为 个长度为 的段,但是二进制上有 ,考虑如何在 的时候做出贡献。
段长依旧是 ,但是在出现 时,只要让固定数量的段可以转移过来即可。
即若 ,就是有前 段可以直接转移到后面,前 段可以直接转移到后面,前 段可以直接转移到后面
就将构造出来的串分为两部分,前面一部分是一些长度为 的段,后面是递增的一些数,每段都是 形式的
当遇到 时,我们后面那一部分的数要扩展到和段数一样多,才能保证如果前面的段转移过来走到结尾是一个最长上升子序列
而且每次转移必须要保证只有前面的 段可以转移过来,即如果 就代表着 只可以通过前面的两段转移过来,达到存在位置贡献 的二进制串
# ✅
inline void Solve () {
int m; cin >> m;
if (m == 1) {
cout << 1 << endl << 1 << endl;
return;
}
vector<int> bit; while (m) bit.push_back(m & 1), m >>= 1;
int num = 1;
vector<int> w;
for (int i = bit.size() - 2; i >= 0; i --) {
if (bit[i]) {
w.push_back(num);
num = 0;
} else w.push_back(0);
num ++;
} reverse(w.begin(), w.end());
vector<int> res1, res2;
int idx = 0;
for (int i : w) {
for (int j = 0; j < i; j ++) res2.push_back(++idx);
res1.push_back(idx + 2);
res1.push_back(idx + 1);
idx += 2;
}
cout << res1.size() + res2.size() << endl;
for (int i : res1) cout << i << " ";
for (int i : res2) cout << i << " ";
cout << endl;
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
# 牛客2022寒假算法基础集训营
# 🔗
# 💡
我们线性往后塞入数,让每一个 的个数依次变成
但是有一个问题,就是我们对于偶数 ,如果选了 ,那么 的方案数也会发生变化
我们只想让它影响 和 后面的数的方案数
所以我们每次选 ,直到 的方案数和数据中给出的相等
这个用生成函数,每加入一个数那么就合并一次括号来影响 后面的
# ✅
const ll N = 2005;
const ll mod = 1e9 + 7;
ll c1[N];
ll c2[N];
ll C[N];
int main(){
ll n; cin >> n;
vector<int> res;
for ( ll i = 1; i <= n; i ++ ) cin >> C[i];
for ( int i = 1; i <= n; i ++ ) {
while ( C[i] > c1[i] ) {
int x = i * 2;
if ( c1[0] == 0 ) {
c1[0] = c1[i] = c1[x] = 1;
} else {
for ( int j = 0; j <= n; j ++ ) {
c2[j + 0] += c1[j]; c2[j] %= mod;
c2[j + i] += c1[j]; c2[j + i] %= mod;
c2[j + x] += c1[j]; c2[j + x] %= mod;
}
for ( int j = 0; j <= n; j ++ ) c1[j] = c2[j], c2[j] = 0;
}
res.push_back(x);
}
}
cout << res.size() << endl;
for ( int i = 0; i < res.size(); i ++ ) cout << res[i] << ' ';
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
# 牛客练习赛92A_D与数列
# 🔗
# 💡
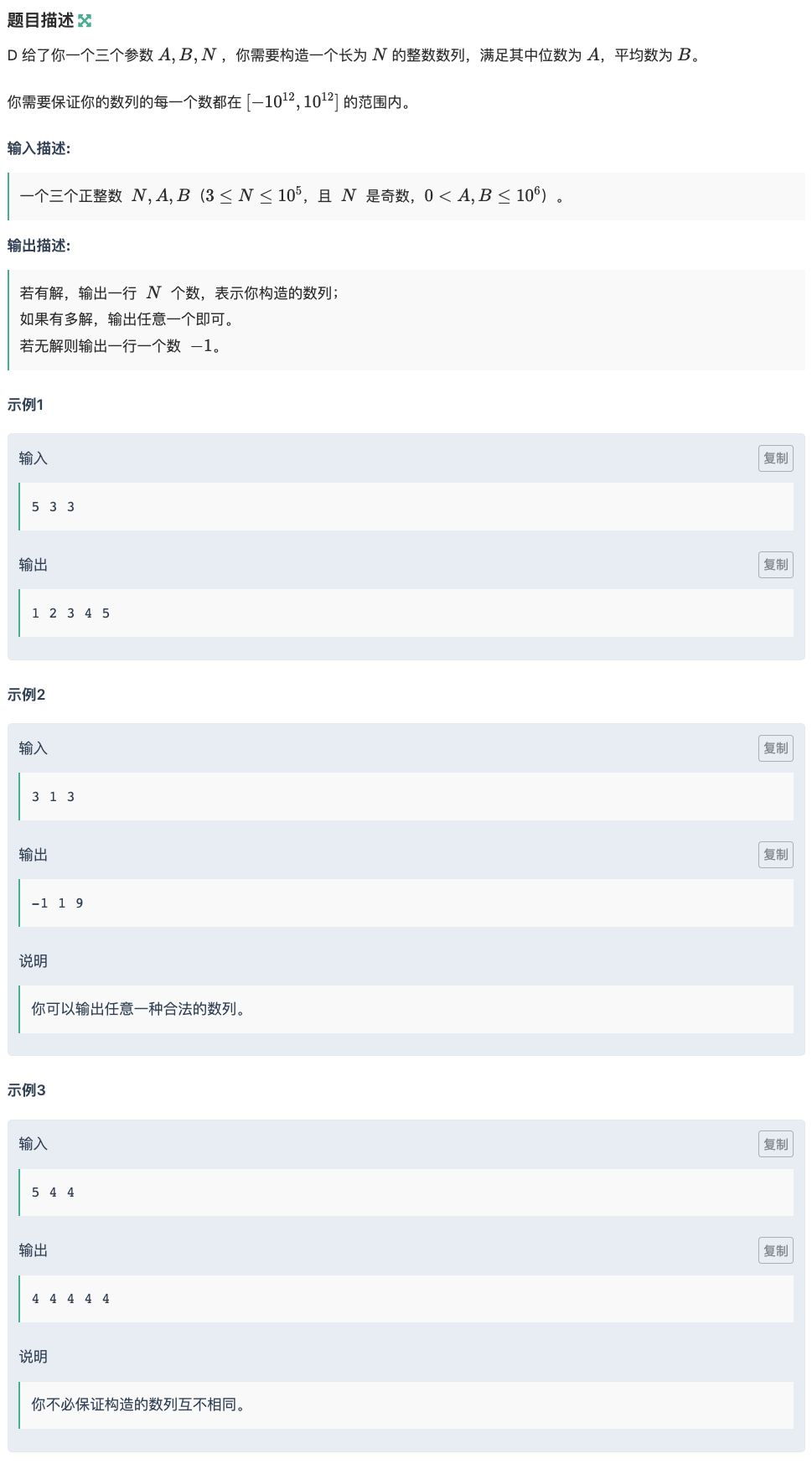
首先我们使中位数固定为的初始构造可以是构造一个全都是的数列
但是平均数达不到
让平均数达到的方式可以是修改某些数让它们总和改变
这样我们可以计算我们现在的总和和想要的总和的差值,然后加上这个差值
如果差值小于0
我们可以在第一个数上加上这个差值,反正缩小前面的数不影响中位数
如果差值大于0
我们可以在最后一个数上加上这个差值,反正增大后面的数不影响中位数
# ✅
int main () {
ll n, a, b; cin >> n >> a >> b;
vector<ll> vec;
vec.push_back(0);
for ( int i = 0; i < n; i ++ ) {
vec.push_back(a);
}
ll sum = a * n;
ll dir = b * n - sum;
if ( dir < 0 ) vec[1] += dir;
else vec.back() += dir;
for ( int i = 1; i < vec.size(); i ++ ) cout << vec[i] << " ";
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
# 牛客练习赛92B_D与集合
# 🔗
# 💡
这道题重点是在考虑要着重处理哪个
0可以跟着整数放
那么问题就在于整数如何放
如果一个集合和为负,那么它再加负数不影响
如果是正数那么再加正数不影响
那么我们可以将分成负数、正数、零,然后先每个集合用一个正负数将k个集合填满(可视作将集合分成一部分正集合和一部分负集合
然后正数放进正数的部分,负数放进负数的部分
最后零随便塞就行了
# ✅
ll n, k;
ll num0;
vector<ll> res[N];
vector<ll> neg, pos;
ll sum = 0;
inline void Print () {
cout << "YES" << endl;
for ( int i = 0; i < k; i ++ ) {
cout << res[i].size();
sort ( res[i].begin(), res[i].end() );
for ( auto v : res[i] ) cout << " " << v;
cout << endl;
}
}
int main () {
cin >> n >> k;
for ( int i = 0; i < n; i ++ ) {
ll x; cin >> x;
if ( x < 0 ) neg.push_back(x);
else if ( x > 0 ) pos.push_back(x);
else num0 ++;
sum += x;
}
if ( k == 1 ) {
if ( sum == 0 ) {
cout << "NO" << endl;
} else {
for ( auto i : neg ) res[0].push_back(i);
for ( auto i : pos ) res[0].push_back(i);
while ( num0 -- ) res[0].push_back(0);
Print();
}
return 0;
}
int div = 0;
if ( k > neg.size() + pos.size() ) { cout << "NO" << endl; return 0; }
if ( neg.size() < k ) {
for ( int i = 0; i < neg.size(); i ++ ) res[i].push_back(neg[i]);
div = neg.size();
for ( int i = div; i < k; i ++ ) res[i].push_back(pos[i - div]);
for ( int i = k - div; i < pos.size(); i ++ ) res[div].push_back(pos[i]);
while ( num0 -- ) res[0].push_back(0);
Print();
} else if ( pos.size() < k ) {
for ( int i = 0; i < pos.size(); i ++ ) res[i].push_back(pos[i]);
div = pos.size();
for ( int i = div; i < k; i ++ ) res[i].push_back(neg[i - div]);
for ( int i = k - div; i < neg.size(); i ++ ) res[div].push_back(neg[i]);
while ( num0 -- ) res[0].push_back(0);
Print();
} else {
div = 1;
for ( int i = 0; i < div; i ++ ) res[i].push_back(pos[i]);
for ( int i = div; i < k; i ++ ) res[i].push_back(neg[i - div]);
for ( int i = 1; i < pos.size(); i ++ ) res[0].push_back(pos[i]);
for ( int i = k - div; i < neg.size(); i ++ ) res[div].push_back(neg[i]);
while ( num0 -- ) res[0].push_back(0);
Print();
}
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
# 牛客练习赛97C_哦~唔西迪西小姐~
# 🔗
# 💡
分开 来看
我们首先默认走每个 的格子
然后我们看看有没有什么地方可以后悔
对于是我们可以走的位置,如果 就意味着我们可以悔成 否则我们就只是变了一下并且走不了,
对于我们不能走的位置,我们可以变并且选择走不走,价值为
然后对这些存起来降序排序,取最大的 个
# ✅
const ll N = 1e5 + 10;
ll n, m;
ll a[N], p[N], b[N];
ll sum;
vector<ll> vec;
int main () {
ios::sync_with_stdio(false);
cin >> n >> m;
for ( ll i = 0; i < n; i ++ ) cin >> a[i];
for ( ll i = 0; i < n; i ++ ) cin >> p[i];
for ( ll i = 0; i < n; i ++ ) cin >> b[i];
ll res = 0;
// 0
sum = 0;
for ( int i = 0; i < n; i ++ ) if ( b[i] == 0 && a[i] >= 0 ) sum += a[i];
for ( int i = 0; i < n; i ++ ) {
if ( b[i] == 0 ) {
if ( a[i] >= 0 ) vec.push_back(-p[i] - a[i]);
else vec.push_back(-p[i]);
} else {
vec.push_back(max(a[i] - p[i], -p[i]));
}
}
sort ( vec.begin(), vec.end(), greater<ll>() );
for ( int i = 0; i < m && i < n; i ++ ) {
if ( vec[i] < 0 ) break;
sum += vec[i];
}
res = max(res, sum);
// 1
vec.clear();
sum = 0;
for ( int i = 0; i < n; i ++ ) if ( b[i] == 1 && a[i] >= 0 ) sum += a[i];
for ( int i = 0; i < n; i ++ ) {
if ( b[i] == 1 ) {
if ( a[i] >= 0 ) vec.push_back(-p[i] - a[i]);
else vec.push_back(-p[i]);
} else {
vec.push_back(max(a[i] - p[i], -p[i]));
}
}
sort ( vec.begin(), vec.end(), greater<ll>() );
for ( int i = 0; i < m && i < n; i ++ ) {
if ( vec[i] < 0 ) break;
sum += vec[i];
}
res = max(res, sum);
cout << res << endl;
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
# 牛客小白月赛41F_小红的375
# 🔗
# 💡
考虑什么样的数能被 整除
(看起来有点乱啊
那就看看什么数具有简单的整除特性
整除的特性是所有数的和是其倍数
又发现 是 的倍数
这样我们可以提前判完 后去判
的特性发现是后三位每八个数一轮,即
那么我们就先从 s 中拆出来其中一个,然后让剩下的最高位不为 即可
# ✅
string s; cin >> s;
function<int()> get_Sum = [&]() { int res = 0; for ( auto i : s ) res += i - '0'; return res; };
if ( get_Sum() % 3 ) {
cout << "-1" << endl;
return 0;
}
vector<string> cans = {"000", "521", "052", "573", "005", "526", "057", "578"}; // 反着搞方便一些
for ( string can : cans ) { // 拆 [can]
string tmp = s, res;
for ( int idx = 0; idx < 3; idx ++ ) {
bool flag = false;
for ( int i = 0; i < tmp.size(); i ++ ) {
if ( tmp[i] == can[idx] ) {
flag = true;
tmp.erase(i, 1);
break;
}
}
if ( !flag ) goto cannot;
}
sort(tmp.begin(), tmp.end()); // 剩下的让最高位不为 0
res = can + tmp;
reverse(res.begin(), res.end());
if ( res[0] == '0' ) continue;
cout << res << endl;
return 0;
cannot:;
}
cout << "-1\n";
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
# 牛客小白月赛44F_幽暗统领
# 🔗
# 💡
不难想到可以求一个别的线能补出来的最小子树和最大子树,这样就有了一个范围
由于你不管怎么对链中点连线,都会有一个限制是最长链的长度化不下来
所以我门从最长链入手
然后就能发现一个性质:
- 若最长链 总链的一半,那么所有点都可以成为重心
- 若最长链 总链的一半,那么只有最长链中的点可以成为重心
第一种情况计个数就行
第二种情况我们找一下在最长链中的范围
左端点是让大树成为一条链,其中心在最长链中的位置
而右端点则是左端点的对称点
# ✅
inline void Solve () {
ll n; cin >> n;
ll mx = 0, sum = 0;
for ( int i = 1; i <= n; i ++ ) {
ll x; cin >> x;
mx = max(mx, x);
sum += x;
}
if ( mx * 2 <= sum ) {
cout << sum << endl;
} else {
ll l = sum / 2 + (sum & 1) - (sum - mx);
ll r = mx - l + 1;
cout << r - l + 1 << endl;
}
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
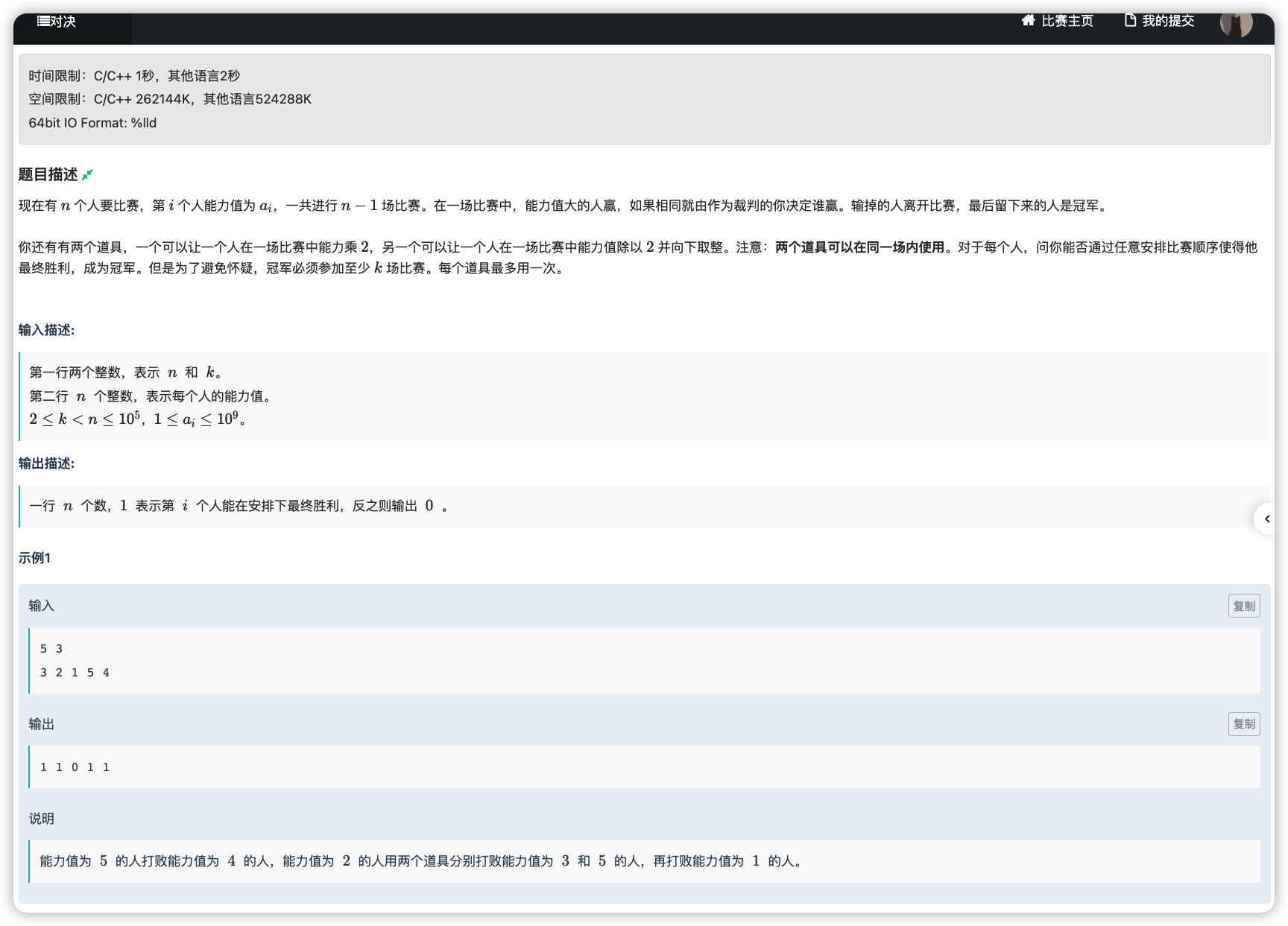
# 牛客小白月赛46E_对决
# 🔗
# 💡
由于 的限制,我们肯定让 干烂比他小和等于它的所有的人
如果个数小于 意味着他需要干三个比他大的,只有两个道具肯定不行
如果个数等于 需要干两个,可以发现向下除 效果是可以包含向上乘 的效果的 ,那么我们干最厉害的用除道具,另一个用乘道具,必须都满足可以赢
如果个数大于等于 那么比 大的人我们再干一个就行,首先考虑让最大的除 让 ,这个如果满足就一定可以
但是还有一种情况,考虑一下中转数值,即
这样 可以打败 , 可以打败 ,但是 用两个道具打不败 ,这种情况下我们需要让 作为中转
我们检查一下中转是否存在以及利用中转是否能打败最大数即可
# ✅
int main () {
cin.tie(0)->sync_with_stdio(0);
cin.exceptions(cin.failbit);
int n, k; cin >> n >> k;
vector<int> a(n);
vector<int> val;
map<int, bool> mp;
for ( int i = 0; i < n; i ++ ) {
cin >> a[i];
val.push_back(a[i]);
mp[a[i]] = true;
}
sort(val.begin(), val.end());
for ( int i = 0; i < n; i ++ ) {
int numles = upper_bound(val.begin(), val.end(), a[i]) - val.begin() - 1;
if ( numles < k - 2 ) {
cout << "0 ";
} else if ( numles == k - 2 ) {
if ( val[n - 1] / 2 > a[i] || val[n - 2] > a[i] * 2 ) cout << "0 ";
else cout << "1 ";
} else {
if ( val[n - 1] / 2 <= a[i] * 2 ) cout << "1 ";
else if ( mp[a[i] * 2 + 1] && (val[n - 1] / 2 <= a[i] * 2 + 1) ) cout << "1 ";
else cout << "0 ";
}
}
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
# 省赛2021江苏C_MagicalRearrangement
# 🔗
# 💡
这种按字典序选数的策略:从前往后构造,对于这一位,从可以保证能顺利构造的字符中选取最小的字符
保证顺利构造:
在选中的字符的数量 的情况下,设出现数量最多的字符为 ,数量为 ,总数量为
如果最多的是当前选中的字符,满足要求要保证 即 这样
如果最多的不是选中的字符,满足要求要保证 ,即 这样
这里有个小技巧,就是如果 和当前选中的字符一样,我们可以看看有没有数量一样多的但是不是 的,这样就能满足更多情况了
对于每一位,我们都从可以选择的数里面扫一下,最小的也就是第一个扫到的就让他做这一位的字符,就能保证字典序最小了
# ✅
vector<pair<char, int> > vec; // 可选字符集
int cnt; // 剩余字符数量
inline bool check (char c) {
pair<char, int> mx = {0, 0};
for ( int i = 0; i < vec.size(); i ++ ) {
char a = vec[i].first; int b = vec[i].second;
if ( a == c ) b --;
if ( b > mx.second ) mx = {a, b};
}
int tmpcnt = cnt; tmpcnt --;
if ( mx.first == c ) { // 看看有没有数量一样的但不是 c 的
for ( int i = 0; i < vec.size(); i ++ ) {
char a = vec[i].first; int b = vec[i].second;
if ( a == c ) b --;
if ( a != mx.first && b == mx.second ) {
mx = vec[i];
break;
}
}
}
if ( mx.first == c ) {
if ( mx.second * 2 > tmpcnt ) return false;
} else {
if ( mx.second * 2 > tmpcnt + 1 ) return false;
}
return true;
}
inline void Solve () {
vec.clear(); cnt = 0;
for ( int i = 0; i < 10; i ++ ) {
int x; cin >> x;
if ( x ) vec.push_back({i + '0', x});
cnt += x;
}
if ( cnt == 1 && vec[0].first == '0' ) { // 特判是不是只有一个 0
cout << "0" << endl;
return;
}
string res;
while ( vec.size() ) {
bool flag = false;
for ( int i = 0; i < vec.size(); i ++ ) {
if ( !res.size() && vec[i].first == '0' ) continue; // 第一位不能为0
if ( res.size() && res.back() == vec[i].first ) continue; // 不能和上一个一样
if ( check(vec[i].first) ) {
res += vec[i].first;
cnt --;
vec[i].second --;
if ( vec[i].second == 0 ) vec.erase(vec.begin() + i, vec.begin() + i + 1);
flag = true;
break;
}
}
if ( !flag ) {
cout << "-1" << endl;
return;
}
}
if ( !res.size() ) cout << "-1" << endl;
else cout << res << endl;
}
int main () {
ios::sync_with_stdio(false);
int cass; cin >> cass; while ( cass -- ) {
Solve ();
}
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
# 省赛2021江苏D_PatternLock
# 🔗
# 💡
从样例获得启发
我们可以 字形构造,但是多行翻来翻去会很麻烦,所以我们变一下

横向就这样画
那么可以看到这种画法是不看列数的,但是行数要满足偶数
而我们对于列数是偶数的,可以把这种画法竖过来就可以了
所以行和列有一个是偶数我们就可以按这种画法把图填满
那么问题来了,如果都是奇数的话
那么我们可以思考一下,这种画法横着摆不看列数,竖着摆不看行数,而他们也同时都受到偶数的限制
也就是说,我们先横着摆,留三行从左到右竖着摆,那么最后还是会摆不完
那么我们依旧可以留三行,那么就在左下角形成了一个边长为 的正方形点阵,这个随便造就可以了
例如:

可以看出,右下角这么搞是安全的
注意:一条线不能穿过已经走过的点
# ✅
int main () {
ios::sync_with_stdio(false);
int n, m; cin >> n >> m;
if ( n == 1 && m == 1 ) { // 特判
cout << 1 << " " << 1 << endl;
return 0;
}
if ( (n & 1) && (m & 1) ) {
for ( int i = 1; i <= n - 3; i += 2 ) { // 横 Z
cout << i << " " << 1 << endl;
for ( int j = 1; j < m; j ++ ) {
cout << i << " " << j + 1 << endl << i + 1 << " " << j << endl;
}
cout << i + 1 << " " << m << endl;
}
// 3*3点阵
cout << n - 2 << " " << m - 2 << endl;
cout << n - 1 << " " << m - 1 << endl;
cout << n - 2 << " " << m - 1 << endl;
cout << n - 1 << " " << m << endl;
cout << n - 2 << " " << m << endl;
cout << n << " " << m - 1 << endl;
cout << n << " " << m << endl;
cout << n - 1 << " " << m - 2 << endl;
cout << n << " " << m - 2 << endl;
// 竖 Z
for ( int j = m - 3; j >= 1; j -= 2 ) {
cout << n - 2 << " " << j << endl;
cout << n - 1 << " " << j << endl;
cout << n - 2 << " " << j - 1 << endl;
cout << n << " " << j << endl;
cout << n - 1 << " " << j - 1 << endl;
cout << n << " " << j - 1 << endl;
}
} else if ( n & 1 ) { // 竖 Z
for ( int j = 1; j <= m; j += 2 ) {
cout << 1 << " " << j << endl;
for ( int i = 1; i < n; i ++ ) {
cout << i + 1 << " " << j << endl;
cout << i << " " << j + 1 << endl;
}
cout << n << " " << j + 1 << endl;
}
} else { // 横 Z
for ( int i = 1; i <= n; i += 2 ) {
cout << i << " " << 1 << endl;
for ( int j = 1; j < m; j ++ ) {
cout << i << " " << j + 1 << endl << i + 1 << " " << j << endl;
}
cout << i + 1 << " " << m << endl;
}
}
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
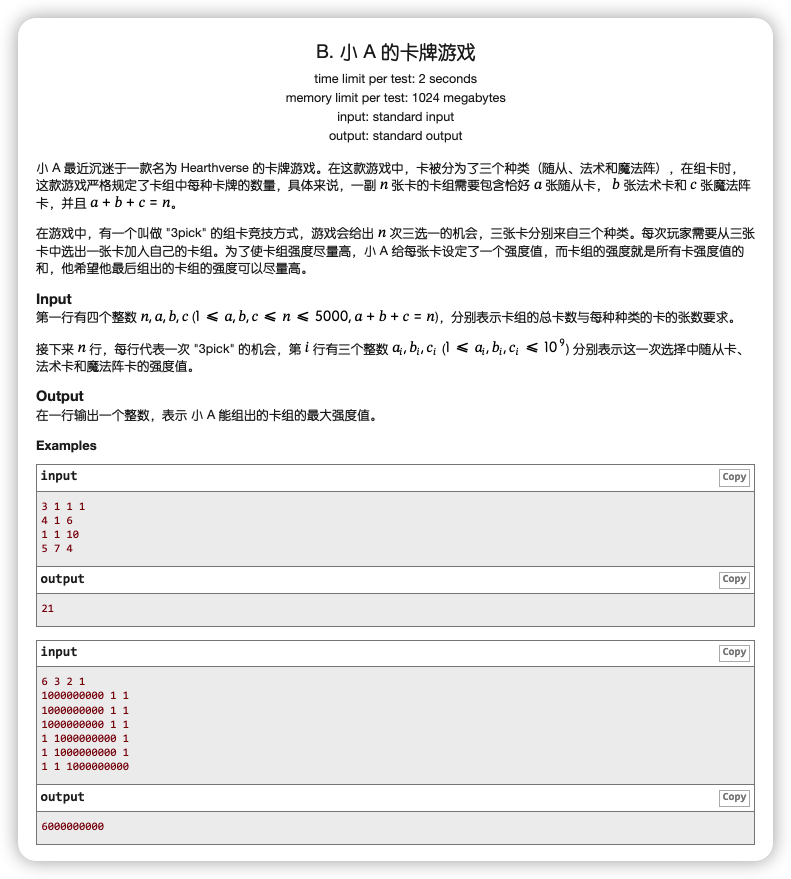
# 省赛2021上海B_小A的卡牌游戏
# 🔗
# 💡
这是一个三元组,问题化简到二元组去思考
即如果只有 的话,可以让 先选,但要求是不能过度影响 的选择
一个基础的想法是让 选第二列最大的几个,但是这样可能会导致出现类似于 这样的两个二元组,如果 先选了第二个二元组的 ,然后 只能选 ,是比较亏的
所以我们肯定是希望 选的二元组中,在不选 选 的情况下,赚得多或者亏得少,转化过来就是 尽可能大
所以按 从大到小排序,然后顺次选择即可
回归到三元组上,多了一个 , 是一个分配问题,而且在排序完之后就是一个二维的,怎么写都行,这里开一个 表示第 个之前, 选了 个
那么在转移的时候,如果 ,这一个可以选 ,
如果不选 ,看看到这一步为止有多少个不选 的,即 ,如果不够 个,那么优先选 ,否则选
update2022/11/13新解法
虽然依然是 多赚/少亏 的思想,但是这种思路会更清晰
由上面可以看出,我们希望按某两个差值降序排序后,优先选前面的那个
且在前 个里面选 个 ,选 个 的转移很好想,那么我们初始全选 ,剩下的就是换数的情况
至于换成 还是换成 ,就是上面说的优先问题,按 降序就是优先选
说明前面有一部分换也是换成 ,后面换也是换成 ,那么就可以枚举分界
做一个前缀 表示 选 个 的最大值, 表示 选 个 的最大值
然后枚举分界线后,就维护 的最大值
# ✅
struct Pick {
int a, b, c;
inline friend bool operator < (Pick A, Pick B) {
return A.b - A.a > B.b - B.a;
}
};
ll dp[5100][5100];
int main () {
ios::sync_with_stdio(false);
cin.tie(nullptr);
int n; cin >> n;
int A, B, C; cin >> A >> B >> C;
vector<Pick> v(n + 1);
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i ++) {
cin >> v[i].a >> v[i].b >> v[i].c;
} sort(v.begin() + 1, v.end());
memset(dp, -0x3f, sizeof dp);
for (int i = 0; i < 5100; i ++) dp[i][0] = 0;
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i ++) {
for (int j = 0; j <= i && j <= C; j ++) {
if (j) dp[i][j] = max(dp[i][j], dp[i - 1][j - 1] + v[i].c);
if (i - j <= B) dp[i][j] = max(dp[i][j], dp[i - 1][j] + v[i].b);
else dp[i][j] = max(dp[i][j], dp[i - 1][j] + v[i].a);
}
}
cout << dp[n][C] << endl;
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
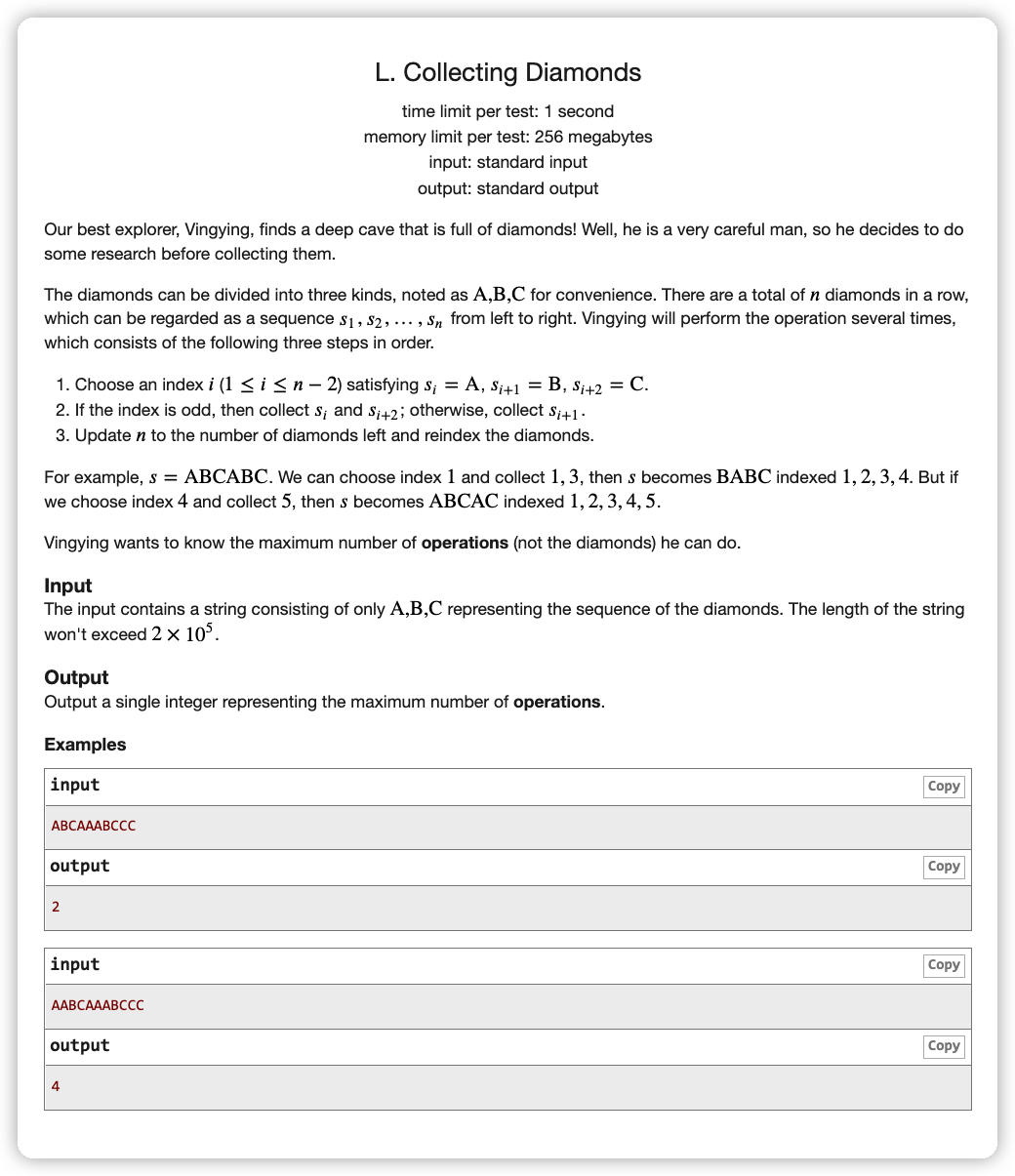
# 省赛2022江苏L_CollectingDiamonds
# 🔗
# 💡
注意一个形如 这样的串,我们一旦拿掉 ,那么便不能再拿这一个部分里面任意一个 或 了
拿谁也与奇偶性有关,那么来分析一下对于每个操作奇偶性的变化。
拿 :改变本块的奇偶性,不改变后面块的奇偶性
拿 : 断掉本块,改变后面所有块的奇偶性
由于存在能改变奇偶性的操作,那么就存在可以反复拿 的情况(即该块为偶数,前面需要一个拿 的操作让本块变成奇数,然后再拿一次 变成偶数)
所以对每一块贪心的方法是:尽量在最后拿一次 ,在拿 之前尽可能地拿
这样就可以用一个变量 lazy 记录前面拿过多少次
如果本块是奇数块,就可以拿 次 ,但不能超过本块的 数量 ,因为我们要让最后一次操作为拿 ,对答案的贡献要 表示拿一次
如果本块是奇数块,就可以拿 次 ,同样不能超过本块 数量 ,对答案的贡献要 表示拿一次
同时要注意如果前面没有能拿 的,且本块是奇数块且只有一套 ,那么就被迫去拿一次 就停止了
# ✅
const int N = 1e6 + 10;
vector<pair<int, ll> > vec; // first:od/ev second:num
int n;
int main () {
ios::sync_with_stdio(false);
string s; cin >> s;
vec.push_back({0, 0});
for (int i = 0; i < s.size(); i ++) {
if (s[i] != 'B') continue;
int num = 1;
while (i - num >= 0 && i + num < s.size() && s[i - num] == 'A' && s[i + num] == 'C') {
num ++;
}
num --;
if (num) vec.push_back({i & 1, num});
}
n = vec.size() - 1;
ll lazy = 0;
ll res = 0;
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i ++) {
if (vec[i].first & 1) {
if (!lazy && vec[i].second == 1) res ++;
else {
res += min(lazy + 1, vec[i].second - 1) + 1;
lazy ++;
}
} else {
res += min(lazy, vec[i].second - 1) + 1;
lazy ++;
}
}
cout << res << endl;
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
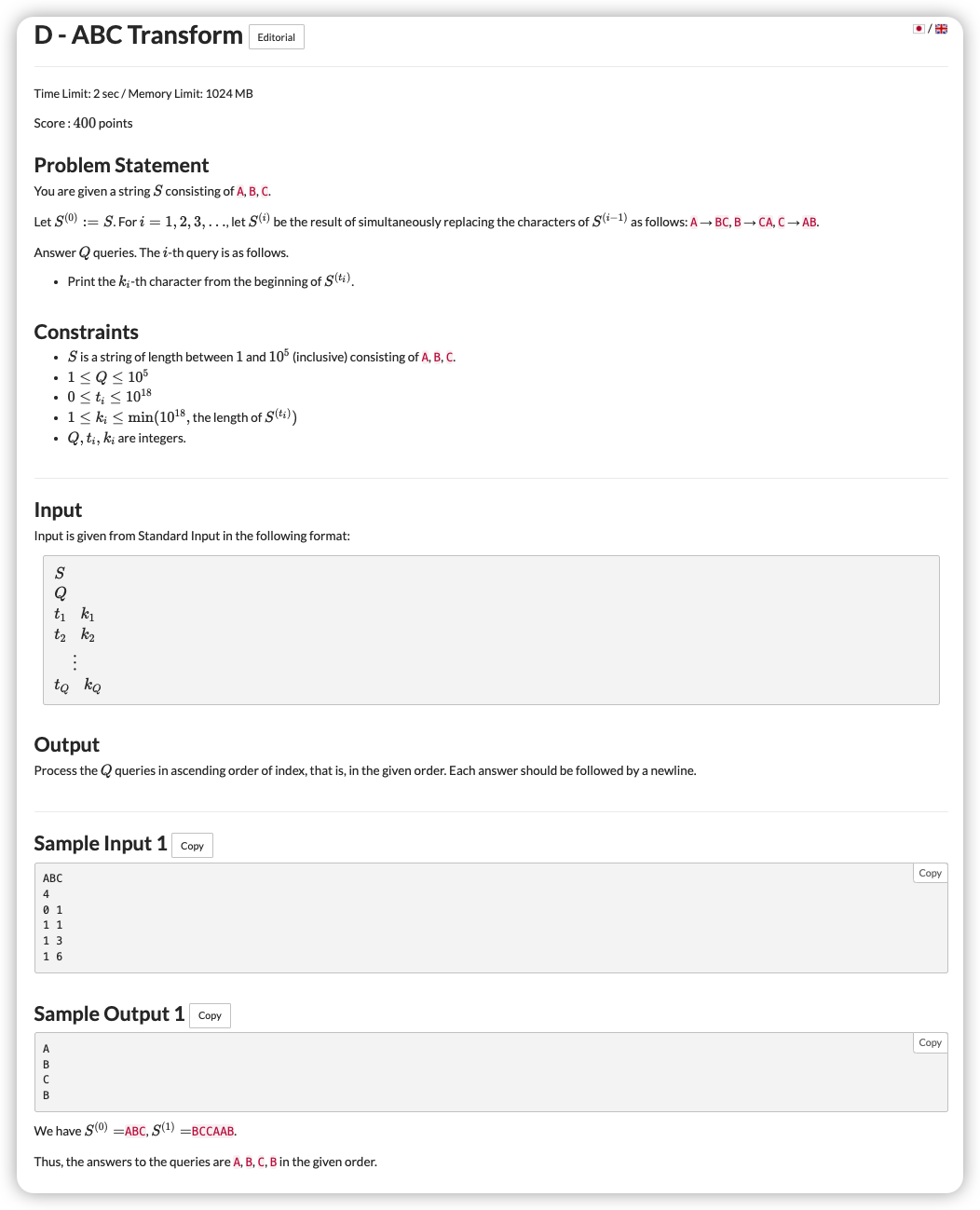
# ABC242D_ABCTransform
# 🔗
# 💡
一种构造建模方式
由于 看出
考虑建立一棵二叉树
左边操作为 ,右边操作为
这个左右边很好看出是 的 个数
那么就让 向上走,固定出 是属于哪个位置的
让这个位置加上我们向上走时获取的要加的数然后模 即可
# ✅
string s;
ll q;
inline void Solve () {
ll t, k; cin >> t >> k; k --;
ll sum = 0;
for ( int i = 1; i <= t; i ++ ) {
sum += k % 2 == 0 ? 1 : 2;
k >>= 1;
if ( k == 0 ) {
sum += t - i;
break;
}
}
cout << char((1ll * s[k] - 'A' + sum) % 3 + 'A') << endl;
}
int main () {
ios::sync_with_stdio(false);
cin >> s >> q;
while ( q -- ) {
Solve();
}
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
# ABC198D_SendMoreMoney
# 🔗
https://atcoder.jp/contests/abc198/tasks/abc198_d
# 💡
因为最多只有十个字符,所以在全排列之后有最多3628800种可能性,时间还可以
所以可以直接开全排列对这些不超过十个字符一一映射一下搜索一下即可
# ✅
#include <iostream>
#include <algorithm>
#include <vector>
#include <string>
#include <map>
#define ll long long
using namespace std;
vector<char> Char; // 存三个字符串中出现过的字符
vector<ll> Num; // 存0~9十个数
map<char, bool> vis; // 去重
map<char, int> chg; // 存当前排列每个字符代表什么
string s[3];
inline void Init () {
for ( int i = 0; i < 3; i ++ ) for ( int j = 0; j < s[i].size(); j ++ ) if ( !vis[s[i][j]] )
Char.push_back(s[i][j]), vis[s[i][j]] = 1;
if ( Char.size() > 10 ) { // 超过十个数直接无解
puts("UNSOLVABLE"); exit(0);
}
for ( int i = 0; i < 10; i ++ ) Num.push_back(i);
}
inline ll get ( string s ) { // 获取在当前排列下,字符串s的意思是什么
ll res = 0;
for ( int i = 0; i < s.size(); i ++ ) {
res = res * 10 + chg[s[i]];
} return res;
}
int main () {
cin >> s[0] >> s[1] >> s[2]; Init();
do {
chg.clear();
for ( int i = 0; i < Char.size(); i ++ ) chg[Char[i]] = Num[i]; // 当前排列和这些字符对应起来
if ( !chg[s[0][0]] || !chg[s[1][0]] || !chg[s[2][0]]) continue; // 不含前导零
ll res0 = get(s[0]), res1 = get(s[1]), res2 = get(s[2]);
if ( res0 + res1 == res2 ) cout << res0 << endl << res1 << endl << res2, exit(0);
} while ( next_permutation(Num.begin(), Num.end()) );
puts("UNSOLVABLE"); // 全排列后还无解就是无解了
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
# ABC239F_ConstructHighway
# 🔗
# 💡
给点的度数和几条已知边,让建树
树的形状小了来说是没有回路,大了来说是给定的连通块没有回路
那么我们按连通块合并,然后让每个连通块内的度数消为
都消到零可以用优先队列消减的思想,让大的之间先互消
那么我们存入每个连通块的总度数并对其降序排序
然后让前面的连通块去合并后面的连通块
这里有一个菊花图的思想
就是默认 号连通块为中心点,然后往后面的连通块合并
如果 号连通块的总度数降到 ,那么就让下一个连通块作为 号连通块进行之后的合并
注意好特判 的情况,即连不成一棵树
- 给的边有环
- 剩余度数和为奇数或者 加上已有的边不等于
- 给的一个点出现的次数大于给的度数
- 给的度数在构造后有不为 的情况
# ✅
const int N = 2e5 + 10;
int n, m;
int d[N];
namespace UnionSet {
int nod[N];
inline void Init () { for ( int i = 0; i < N; i ++ ) nod[i] = i; }
inline int Find ( int x ) { return x == nod[x] ? x : nod[x] = Find(nod[x]); }
inline void Merge ( int x, int y ) { int fx = Find(x); int fy = Find(y); if ( fx != fy ) nod[fx] = fy; }
inline bool Check ( int x, int y) { int fx = Find(x), fy = Find(y); return fx == fy; }
}
queue<int> que[N];
vector<pair<int, int> > vec;
vector<pair<int, int> > res;
int main () {
UnionSet::Init();
scanf("%d%d", &n, &m);
for ( int i = 1; i <= n; i ++ ) scanf("%d", &d[i]);
for ( int i = 0; i < m; i ++ ) {
int a, b; scanf("%d%d", &a, &b);
d[a] --; d[b] --;
if ( UnionSet::Check(a, b) || d[a] < 0 || d[b] < 0 ) { puts("-1"); return 0; }
UnionSet::Merge(a, b);
}
int sum = 0;
for ( int i = 1; i <= n; i ++ ) if ( d[i] > 0 ) sum += d[i];
if ( sum / 2 + m != n - 1 || sum % 2 != 0 ) { puts("-1"); return 0; }
for ( int i = 1; i <= n; i ++ )
for ( int j = 0; j < d[i]; j ++ ) que[UnionSet::Find(i)].push(i);
for ( int i = 1; i <= n; i ++ ) if ( que[i].size() ) vec.push_back({que[i].size(), i});
sort ( vec.begin(), vec.end(), [&]( pii a, pii b ) { return a.first > b.first; } );
for ( int i = 1; i < vec.size(); i ++ ) {
if ( vec[0].first ) {
int u = que[vec[i].second].front(); que[vec[i].second].pop();
int v = que[vec[0].second].front(); que[vec[0].second].pop();
res.push_back({u, v});
d[u] --, d[v] --;
vec[i].first --; vec[0].first --;
}
vec[0].first += vec[i].first;
while ( que[vec[i].second].size() )
que[vec[0].second].push(que[vec[i].second].front()),
que[vec[i].second].pop();
}
for ( int i = 1; i <= n; i ++ ) if ( d[i] ) { puts("-1"); return 0; }
for ( auto i : res ) printf("%d %d\n", i.first, i.second);
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
# ABC240F_SumSumMax
# 🔗
# 💡
我们关注一下 都等于什么
可以看出这是个等差数列
那么我们分析一波 中需要维护最大值的位置
- 每 或者最后是 维护一次
- 每段 中间维护一次
我们设 为当前的 下标,
第一个很好求,直接用等差数列计算即可
第二个只会存在于 且
令加的量 ,减的量
那么加的速度即 ,减的速度即
在这个段内找到最后让 的位置
即
如果这个位置在所求段内,即可算上这个位置的价值
# ✅
const int N = 2e5 + 10;
int n, m;
ll a[N], b[N];
inline void Solve () {
cin >> n >> m;
for ( int i = 0; i < n; i ++ ) cin >> a[i] >> b[i];
ll res = a[0];
ll idx = 0; // 保证 A 的下标不超过 m
ll cur = 0; // 维护当前值
ll sum = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < n; i ++ ) {
if ( a[i] < 0 && sum > 0 ) {
ll ad = sum;
ll dl = - a[i];
ll ps = ad / dl;
if ( ps >= 0 && idx + ps <= m && ps <= b[i] ) {
res = max(res, cur + ad * ps - dl * (ps + 1) * ps / 2);
}
}
if ( idx + b[i] <= m ) {
cur += (1ll + b[i]) * b[i] / 2 * a[i] + sum * b[i];
idx += b[i];
res = max(res, cur);
if ( idx == m ) break;
} else {
cur += a[i] * ((1 + m - idx) * (m - idx) / 2) + sum * (m - idx);
res = max(res, cur);
break;
}
sum += a[i] * b[i];
}
cout << res << endl;
}
int main () {
ios::sync_with_stdio(false);
int cass; cin >> cass; while ( cass -- ) {
Solve ();
}
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
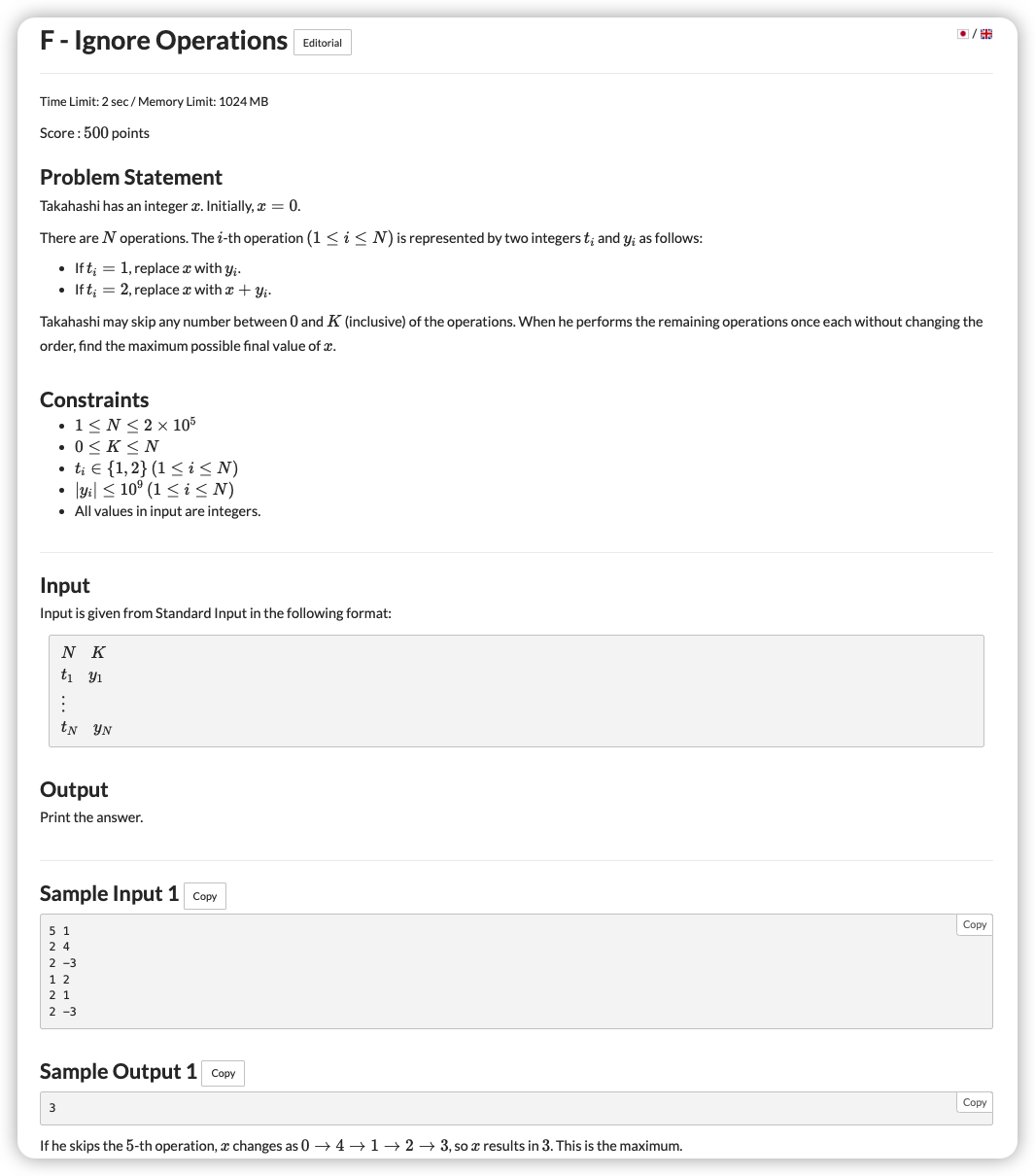
# ABC249F_IgnoreOperations
# 🔗
# 💡
首先需考虑到的是操作一,这里直接让 替换为 ,那么就代表我们之前做的所有操作就前功尽弃,那么在这里我们可以枚举最后一个操作一在哪
这之后的操作一都不统计,则我们剩下的可以跳步的次数 为 后面的操作一个数
这样的话我们肯定是要跳过操作二里面最小的 个负数
正着去查肯定是非常麻烦的,还要去写一个线段树或者平衡树
那么我们可以倒着去查,维护后面的所有操作二的 的和
至于最小的 个负数我们可以用一个大根堆去维护,遇见比当前最大值小的都要替换掉,同时用 去维护这个大根堆的和
在遇见操作一的时候,我们首先要看一下 是否可以更大
然后意味着我们再往前走就要多跳一个操作一,少跳一个操作二
让堆顶弹出一个即可
注意如果我们后面能跳的操作二的数量变成了负数,就说明我们没有再往前枚举的必要了,及时退出就行
还有就是我们往前走在走完其实还要判一下,但是如果我们是退出循环了话就不需要判了。所以我们可以开一个队首哨兵去帮助我们统计第一个
# ✅
int main () {
ios::sync_with_stdio(false);
int n, k; cin >> n >> k;
vector<pair<int, int> > a(n + 1);
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i ++) cin >> a[i].first >> a[i].second;
a[0] = {1, 0};
priority_queue<int> heap;
int maxsize = k; ll sumheap = 0;
ll sum = 0;
ll res = -1e18;
for (int i = n; i >= 0; i --) {
if (a[i].first == 1) {
res = max(res, a[i].second + sum - sumheap);
if (maxsize == 0) break;
maxsize --;
if (heap.size() > maxsize)
sumheap -= heap.top(),
heap.pop();
} else {
if (a[i].second < 0) {
if (heap.size() < maxsize) {
heap.push(a[i].second);
sumheap += a[i].second;
} else if (heap.size() && heap.top() > a[i].second) {
sumheap -= heap.top();
heap.pop();
sumheap += a[i].second;
heap.push(a[i].second);
}
}
sum += a[i].second;
}
}
cout << res << endl;
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
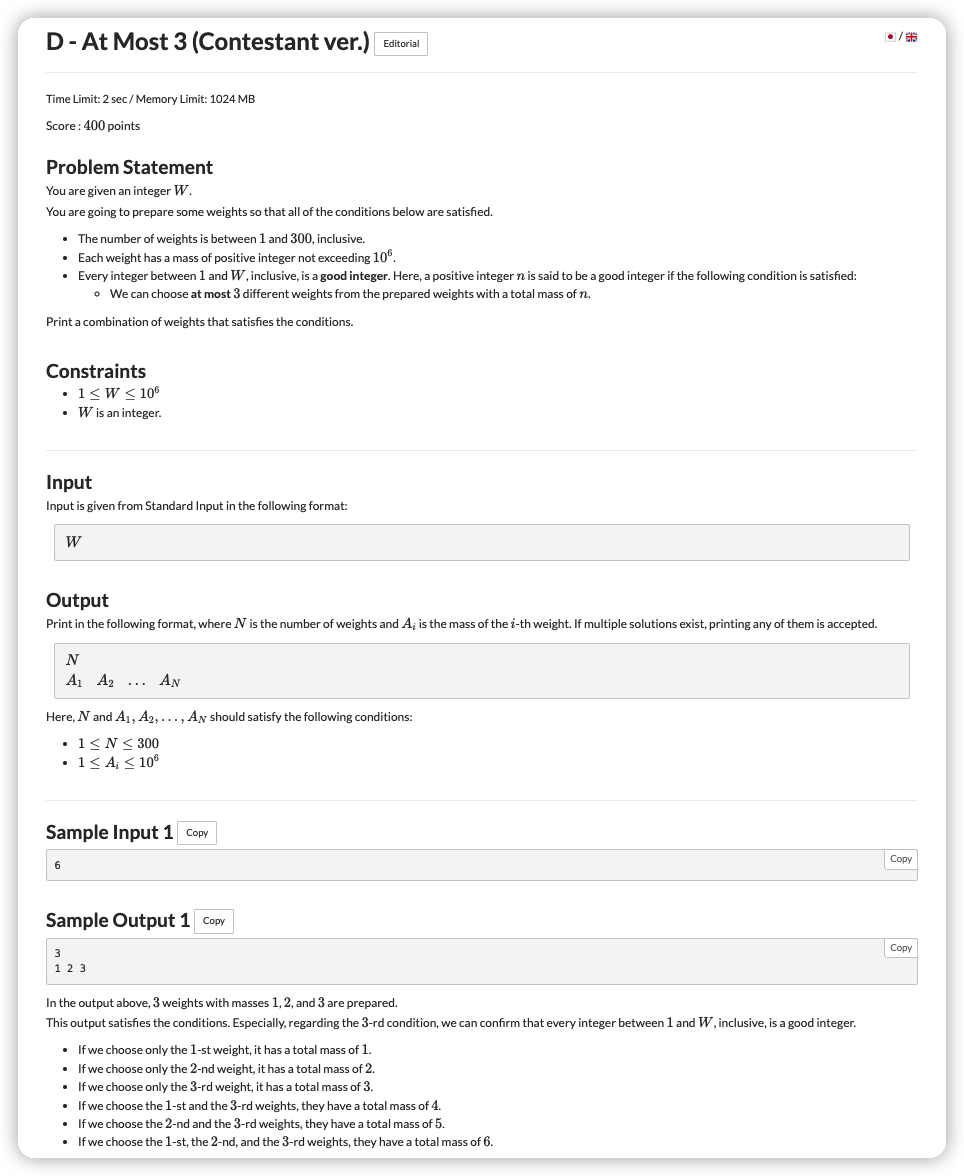
# ABC251D_AtMost3(ContestantVer.)
# 🔗
# 💡
一个比较有趣的构造方式
众所周知如果集完所有的二进制,那么任意一个数都能拼出来
但是这里我们最多只能用三个数,要构造出 以内的任何数
又发现我们最多有 的数组
六位数,要拆成三个数,在字符串下可以拆成三个两位数
在数字下则是 ,那么这样看基本上就很明确了,一百进制即可
将 都给弄出来,这样的话每一个数可以最多这三个集合任意取一个就可以
(比同场 题思维量大多了好吧 -_-||)
# ✅
int main () {
ios::sync_with_stdio(false);
cin.tie(nullptr);
int w; cin >> w;
vector<int> res;
for (int bas = 1; bas <= 10000; bas *= 100)
for (int i = 1; i <= 99; i ++)
res.push_back(bas * i);
cout << res.size() << endl;
for (int i : res) cout << i << " ";
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
# AcWing3766_数字矩阵
# 🔗
https://www.acwing.com/problem/content/3766/
# 💡
这种一变就要好几个一起变的题
可以思考思考有没有可能在变的时候,只有一个变了
在本题中
若出现两个负数我们可以两个负数一起变
若出现一个负数我们可以不断移动负号直至移到我们像移到的位置
所以出现这样一个结论:
如果有偶数个负数,全部变成正数:绝对值求和
如果有奇数个负数,那么我们可以让矩阵内只有一个负数(绝对值最小的那个):绝对值求和后减 2*最小的绝对值
# ✅
/*
________ _ ________ _
/ ______| | | | __ | | |
/ / | | | |__| | | |
| | | |___ _ _ _ ___ _ _____ | ___| ______ _____ ___ _ | |
| | | __ \ |_| | | | | | _\| | | ____| | |\ \ | __ | | _ | | _\| | | |
| | | | \ | _ | | | | | | \ | | \___ | | \ \ | |_/ _| | |_| | | | \ | | |
\ \______ | | | | | | \ |_| / | |_/ | ___/ | | | \ \ | /_ \__ | | |_/ | | |
Author : \________| |_| |_| |_| \___/ |___/|_| |_____| _________|__| \__\ |______| | | |___/|_| |_|
____| |
\_____/
*/
#include <unordered_map>
#include <algorithm>
#include <iostream>
#include <cstring>
#include <utility>
#include <string>
#include <vector>
#include <cstdio>
#include <stack>
#include <queue>
#include <cmath>
#include <map>
#include <set>
#define G 10.0
#define LNF 1e18
#define EPS 1e-6
#define PI acos(-1.0)
#define INF 0x7FFFFFFF
#define ll long long
#define ull unsigned long long
#define LOWBIT(x) ((x) & (-x))
#define LOWBD(a, x) lower_bound(a.begin(), a.end(), x) - a.begin()
#define UPPBD(a, x) upper_bound(a.begin(), a.end(), x) - a.begin()
#define TEST(a) cout << "---------" << a << "---------" << '\n'
#define CHIVAS_ int main()
#define _REGAL exit(0)
#define SP system("pause")
#define IOS ios::sync_with_stdio(false)
//#define map unordered_map
#define _int(a) int a; cin >> a
#define _ll(a) ll a; cin >> a
#define _char(a) char a; cin >> a
#define _string(a) string a; cin >> a
#define _vectorInt(a, n) vector<int>a(n); cin >> a
#define _vectorLL(a, b) vector<ll>a(n); cin >> a
#define PB(x) push_back(x)
#define ALL(a) a.begin(),a.end()
#define MEM(a, b) memset(a, b, sizeof(a))
#define EACH_CASE(cass) for (cass = inputInt(); cass; cass--)
#define LS l, mid, rt << 1
#define RS mid + 1, r, rt << 1 | 1
#define GETMID (l + r) >> 1
using namespace std;
template<typename T> inline T MAX(T a, T b){return a > b? a : b;}
template<typename T> inline T MIN(T a, T b){return a > b? b : a;}
template<typename T> inline void SWAP(T &a, T &b){T tp = a; a = b; b = tp;}
template<typename T> inline T GCD(T a, T b){return b > 0? GCD(b, a % b) : a;}
template<typename T> inline void ADD_TO_VEC_int(T &n, vector<T> &vec){vec.clear(); cin >> n; for(int i = 0; i < n; i ++){T x; cin >> x, vec.PB(x);}}
template<typename T> inline pair<T, T> MaxInVector_ll(vector<T> vec){T MaxVal = -LNF, MaxId = 0;for(int i = 0; i < (int)vec.size(); i ++) if(MaxVal < vec[i]) MaxVal = vec[i], MaxId = i; return {MaxVal, MaxId};}
template<typename T> inline pair<T, T> MinInVector_ll(vector<T> vec){T MinVal = LNF, MinId = 0;for(int i = 0; i < (int)vec.size(); i ++) if(MinVal > vec[i]) MinVal = vec[i], MinId = i; return {MinVal, MinId};}
template<typename T> inline pair<T, T> MaxInVector_int(vector<T> vec){T MaxVal = -INF, MaxId = 0;for(int i = 0; i < (int)vec.size(); i ++) if(MaxVal < vec[i]) MaxVal = vec[i], MaxId = i; return {MaxVal, MaxId};}
template<typename T> inline pair<T, T> MinInVector_int(vector<T> vec){T MinVal = INF, MinId = 0;for(int i = 0; i < (int)vec.size(); i ++) if(MinVal > vec[i]) MinVal = vec[i], MinId = i; return {MinVal, MinId};}
template<typename T> inline pair<map<T, T>, vector<T> > DIV(T n){T nn = n;map<T, T> cnt;vector<T> div;for(ll i = 2; i * i <= nn; i ++){while(n % i == 0){if(!cnt[i]) div.push_back(i);cnt[i] ++;n /= i;}}if(n != 1){if(!cnt[n]) div.push_back(n);cnt[n] ++;n /= n;}return {cnt, div};}
template<typename T> vector<T>& operator-- (vector<T> &v){for (auto& i : v) --i; return v;}
template<typename T> vector<T>& operator++ (vector<T> &v){for (auto& i : v) ++i; return v;}
template<typename T> istream& operator>>(istream& is, vector<T> &v){for (auto& i : v) is >> i; return is;}
template<typename T> ostream& operator<<(ostream& os, vector<T> v){for (auto& i : v) os << i << ' '; return os;}
inline int inputInt(){int X=0; bool flag=1; char ch=getchar();while(ch<'0'||ch>'9') {if(ch=='-') flag=0; ch=getchar();}while(ch>='0'&&ch<='9') {X=(X<<1)+(X<<3)+ch-'0'; ch=getchar();}if(flag) return X;return ~(X-1);}
inline void outInt(int X){if(X<0) {putchar('-'); X=~(X-1);}int s[20],top=0;while(X) {s[++top]=X%10; X/=10;}if(!top) s[++top]=0;while(top) putchar(s[top--]+'0');}
inline ll inputLL(){ll X=0; bool flag=1; char ch=getchar();while(ch<'0'||ch>'9') {if(ch=='-') flag=0; ch=getchar();}while(ch>='0'&&ch<='9') {X=(X<<1)+(X<<3)+ch-'0'; ch=getchar();}if(flag) return X;return ~(X-1); }
inline void outLL(ll X){if(X<0) {putchar('-'); X=~(X-1);}ll s[20],top=0;while(X) {s[++top]=X%10; X/=10;}if(!top) s[++top]=0;while(top) putchar(s[top--]+'0');}
inline void solve(){
int n = inputInt(), m = inputInt(); // 行,列
int MinNum = INF; //最小的绝对值
int cntDeg = 0; //负数的个数
int sum = 0; //绝对值和
for(int i = 0; i < n; i ++){
for(int j = 0, x; j < m; j ++){
x = inputInt();
cntDeg += x < 0;
x = abs(x);
MinNum = MIN(MinNum, x);
sum += x;
}
}
if(cntDeg & 1) sum -= 2 * MinNum; //不得不有一个负数,就绝对值最小的当负数即可
outLL(sum); puts("");
}
CHIVAS_{
int cass;
EACH_CASE(cass){
solve();
}
_REGAL;
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
99
100
101
102
103
104
105
106
107
108
109
110
111
112
113
114
# AcWing3767_三元数异或
# 🔗
https://www.acwing.com/problem/content/3767/
# 💡
首先要意识到一个点:两个子字符串分工明确
故如果这一位是偶数的话,两子字符串均分
如果是奇数,有一个在整数和同长字符串中共同出现的性质:
如果某一位上 a[i] > b[i], 那么 a > b
所以如果出现奇数,a分到的数比b多,那么后面就不能让a再增加了,后面所有的数分给b就行了
# ✅
/*
________ _ ________ _
/ ______| | | | __ | | |
/ / | | | |__| | | |
| | | |___ _ _ _ ___ _ _____ | ___| ______ _____ ___ _ | |
| | | __ \ |_| | | | | | _\| | | ____| | |\ \ | __ | | _ | | _\| | | |
| | | | \ | _ | | | | | | \ | | \___ | | \ \ | |_/ _| | |_| | | | \ | | |
\ \______ | | | | | | \ |_| / | |_/ | ___/ | | | \ \ | /_ \__ | | |_/ | | |
Author : \________| |_| |_| |_| \___/ |___/|_| |_____| _________|__| \__\ |______| | | |___/|_| |_|
____| |
\_____/
*/
#include <unordered_map>
#include <algorithm>
#include <iostream>
#include <cstring>
#include <utility>
#include <string>
#include <vector>
#include <cstdio>
#include <stack>
#include <queue>
#include <cmath>
#include <map>
#include <set>
#define G 10.0
#define LNF 1e18
#define EPS 1e-6
#define PI acos(-1.0)
#define INF 0x7FFFFFFF
#define ll long long
#define ull unsigned long long
#define LOWBIT(x) ((x) & (-x))
#define LOWBD(a, x) lower_bound(a.begin(), a.end(), x) - a.begin()
#define UPPBD(a, x) upper_bound(a.begin(), a.end(), x) - a.begin()
#define TEST(a) cout << "---------" << a << "---------" << '\n'
#define CHIVAS_ int main()
#define _REGAL exit(0)
#define SP system("pause")
#define IOS ios::sync_with_stdio(false)
//#define map unordered_map
#define _int(a) int a; cin >> a
#define _ll(a) ll a; cin >> a
#define _char(a) char a; cin >> a
#define _string(a) string a; cin >> a
#define _vectorInt(a, n) vector<int>a(n); cin >> a
#define _vectorLL(a, b) vector<ll>a(n); cin >> a
#define PB(x) push_back(x)
#define ALL(a) a.begin(),a.end()
#define MEM(a, b) memset(a, b, sizeof(a))
#define EACH_CASE(cass) for (cass = inputInt(); cass; cass--)
#define LS l, mid, rt << 1
#define RS mid + 1, r, rt << 1 | 1
#define GETMID (l + r) >> 1
using namespace std;
template<typename T> inline T MAX(T a, T b){return a > b? a : b;}
template<typename T> inline T MIN(T a, T b){return a > b? b : a;}
template<typename T> inline void SWAP(T &a, T &b){T tp = a; a = b; b = tp;}
template<typename T> inline T GCD(T a, T b){return b > 0? GCD(b, a % b) : a;}
template<typename T> inline void ADD_TO_VEC_int(T &n, vector<T> &vec){vec.clear(); cin >> n; for(int i = 0; i < n; i ++){T x; cin >> x, vec.PB(x);}}
template<typename T> inline pair<T, T> MaxInVector_ll(vector<T> vec){T MaxVal = -LNF, MaxId = 0;for(int i = 0; i < (int)vec.size(); i ++) if(MaxVal < vec[i]) MaxVal = vec[i], MaxId = i; return {MaxVal, MaxId};}
template<typename T> inline pair<T, T> MinInVector_ll(vector<T> vec){T MinVal = LNF, MinId = 0;for(int i = 0; i < (int)vec.size(); i ++) if(MinVal > vec[i]) MinVal = vec[i], MinId = i; return {MinVal, MinId};}
template<typename T> inline pair<T, T> MaxInVector_int(vector<T> vec){T MaxVal = -INF, MaxId = 0;for(int i = 0; i < (int)vec.size(); i ++) if(MaxVal < vec[i]) MaxVal = vec[i], MaxId = i; return {MaxVal, MaxId};}
template<typename T> inline pair<T, T> MinInVector_int(vector<T> vec){T MinVal = INF, MinId = 0;for(int i = 0; i < (int)vec.size(); i ++) if(MinVal > vec[i]) MinVal = vec[i], MinId = i; return {MinVal, MinId};}
template<typename T> inline pair<map<T, T>, vector<T> > DIV(T n){T nn = n;map<T, T> cnt;vector<T> div;for(ll i = 2; i * i <= nn; i ++){while(n % i == 0){if(!cnt[i]) div.push_back(i);cnt[i] ++;n /= i;}}if(n != 1){if(!cnt[n]) div.push_back(n);cnt[n] ++;n /= n;}return {cnt, div};}
template<typename T> vector<T>& operator-- (vector<T> &v){for (auto& i : v) --i; return v;}
template<typename T> vector<T>& operator++ (vector<T> &v){for (auto& i : v) ++i; return v;}
template<typename T> istream& operator>>(istream& is, vector<T> &v){for (auto& i : v) is >> i; return is;}
template<typename T> ostream& operator<<(ostream& os, vector<T> v){for (auto& i : v) os << i << ' '; return os;}
inline int inputInt(){int X=0; bool flag=1; char ch=getchar();while(ch<'0'||ch>'9') {if(ch=='-') flag=0; ch=getchar();}while(ch>='0'&&ch<='9') {X=(X<<1)+(X<<3)+ch-'0'; ch=getchar();}if(flag) return X;return ~(X-1);}
inline void outInt(int X){if(X<0) {putchar('-'); X=~(X-1);}int s[20],top=0;while(X) {s[++top]=X%10; X/=10;}if(!top) s[++top]=0;while(top) putchar(s[top--]+'0');}
inline ll inputLL(){ll X=0; bool flag=1; char ch=getchar();while(ch<'0'||ch>'9') {if(ch=='-') flag=0; ch=getchar();}while(ch>='0'&&ch<='9') {X=(X<<1)+(X<<3)+ch-'0'; ch=getchar();}if(flag) return X;return ~(X-1); }
inline void outLL(ll X){if(X<0) {putchar('-'); X=~(X-1);}ll s[20],top=0;while(X) {s[++top]=X%10; X/=10;}if(!top) s[++top]=0;while(top) putchar(s[top--]+'0');}
inline void solve(){
int n = inputInt();
string s; cin >> s;
string res1, res2;
for(int i = 0; i < s.size(); i ++){
if(s[i] == '0') res1 += "0", res2 += "0"; // 均分
else if(s[i] == '2') res1 += "1", res2 += "1"; // 均分
else{
res1 += (s[i] - '0') / 2 + '0'; //少担一点
res2 += (s[i] - '0') / 2 + '1';
i ++;
while(i < s.size()){
res1 += s[i]; //因为res1少分担了,后面的都给res1
res2 += "0";
i ++;
}
cout << res1 << endl << res2 << endl; return;
}
}cout << res1 << endl << res2 << endl;
}
CHIVAS_{
int cass;
EACH_CASE(cass){
solve();
}
_REGAL;
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
99
100
101
102
103
104
105
106
107
108
109
110
111
112
113
# AcWing3770_最小的值
# 🔗
https://www.acwing.com/problem/content/3770/
# 💡
首先分析 -1 的情况,即 p 无法对 a 产生特殊贡献, 即: a[i] 就算等于1, b[i] 也等于1
同时我们得到一个信息,p 在 a[i] = 1 的时候 b[i] = 0 能产生特殊贡献
同理b[i] = 1, a[i] = 0的时候 p 也能对 b 产生特殊贡献
那么我们要 p 对 a 的贡献最小,使得 MAX(p[i]) 最小
在别的位置上p[i] = 1即可
多出来的 b 的贡献让几个满足条件的 i 位置平分
# ✅
/*
________ _ ________ _
/ ______| | | | __ | | |
/ / | | | |__| | | |
| | | |___ _ _ _ ___ _ _____ | ___| ______ _____ ___ _ | |
| | | __ \ |_| | | | | | _\| | | ____| | |\ \ | __ | | _ | | _\| | | |
| | | | \ | _ | | | | | | \ | | \___ | | \ \ | |_/ _| | |_| | | | \ | | |
\ \______ | | | | | | \ |_| / | |_/ | ___/ | | | \ \ | /_ \__ | | |_/ | | |
Author : \________| |_| |_| |_| \___/ |___/|_| |_____| _________|__| \__\ |______| | | |___/|_| |_|
____| |
\_____/
*/
#include <unordered_map>
#include <algorithm>
#include <iostream>
#include <cstring>
#include <utility>
#include <string>
#include <vector>
#include <cstdio>
#include <stack>
#include <queue>
#include <cmath>
#include <map>
#include <set>
#define G 10.0
#define LNF 1e18
#define EPS 1e-6
#define PI acos(-1.0)
#define INF 0x7FFFFFFF
#define ll long long
#define ull unsigned long long
#define LOWBIT(x) ((x) & (-x))
#define LOWBD(a, x) lower_bound(a.begin(), a.end(), x) - a.begin()
#define UPPBD(a, x) upper_bound(a.begin(), a.end(), x) - a.begin()
#define TEST(a) cout << "---------" << a << "---------" << '\n'
#define CHIVAS_ int main()
#define _REGAL exit(0)
#define SP system("pause")
#define IOS ios::sync_with_stdio(false)
//#define map unordered_map
#define _int(a) int a; cin >> a
#define _ll(a) ll a; cin >> a
#define _char(a) char a; cin >> a
#define _string(a) string a; cin >> a
#define _vectorInt(a, n) vector<int>a(n); cin >> a
#define _vectorLL(a, b) vector<ll>a(n); cin >> a
#define PB(x) push_back(x)
#define ALL(a) a.begin(),a.end()
#define MEM(a, b) memset(a, b, sizeof(a))
#define EACH_CASE(cass) for (cass = inputInt(); cass; cass--)
#define LS l, mid, rt << 1
#define RS mid + 1, r, rt << 1 | 1
#define GETMID (l + r) >> 1
using namespace std;
template<typename T> inline T MAX(T a, T b){return a > b? a : b;}
template<typename T> inline T MIN(T a, T b){return a > b? b : a;}
template<typename T> inline void SWAP(T &a, T &b){T tp = a; a = b; b = tp;}
template<typename T> inline T GCD(T a, T b){return b > 0? GCD(b, a % b) : a;}
template<typename T> inline void ADD_TO_VEC_int(T &n, vector<T> &vec){vec.clear(); cin >> n; for(int i = 0; i < n; i ++){T x; cin >> x, vec.PB(x);}}
template<typename T> inline pair<T, T> MaxInVector_ll(vector<T> vec){T MaxVal = -LNF, MaxId = 0;for(int i = 0; i < (int)vec.size(); i ++) if(MaxVal < vec[i]) MaxVal = vec[i], MaxId = i; return {MaxVal, MaxId};}
template<typename T> inline pair<T, T> MinInVector_ll(vector<T> vec){T MinVal = LNF, MinId = 0;for(int i = 0; i < (int)vec.size(); i ++) if(MinVal > vec[i]) MinVal = vec[i], MinId = i; return {MinVal, MinId};}
template<typename T> inline pair<T, T> MaxInVector_int(vector<T> vec){T MaxVal = -INF, MaxId = 0;for(int i = 0; i < (int)vec.size(); i ++) if(MaxVal < vec[i]) MaxVal = vec[i], MaxId = i; return {MaxVal, MaxId};}
template<typename T> inline pair<T, T> MinInVector_int(vector<T> vec){T MinVal = INF, MinId = 0;for(int i = 0; i < (int)vec.size(); i ++) if(MinVal > vec[i]) MinVal = vec[i], MinId = i; return {MinVal, MinId};}
template<typename T> inline pair<map<T, T>, vector<T> > DIV(T n){T nn = n;map<T, T> cnt;vector<T> div;for(ll i = 2; i * i <= nn; i ++){while(n % i == 0){if(!cnt[i]) div.push_back(i);cnt[i] ++;n /= i;}}if(n != 1){if(!cnt[n]) div.push_back(n);cnt[n] ++;n /= n;}return {cnt, div};}
template<typename T> vector<T>& operator-- (vector<T> &v){for (auto& i : v) --i; return v;}
template<typename T> vector<T>& operator++ (vector<T> &v){for (auto& i : v) ++i; return v;}
template<typename T> istream& operator>>(istream& is, vector<T> &v){for (auto& i : v) is >> i; return is;}
template<typename T> ostream& operator<<(ostream& os, vector<T> v){for (auto& i : v) os << i << ' '; return os;}
inline int inputInt(){int X=0; bool flag=1; char ch=getchar();while(ch<'0'||ch>'9') {if(ch=='-') flag=0; ch=getchar();}while(ch>='0'&&ch<='9') {X=(X<<1)+(X<<3)+ch-'0'; ch=getchar();}if(flag) return X;return ~(X-1);}
inline void outInt(int X){if(X<0) {putchar('-'); X=~(X-1);}int s[20],top=0;while(X) {s[++top]=X%10; X/=10;}if(!top) s[++top]=0;while(top) putchar(s[top--]+'0');}
inline ll inputLL(){ll X=0; bool flag=1; char ch=getchar();while(ch<'0'||ch>'9') {if(ch=='-') flag=0; ch=getchar();}while(ch>='0'&&ch<='9') {X=(X<<1)+(X<<3)+ch-'0'; ch=getchar();}if(flag) return X;return ~(X-1); }
inline void outLL(ll X){if(X<0) {putchar('-'); X=~(X-1);}ll s[20],top=0;while(X) {s[++top]=X%10; X/=10;}if(!top) s[++top]=0;while(top) putchar(s[top--]+'0');}
const int N = 110;
int n, a[N], b[N];
inline bool check(int &cnta, int &cntb){
bool flag = false;
for(int i = 0; i < n; i ++){
if(a[i] == 1 && b[i] == 0) flag = true, cnta ++;
else if(a[i] == 0 && b[i] == 1) cntb ++;
}return flag;
}
CHIVAS_{
n = inputInt();
for(int i = 0; i < n; i ++) a[i] = inputInt();
for(int i = 0; i < n; i ++) b[i] = inputInt();
int cnta = 0, cntb = 0;
if(!check(cnta, cntb)) outInt(-1);
else{
cntb ++; // cnta 需要比 cntb 多1,这里放在这里加1了
outInt(cntb / cnta + (cntb % cnta != 0));
}
_REGAL;
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
99
100
101
102
103
104
105
106
107
108
109
110
# CCPC2021网络赛_JumpingMonkey
# 🔗
# 💡
由于每一个很大的点都可以挡住一定范围的点对互相连通
所以每一个点所能到达的范围,其实是一个被拆开之后的连通块
那么拆的方式也就是从最大的点向最小的点递进
每一次可以拆掉每个连通块内最大的点,同一次被拆掉的点都是同级的
如:第一次是整棵树最大的点x,第二次是拆掉x后剩下的连通块的最大的点...
他们的级数就是他们能跳到的点数
这样去拆很难把时间复杂度降低下来
我们可以试着反向模拟
从最小的点开始枚举
每一次它将连接"与它相连且已经枚举过了的连通块",并将它作为这个连通块的根节点(也就是连接它和这个连通块的根节点)
这样构建出的一棵树,其中每个点的深度就是他们能跳到的点树
在构造树的过程中我们可以使用并查集
可以发现在最后一次遍历新树之前,所有连通块除了根节点之外毫无作用
我们就可以用并查集记录这个连通块的根节点,然后每次连接枚举的点x和与x相连的且已经枚举过的儿子节点to的根节点nod[to]
最后跑一次记录一下深度即可
# ✅
const int N = 2e5 + 10;
struct Edge {
int nxt, to;
} edge[2][N];
int head[2][N], cnt[2]; // edge[0][]老树, edge[1][]新树
inline void add_Edge ( int op, int from, int to ) { // 连边
edge[op][++ cnt[op]] = { head[op][from], to };
head[op][from] = cnt[op];
}
namespace union_Find { // 并查集
int nod[N];
inline void Init ( int n ) { for ( int i = 1; i <= n; i ++ ) nod[i] = i; }
inline int Find ( int x ) { return x == nod[x] ? x : nod[x] = Find(nod[x]); }
inline void Merge ( int x, int y ) { int fx = Find(x), fy = Find(y); nod[fx] = fy; }
}
#define pii pair<int, int>
#define x first
#define y second
pii a[N]; // x: val, y: id, 输入的a
int n, depth[N]; // 输入的n,深度
inline void dfs ( int x, int fath ) { // 求深度的dfs
depth[x] = depth[fath] + 1;
for ( int i = head[1][x]; ~i; i = edge[1][i].nxt ) {
int to = edge[1][i].to;
if ( to == fath ) continue;
dfs ( to, x );
}
}
inline void Solve () {
memset ( head[0], -1, sizeof head[0] );
memset ( head[1], -1, sizeof head[1] );
cnt[0] = cnt[1] = 0;
scanf("%d", &n);
for ( int i = 0, x, y; i < n - 1; i ++ )
scanf("%d%d", &x, &y),
add_Edge ( 0, x, y ),
add_Edge ( 0, y, x );
for ( int i = 1; i <= n; i ++ )
scanf("%d", &a[i].x),
a[i].y = i;
sort ( a + 1, a + n + 1, [&](pair<int, int> a, pair<int, int> b){ // 按val升序排序
return a.first < b.first;
});
union_Find::Init( n );
map<int, bool> vis;
for ( int i = 1; i <= n; i ++ ) { // 枚举
vis[a[i].y] = true; // 枚举过了
for ( int j = head[0][a[i].y]; ~j; j = edge[0][j].nxt ) { // 跑一遍这个编号的儿子
if ( !vis[edge[0][j].to] ) continue; // 如果还没有枚举过,就不连接
int fj = union_Find::Find(edge[0][j].to); // 它儿子所在连通块的根节点
if ( union_Find::nod[fj] != a[i].y ) // 如果它儿子没有和它连接过
add_Edge ( 1, a[i].y, fj ),
add_Edge ( 1, fj, a[i].y ),
union_Find::nod[fj] = a[i].y; // 同时儿子的连通快根节点认父为连通块根节点
}
}
depth[a[n].y] = 0; dfs ( a[n].y, a[n].y ); // 建立深度
for ( int i = 1; i <= n; i ++ ) printf("%d\n", depth[i]);
}
int main () {
int cass; scanf("%d", &cass); while ( cass -- ) {
Solve();
}
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
# CodeForces353_TwoHeaps
# 🔗
# 💡
就是将 个数分成两组,让第一个集合大小乘上第二个集合大小尽可能大
注意到如果有 个 ,此时我们可能会让两个集合的大小变小,此时就要让 均匀分配
这是一个小学性质,对于周长相同的矩形,正方形的面积最大
而如果有很多个奇数个数的数,我们让它们这样分配最合理:
也就是让奇数个数多出来的一个的交叉分配,由于一共有 个数,所以奇数个数的数是有偶数个的,那么就先让他们互相交叉分配,然后再给偶数均匀分配
# ✅
vector<pair<int, vector<int> > > v(110);
vector<int> id(210);
vector<int> a(210);
int main () {
ios::sync_with_stdio(false);
cin.tie(nullptr);
int n; cin >> n;
for (int i = 0; i < 2 * n; i ++) {
int x; cin >> x;
a[i] = x;
v[x].first = x;
v[x].second.push_back(i);
}
sort(v.begin(), v.end(), [&](pair<int, vector<int> > a, pair<int, vector<int> > b) {
int asz = a.second.size();
int bsz = b.second.size();
if (asz % 2 != bsz % 2) return (asz % 2) > (bsz % 2);
return asz > bsz;
}); // 奇数个数的排在前面
int anum = 0, bnum = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < v.size(); i ++) {
if (!v[i].second.size()) continue;
int all = v[i].second.size() / 2;
anum += all;
bnum += all;
for (int j = 0; j < v[i].second.size() / 2; j ++) id[v[i].second[j]] = 1;
for (int j = 0; j < v[i].second.size() / 2; j ++) id[v[i].second[j + v[i].second.size() / 2]] = 2;
if (all * 2 != v[i].second.size()) {
// 看多出来的一个分给谁
if (anum <= bnum) {
id[v[i].second.back()] = 1;
anum ++;
} else {
id[v[i].second.back()] = 2;
bnum ++;
}
}
}
set<int> sta, stb; // 两个集合大小相乘计算结果
for (int i = 0; i < n * 2; i ++) {
if (id[i] == 1) sta.insert(a[i]);
else stb.insert(a[i]);
}
cout << sta.size() * stb.size() << endl;
for (int i = 0; i < n * 2; i ++) cout << id[i] << " ";
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
# CodeForces508C_AnyaAndGhosts
# 🔗
# 💡
整个条的数据量不算大,我们可以使用数组当时间轴表示在i时刻是否点了蜡烛
我们在每个鬼出现的时间前t个节点看看存在几根没灭的蜡烛
如果少了话就贪心地在后面尽可能补蜡烛
这样维护每一只鬼出现的时刻都有r根蜡烛
最后统计一下我们点了几根蜡烛即可
# ✅
#include <iostream>
#include <cmath>
#include <map>
#include <deque>
#include <algorithm>
#include <cstring>
#define ll long long
using namespace std;
const int N = 310;
int a[N], n, t, r;
map<int, int> vis;
int main () {
#ifndef ONLINE_JUDGE
freopen("in.in", "r", stdin);
freopen("out.out", "w", stdout);
#endif
cin >> n >> t >> r;
if ( t < r ) { // t时间内点不了r根蜡烛
cout << "-1" << endl;
return 0;
}
int res = 0;
for ( int i = 0; i < n; i ++ ) {
cin >> a[i];
int ned = r;
for ( int j = a[i] - t; j <= a[i] - 1 && ned > 0; j ++ ) ned -= vis[j] == 1;
for ( int j = a[i] - 1; ned; j -- ) { // 补蜡烛
ned -= vis[j] == 0;
vis[j] = 1;
}
}
for ( auto i : vis ) res += (i.second == 1);
cout << res << endl;
return 0;
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
# CodeForces509C_SumsOfDigits
# 🔗
# 💡
如果新开一个字符串重新构造,那么要考虑的太多
既然题目要求我们每一个数都是递增的,那么我们可以直接在上一步求得的数上进行更改
1.如果给的数相等,就从最低位向前进一位即可
2.如果给的a[i]比上一步大,那么就从最低位看看有没有哪一位没到9,往上加就行
3.如果当前给的a[i]比上一步的小,那么就模仿加运算,从最低位向前进位,直到a[i]>a[i-1],然后在进行第二步
# ✅
#ifndef ONLINE_JUDGE
freopen("in.in", "r", stdin);
freopen("out.out", "w", stdout);
#endif
cin >> n;
for ( int i = 1; i <= n; i ++ ) cin >> a[i];
for ( int i = 1; i <= 1000; i ++ ) res[0] += "0";
for ( int i = 1; i <= n; i ++ ) {
int d = a[i] - a[i - 1];
int j = res[i - 1].size() - 1;
res[i] = res[i - 1];
if ( d == 0 ) { // 相等
int jj = j;
d += res[i][jj] - '0' - 1;
res[i][jj] = '0';
res[i][jj - 1] ++;
jj --;
while ( res[i][jj] == '0' + 10 )
d += res[i][jj] - '0' - 1,
res[i][jj] = '0',
res[i][jj - 1] ++,
jj --;
}
bool flag = false;
while ( d > 0 ) { // 如果大了就操作一次就不管了
flag = true;
if ( d > '9' - res[i][j] )
d -= '9' - res[i][j],
res[i][j] = '9';
else
res[i][j] += d,
d = 0;
j --;
}
if ( flag ) continue;
while ( d < 0 ) { // 如果小于上一步
if ( res[i][j] != '0' ) {
d += res[i][j] - '0' - 1,
res[i][j] = '0',
res[i][j - 1] ++;
}
j --;
while ( res[i][j] == '0' + 10 )
d += res[i][j] - '0' - 1,
res[i][j] = '0',
res[i][j - 1] ++,
j --;
}
j = res[i].size() - 1;
while ( d > 0 ) {
if ( d > '9' - res[i][j] )
d -= '9' - res[i][j],
res[i][j] = '9';
else
res[i][j] += d,
d = 0;
j --;
}
}
for ( int i = 1; i <= n; i ++ ) {
int j = 0;
while ( res[i][j] == '0' ) j ++;
for ( ; j < res[i].size(); j ++ ) cout << res[i][j];
cout << endl;
}
return 0;
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
# CodeForces534D_Handshakes
# 🔗
# 💡
首先分析一下题意:室内人数不断增加,也就是有一个计数变量cur,每次若cur大于3,可以选择减任意个3,从给定数组中挑出一个cur并输出下标,然后cur+1,执行n次
那么我们可以存一下每个值对应的下标集合
计数变量cur从1往上走,先不减,把大的数用了
如果这一步没有能放的数的话就不断-3直到有为止
如果到负数还没有的话就输出不可能
# ✅
#include <iostream>
#include <cmath>
#include <map>
#include <deque>
#include <algorithm>
#include <cstring>
#include <vector>
#define ll long long
using namespace std;
int main () {
#ifndef ONLINE_JUDGE
freopen("in.in", "r", stdin);
freopen("out.out", "w", stdout);
#endif
int n; cin >> n;
vector<int> vec[n + 10];
int a[n + 10];
for ( int i = 1; i <= n; i ++ ) {
cin >> a[i];
vec[a[i]].push_back(i);
}
int cur = 0; // 时间戳
int res[n + 10];
for ( int i = 1; i <= n; i ++ ) {
while ( !vec[cur].size() ) { // 如果没有,不断减3
cur -= 3;
if ( cur < 0 ) {
cout << "Impossible" << endl;
return 0;
}
}
res[i] = vec[cur].back();
vec[cur].pop_back();
cur ++;
}
cout << "Possible" << endl;
for ( int i = 1; i <= n; i ++ ) {
cout << res[i] << " ";
}
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
# CodeForces538C_Tourist'sNots
# 🔗
# 💡
两两之间有一个山峰形的折线图
直接算有些麻烦,可以将两个点挪到同一高度(低的补上来,时间也要补)
如果补到同一高度发现时间交错了,就不行
然后在同一高度下利用两者中间的时间来计算他俩之间的峰顶高度
要注意时间为1的位置和n的位置都是由两端的值向左和向右增出来的,也要维护一下
# ✅
#include <iostream>
#include <cmath>
#include <map>
#include <deque>
#include <algorithm>
#include <cstring>
#define ll long long
using namespace std;
int main () {
#ifndef ONLINE_JUDGE
freopen("in.in", "r", stdin);
freopen("out.out", "w", stdout);
#endif
int n, m; cin >> n >> m;
pair<int, int> pr[m + 10];
for ( int i = 1; i <= m; i ++ ) cin >> pr[i].first >> pr[i].second;
pr[0].first = 1, pr[0].second = pr[1].second + pr[1].first - 1; // 时间为1的位置
pr[m + 1].first = n, pr[m + 1].second = pr[m].second + n - pr[m].first; // 时间为n的位置
int res = 0;
for ( int i = 1; i <= m + 1; i ++ ) {
if ( abs(pr[i].first - pr[i - 1].first) < abs(pr[i].second - pr[i - 1].second) ) {
puts("IMPOSSIBLE");
return 0;
}
int t1 = pr[i - 1].first, h1 = pr[i - 1].second;
int t2 = pr[i].first, h2 = pr[i].second;
// 两者要齐平一下,然后矮的那个时间也更改一下
if ( h1 < h2 ) {
t1 += h2 - h1;
h1 = h2;
} else if ( h2 < h1 ) {
t2 -= h1 - h2;
h2 = h1;
}
int dt = t2 - t1 - 1; // 时间差
dt = max (dt, 0);
res = max ( res, dt / 2 + (dt & 1) + h1 ); // 计算峰值
}
cout << res << endl;
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
# CodeForces610C_HarmonyAnalysis
# 🔗
# 💡
化简一下,给个n,构造边长为2^n的方阵,其中行两两之间有一半的数不同
那么对于n-1的时候,我们每一行也有一半的不同,可以利用上一步的每一行横向复制一下("10"->"1010")
那么还少一半,我们设当前对第i行复制,那么发现"第i行"加上"它自己的反"可以和自己复制产生一半的不同(因为后一半都不相同)
我们将这两种复制方式设为构造1和构造2
接下来检验正确性
其中第i行的构造1和构造2形成的行明显成立
对于第i+1行的构造2和第i行的构造1来看,第i行和第i-1行的不同数量设为x,长度设为sz
第i行的反和第i-1行的不同数量为sz-x
因为x是sz的一半(前面一个矩阵一定成立),那么sz-x=x
因为第i行的构造1和第i-1行的构造1由于复制的缘故使得相似度乘2依旧满足
则第i行的构造1和第i-1行的构造2依旧满足
则得到一种递推方式:
对于当前边长为 2^i 的方阵设为 a,b c,d
我们下一步可以推出 a,b,a,b a,b,-a,-b c,d,-c,-d c,d,-c,-d
这样对每一行进行一次构造1和构造2推出下一次的方阵
从2^0开始递推构造
# ✅
#include <iostream>
#include <algorithm>
#include <map>
#include <cmath>
#include <vector>
#include <list>
using namespace std;
#define ll long long
const int N = 1000;
string s1[N], s2[N]; // 轮流构造,滚动数组
int main () {
#ifndef ONLINE_JUDGE
freopen("in.in", "r", stdin);
freopen("out.out", "w", stdout);
#endif
int n; cin >> n;
s1[0] = "1";
if ( n == 0 ) {
cout << "+" << endl;
return 0;
}
for ( int k = 1; k <= n; k ++ ) {
if ( k & 1 ) {
int cnt = 0;
for ( int i = 0; i < (1 << (k - 1)); i ++ ) {
string cur1 = s1[i] + s1[i];
string cur2 = s1[i];
for ( int j = 0; j < s1[i].size(); j ++ ) cur2 += (!(s1[i][j] - '0')) + '0';
s2[cnt++] = cur1, s2[cnt++] = cur2;
}
} else {
int cnt = 0;
for ( int i = 0; i < (1 << (k - 1)); i ++ ) {
string cur1 = s2[i] + s2[i];
string cur2 = s2[i];
for ( int j = 0; j < s2[i].size(); j ++ ) cur2 += (!(s2[i][j] - '0')) + '0';
s1[cnt++] = cur1, s1[cnt++] = cur2;
}
}
}
if ( n & 1 ) {
for ( int i = 0; i < (1 << n); i ++ ) {
for ( int j = 0; j < s2[i].size(); j ++ ) {
if ( s2[i][j] == '0' ) cout << '*';
else cout << '+';
}cout << endl;
}
} else {
for ( int i = 0; i < (1 << n); i ++ ) {
for ( int j = 0; j < s1[i].size(); j ++ ) {
if ( s1[i][j] == '0' ) cout << '*';
else cout << '+';
}cout << endl;
}
}
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
# CodeForces978D_AlmostArithmeticProgression
# 🔗
# 💡
处理每一个数的修改量是件很麻烦的事情
每个数的最大修改量是1
且考虑等差数列的性质:a[x] = a[1] + (x - 1) * d
所以枚举第一项和第二项就行了,后面的也就自然都确定下来了
我们在这个确定的数组中跑一遍,如果没有修改不了的那么就维护一下修改量的总和最小值
# ✅
const ll N = 1e5 + 10;
ll a[N];
int main () {
#ifndef ONLINE_JUDGE
freopen("in.in", "r", stdin);
freopen("out.out", "w", stdout);
#endif
ll n; cin >> n;
for ( ll i = 1; i <= n; i ++ ) cin >> a[i];
if ( n == 1 || n == 2 ) {
cout << "0" << endl;
return 0;
}
ll res = 1e18;
for ( ll x = a[1] - 1; x <= a[1] + 1; x ++ ) {
for ( ll y = a[2] - 1; y <= a[2] + 1; y ++ ) {
bool flag = true;
ll dir = y - x;
ll cur = llabs(a[1] - x) + llabs(a[2] - y);
for ( ll i = 3, id = y + dir; i <= n; i ++, id += dir ) {
if ( llabs(a[i] - id) > 1 ) flag = false;
cur += llabs(a[i] - id);
}
if ( flag ) res = min ( res, cur );
}
}
if ( res == 1e18 ) cout << "-1" << endl;
else cout << res << endl;
return 0;
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
# CodeForces1202D_Printa1337-string...
# 🔗
# 💡
的贡献只是一个乘,如果是质数会很难受,所以不考虑这个
对于后面的
我们先不看 ,设以 分割的 有 段,每段分别有 个
则个数为 个
现在就是考虑形如 这样的数是否可以合理拆掉这个 ,它们是一类平方数,值的递增关系很大 , 时 ,是可以的
所以我们每次找 下面最大的 满足
这样拆出来的还不优,因为可能出现很多个相同的 ,这里可以利用上面的 了,这个 的个数也是为前面的 提供一个乘法,我们就每次找到 后,用 作为后面跟着的 的个数即可
我们得到的 组是从大到小的,翻转一下,这样每段 的个数就是当前的 减去上一个 , 的个数就是我们之前标记的倍数
# ✅
inline void Solve () {
ll n; cin >> n;
vector<pair<int, int> > vec; // val, tim
while (n) { // 拆分
int i = 1;
for (;;i ++) {
if (i * (i - 1) / 2 > n) break;
} i --;
vec.push_back({i, n / (i * (i - 1) / 2)});
n -= vec.back().second * i * (i - 1) / 2;
}
vec.push_back({0, 0});
reverse(vec.begin(), vec.end());
cout << 1;
for (int i = 1; i < vec.size(); i ++) {
cout << string(vec[i].first - vec[i - 1].first, '3');
cout << string(vec[i].second, '7');
} cout << endl;
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
# CodeForces1307B_CowAndFriend
# 🔗
https://codeforces.com/problemset/problem/1307/B
# 💡
我们都想让走的步数最少所以用最大距离,首先有两种情况:
- x 小于最大距离,那我们如果可以找到一个存在的与 x 相等的距离,那么就1,否则就2
- x 大于等于最大距离,那我们可以通过折步来使 d 次移动的贪心距离控制在 ((d - 1) * max, d * max],所以利用 x / max 向上取整(也就是 (x + max + 1) / max) 计算此时的步数
# ✅
/*
________ _ ________ _
/ ______| | | | __ | | |
/ / | | | |__| | | |
| | | |___ _ _ _ ___ _ _____ | ___| ______ _____ ___ _ | |
| | | __ \ |_| | | | | | _\| | | ____| | |\ \ | __ | | _ | | _\| | | |
| | | | \ | _ | | | | | | \ | | \___ | | \ \ | |_/ _| | |_| | | | \ | | |
\ \______ | | | | | | \ |_| / | |_/ | ___/ | | | \ \ | /_ \__ | | |_/ | | |
Author : \________| |_| |_| |_| \___/ |___/|_| |_____| _________|__| \__\ |______| | | |___/|_| |_|
____| |
\_____/
*/
//#include <unordered_map>
#include <algorithm>
#include <iostream>
#include <cstring>
#include <utility>
#include <string>
#include <vector>
#include <cstdio>
#include <stack>
#include <queue>
#include <cmath>
#include <map>
#include <set>
#define G 10.0
#define LNF 1e18
#define EPS 1e-6
#define PI acos(-1.0)
#define INF 0x7FFFFFFF
#define ll long long
#define ull unsigned long long
#define LOWBIT(x) ((x) & (-x))
#define LOWBD(a, x) lower_bound(a.begin(), a.end(), x) - a.begin()
#define UPPBD(a, x) upper_bound(a.begin(), a.end(), x) - a.begin()
#define TEST(a) cout << "---------" << a << "---------" << endl
#define CHIVAS_ int main()
#define _REGAL exit(0)
#define SP system("pause")
#define IOS ios::sync_with_stdio(false)
//#define map unordered_map
#define PB(x) push_back(x)
#define ALL(a) a.begin(),a.end()
#define MEM(a, b) memset(a, b, sizeof(a))
#define EACH_CASE(cass) for (cass = inputInt(); cass; cass--)
#define LS l, mid, rt << 1
#define RS mid + 1, r, rt << 1 | 1
#define GETMID (l + r) >> 1
using namespace std;
template<typename T> inline T MAX(T a, T b){return a > b? a : b;}
template<typename T> inline T MIN(T a, T b){return a > b? b : a;}
template<typename T> inline void SWAP(T &a, T &b){T tp = a; a = b; b = tp;}
template<typename T> inline T GCD(T a, T b){return b > 0? GCD(b, a % b) : a;}
template<typename T> inline void ADD_TO_VEC_int(T &n, vector<T> &vec){vec.clear(); cin >> n; for(int i = 0; i < n; i ++){T x; cin >> x, vec.PB(x);}}
template<typename T> inline pair<T, T> MaxInVector_ll(vector<T> vec){T MaxVal = -LNF, MaxId = 0;for(int i = 0; i < (int)vec.size(); i ++) if(MaxVal <vec[i]) MaxVal = vec[i], MaxId = i; return {MaxVal, MaxId};}
template<typename T> inline pair<T, T> MinInVector_ll(vector<T> vec){T MinVal = LNF, MinId = 0;for(int i = 0; i < (int)vec.size(); i ++) if(MinVal > vec[i])MinVal = vec[i], MinId = i; return {MinVal, MinId};}
template<typename T> inline pair<T, T> MaxInVector_int(vector<T> vec){T MaxVal = -INF, MaxId = 0;for(int i = 0; i < (int)vec.size(); i ++) if(MaxVal <vec[i]) MaxVal = vec[i], MaxId = i; return {MaxVal, MaxId};}
template<typename T> inline pair<T, T> MinInVector_int(vector<T> vec){T MinVal = INF, MinId = 0;for(int i = 0; i < (int)vec.size(); i ++) if(MinVal > vec[i])MinVal = vec[i], MinId = i; return {MinVal, MinId};}
template<typename T> inline pair<map<T, T>, vector<T> > DIV(T n){T nn = n;map<T, T> cnt;vector<T> div;for(ll i = 2; i * i <= nn; i ++){while(n % i == 0){if(!cnt[i]) div.push_back(i);cnt[i] ++;n /= i;}}if(n != 1){if(!cnt[n]) div.push_back(n);cnt[n] ++;n /= n;}return {cnt, div};}
template<typename T> vector<T>& operator-- (vector<T> &v){for (auto& i : v) --i; return v;}
template<typename T> vector<T>& operator++ (vector<T> &v){for (auto& i : v) ++i; return v;}
template<typename T> istream& operator>>(istream& is, vector<T> &v){for (auto& i : v) is >> i; return is;}
template<typename T> ostream& operator<<(ostream& os, vector<T> v){for (auto& i : v) os << i << ' '; return os;}
inline int inputInt(){int X=0; bool flag=1; char ch=getchar();while(ch<'0'||ch>'9') {if(ch=='-') flag=0; ch=getchar();}while(ch>='0'&&ch<='9') {X=(X<<1)+(X<<3)+ch-'0'; ch=getchar();}if(flag) return X;return ~(X-1);}
inline void outInt(int X){if(X<0) {putchar('-'); X=~(X-1);}int s[20],top=0;while(X) {s[++top]=X%10; X/=10;}if(!top) s[++top]=0;while(top) putchar(s[top--]+'0');}
inline ll inputLL(){ll X=0; bool flag=1; char ch=getchar();while(ch<'0'||ch>'9') {if(ch=='-') flag=0; ch=getchar();}while(ch>='0'&&ch<='9') {X=(X<<1)+(X<<3)+ch-'0'; ch=getchar();}if(flag) return X;return ~(X-1); }
inline void outLL(ll X){if(X<0) {putchar('-'); X=~(X-1);}ll s[20],top=0;while(X) {s[++top]=X%10; X/=10;}if(!top) s[++top]=0;while(top) putchar(s[top--]+'0');}
const int N = 1e5 + 10;
int a[N];
map<int, int> mp;
inline void solve ( ) {
int n = inputInt(), x = inputInt(); mp.clear();
for ( int i = 1; i <= n; i ++ ) a[i] = inputInt(), mp[a[i]] = 1 ;
sort ( a + 1, a + 1 + n, greater<int>() );
if ( x < a[1] ) outInt(1 + (!mp[x]));
else outInt((x + a[1] - 1) / a[1]);
puts("");
}
CHIVAS_{
int cass;
EACH_CASE ( cass ) {
solve();
}
_REGAL;
};
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
99
100
101
102
103
104
105
106
# CodeForces1352F_BinaryStringReconstruction
# 🔗
https://codeforces.com/problemset/problem/1352/F
# 💡
模拟的套路就是:如何模拟能减少判断,减少错误可能性
在这里,我们可以发现:如果 a1 = 0 的话,那么 a0 和 a2 不会同时出现
我们想方便简洁,可以把 11.01.00 分一下区 然后发现 01 放在最后构造会更安全
所以我们可以先写一下主体:
构造 a2+1 个 1,构造 a0+1 个 0,构造 a1 个 (!vector.back)
然后就需要加入特判,
1.如果 a0 = a2 = 0 ,那么我们单独构造 a1 的时候应该提前插入一个数(01都行)
2.如果 a0 = a2 != 0,那么我们前面在交界处肯定会消掉一个 a1 ,所以 a1--
# ✅
/*
________ _ ________ _
/ ______| | | | __ | | |
/ / | | | |__| | | |
| | | |___ _ _ _ ___ _ _____ | ___| ______ _____ ___ _ | |
| | | __ \ |_| | | | | | _\| | | ____| | |\ \ | __ | | _ | | _\| | | |
| | | | \ | _ | | | | | | \ | | \___ | | \ \ | |_/ _| | |_| | | | \ | | |
\ \______ | | | | | | \ |_| / | |_/ | ___/ | | | \ \ | /_ \__ | | |_/ | | |
Author : \________| |_| |_| |_| \___/ |___/|_| |_____| _________|__| \__\ |______| | | |___/|_| |_|
____| |
\_____/
*/
//#include <unordered_map>
#include <algorithm>
#include <iostream>
#include <cstring>
#include <utility>
#include <string>
#include <vector>
#include <cstdio>
#include <stack>
#include <queue>
#include <cmath>
#include <map>
#include <set>
#define G 10.0
#define LNF 1e18
#define EPS 1e-6
#define PI acos(-1.0)
#define INF 0x7FFFFFFF
#define ll long long
#define ull unsigned long long
#define LOWBIT(x) ((x) & (-x))
#define LOWBD(a, x) lower_bound(a.begin(), a.end(), x) - a.begin()
#define UPPBD(a, x) upper_bound(a.begin(), a.end(), x) - a.begin()
#define TEST(a) cout << "---------" << a << "---------" << '<br>'
#define CHIVAS_ int main()
#define _REGAL exit(0)
#define SP system("pause")
#define IOS ios::sync_with_stdio(false)
//#define map unordered_map
#define PB(x) push_back(x)
#define ALL(a) a.begin(),a.end()
#define MEM(a, b) memset(a, b, sizeof(a))
#define EACH_CASE(cass) for (cass = inputInt(); cass; cass--)
#define LS l, mid, rt << 1
#define RS mid + 1, r, rt << 1 | 1
#define GETMID (l + r) >> 1
using namespace std;
template<typename T> inline T MAX(T a, T b){return a > b? a : b;}
template<typename T> inline T MIN(T a, T b){return a > b? b : a;}
template<typename T> inline void SWAP(T &a, T &b){T tp = a; a = b; b = tp;}
template<typename T> inline T GCD(T a, T b){return b > 0? GCD(b, a % b) : a;}
template<typename T> inline void ADD_TO_VEC_int(T &n, vector<T> &vec){vec.clear(); cin >> n; for(int i = 0; i < n; i ++){T x; cin >> x, vec.PB(x);}}
template<typename T> inline pair<T, T> MaxInVector_ll(vector<T> vec){T MaxVal = -LNF, MaxId = 0;for(int i = 0; i < (int)vec.size(); i ++) if(MaxVal <vec[i]) MaxVal = vec[i], MaxId = i; return {MaxVal, MaxId};}
template<typename T> inline pair<T, T> MinInVector_ll(vector<T> vec){T MinVal = LNF, MinId = 0;for(int i = 0; i < (int)vec.size(); i ++) if(MinVal > vec[i])MinVal = vec[i], MinId = i; return {MinVal, MinId};}
template<typename T> inline pair<T, T> MaxInVector_int(vector<T> vec){T MaxVal = -INF, MaxId = 0;for(int i = 0; i < (int)vec.size(); i ++) if(MaxVal <vec[i]) MaxVal = vec[i], MaxId = i; return {MaxVal, MaxId};}
template<typename T> inline pair<T, T> MinInVector_int(vector<T> vec){T MinVal = INF, MinId = 0;for(int i = 0; i < (int)vec.size(); i ++) if(MinVal > vec[i])MinVal = vec[i], MinId = i; return {MinVal, MinId};}
template<typename T> inline pair<map<T, T>, vector<T> > DIV(T n){T nn = n;map<T, T> cnt;vector<T> div;for(ll i = 2; i * i <= nn; i ++){while(n % i == 0){if(!cnt[i]) div.push_back(i);cnt[i] ++;n /= i;}}if(n != 1){if(!cnt[n]) div.push_back(n);cnt[n] ++;n /= n;}return {cnt, div};}
template<typename T> vector<T>& operator-- (vector<T> &v){for (auto& i : v) --i; return v;}
template<typename T> vector<T>& operator++ (vector<T> &v){for (auto& i : v) ++i; return v;}
template<typename T> istream& operator>>(istream& is, vector<T> &v){for (auto& i : v) is >> i; return is;}
template<typename T> ostream& operator<<(ostream& os, vector<T> v){for (auto& i : v) os << i << ' '; return os;}
inline int inputInt(){int X=0; bool flag=1; char ch=getchar();while(ch<'0'||ch>'9') {if(ch=='-') flag=0; ch=getchar();}while(ch>='0'&&ch<='9') {X=(X<<1)+(X<<3)+ch-'0'; ch=getchar();}if(flag) return X;return ~(X-1);}
inline void outInt(int X){if(X<0) {putchar('-'); X=~(X-1);}int s[20],top=0;while(X) {s[++top]=X%10; X/=10;}if(!top) s[++top]=0;while(top) putchar(s[top--]+'0');}
inline ll inputLL(){ll X=0; bool flag=1; char ch=getchar();while(ch<'0'||ch>'9') {if(ch=='-') flag=0; ch=getchar();}while(ch>='0'&&ch<='9') {X=(X<<1)+(X<<3)+ch-'0'; ch=getchar();}if(flag) return X;return ~(X-1); }
inline void outLL(ll X){if(X<0) {putchar('-'); X=~(X-1);}ll s[20],top=0;while(X) {s[++top]=X%10; X/=10;}if(!top) s[++top]=0;while(top) putchar(s[top--]+'0');}
inline void solve ( ) {
int a0 = inputInt(), a1 = inputInt(), a2 = inputInt();
vector<int> res;
// 两个特判
if ( !a0 && !a2 ) res.push_back(0);
if ( a0 && a2 ) a1 --;
// 硬模拟
if ( a0 ) for ( int i = 0; i <= a0; i ++ ) res.push_back(0);
if ( a2 ) for ( int i = 0; i <= a2; i ++ ) res.push_back(1);
for ( int i = 0; i < a1; i ++ ) res.push_back(!res.back());
for ( int i = 0; i < res.size(); i ++ ) outInt(res[i]); puts("");
}
CHIVAS_{
int cass;
EACH_CASE ( cass ) {
solve();
}
};
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
99
100
101
102
# CodeForces1365F_SwapsAgain
# 🔗
https://codeforces.com/contest/1365/problem/F
# 💡
我们在交换数的时候,可以联想到魔方的小技巧:如何让别的点不变的情况下,只有一个点会变?
那么这题是交换,我们研究一个例子:
1 2 3 4 (交换a[1], a[4])
4 2 3 1 (交换a[1 ~ 2], a[3 ~ 4])
3 1 4 2 (交换a[1], a[4])
2 1 4 3
于是得到结论:
以数组中间为轴
每一个“对称数对”都能移动到同样对称的任何位置
比如
1 _ _ _ _ 2
可以移动到
_ 1 _ _ 2 _
_ _ 1 2 _ _
也可以交换位置
2 _ _ _ _ 1
_ 2 _ _ 1 _
_ _ 2 1 _ _
所以我们先判断两个数组是否可以相同 对两个数组sort一下,判断sort的结果是否相同,如果不相同就是No 然后是对n为奇数时的a和b的中心位置(因为这个位置无法移动),如果不相同就是No 然后就是在a中存“对称数对”了 接着在b中匹配就行了
# ✅
#include <iostream>
#include <algorithm>
#include <vector>
#include <map>
using namespace std;
const int N = 550;
int a[N], b[N];
int n;
inline bool Check_Similar () { // 检查两个数组是否元素相同
int aa[N]; for ( int i = 0; i < n; i ++ ) aa[i] = a[i]; // 复制a数组
int bb[N]; for ( int i = 0; i < n; i ++ ) bb[i] = b[i]; // 复制b数组
sort ( aa, aa + n ); sort ( bb, bb + n ); // 排序一下
for ( int i = 0; i < n; i ++ ) if ( aa[i] != bb[i] ) return false; // 如果有一位不等就不一样
return true;
}
inline void Solve () {
cin >> n;
for ( int i = 0; i < n; i ++ ) cin >> a[i];
for ( int i = 0; i < n; i ++ ) cin >> b[i];
if ( !Check_Similar() ) {
puts("no");
return;
}
map<pair<int, int>, int> mark;
for ( int i = 0; i < n / 2; i ++ ) mark[{ a[i], a[n - i - 1] }] ++; // 对每一对排序
for ( int i = 0; i < n / 2; i ++ )
if ( !mark[{ b[i], b[n - i - 1] }] && !mark[{ b[n - i - 1], b[i] }] ) { // 如果没有
puts("no");
return;
} else if ( mark[{ b[i], b[n - i - 1] }] ) { // 有了就删去一个
mark[{ b[i], b[n - i - 1] }] --;
} else {
mark[{ b[n - i - 1], b[i] }] --;
}
puts("yes");
}
int main () {
int cass;
for ( cin >> cass; cass; cass -- ) {
Solve ();
}
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
# CodeForces1399E1_WeightsDivision(Easy Version)
# 🔗
# 💡
这个是对边进行操作的,每条边的贡献次数为其子树上的叶子结点数
令 子树上的叶子结点数为 ,如果对 操作一次,那么总体减的值为
且这个操作是不影响别的边的贡献次数与值的,所以每次应该选能减的量最大的
然后将其减过之后,重新放入堆中排序
所以先预处理出来子树中叶子结点的数量,然后建立一个优先队列,里面存的都是下标,排序规则为减得多的在前
每次挑选出来堆顶,减完之后重新放入堆中,并判断是否当前值小于 ,如果小了直接退出
# ✅
const int N = 2e5 + 10;
const int M = 4e5 + 10;
struct Edge {
int nxt, to;
int val;
} edge[M];
int head[N], cnt;
inline void add_Edge (int from, int to, int val) {
edge[++cnt] = {head[from], to, val};
head[from] = cnt;
}
ll son_leaves[N];
ll fa_edge[N];
inline void dfs_Son (int u, int fa) {
bool is_leaf = true;
for (int i = head[u]; i; i = edge[i].nxt) {
int v = edge[i].to;
if (v == fa) {
fa_edge[u] = edge[i].val;
continue;
}
dfs_Son(v, u);
is_leaf = false;
son_leaves[u] += son_leaves[v];
}
son_leaves[u] += is_leaf;
}
struct node {
int id;
inline friend bool operator < (node a, node b) {
return (fa_edge[a.id] + 1) / 2 * son_leaves[a.id] < (fa_edge[b.id] + 1) / 2 * son_leaves[b.id];
}
};
int n; ll m;
inline void Solve () {
scanf("%d%lld", &n, &m);
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i ++) head[i] = son_leaves[i] = 0; cnt = 0;
for (int i = 1; i < n; i ++) {
int u, v, w; scanf("%d%d%d", &u, &v, &w);
add_Edge(u, v, w);
add_Edge(v, u, w);
}
dfs_Son(1, 1);
ll sum = 0, res = 0;
priority_queue<node> pque;
for (int i = 2; i <= n; i ++) {
pque.push({i});
sum += fa_edge[i] * son_leaves[i];
}
while (!pque.empty()) {
if (sum <= m) break;
res ++;
int id = pque.top().id; pque.pop();
sum -= (fa_edge[id] + 1) / 2 * son_leaves[id];
fa_edge[id] /= 2;
pque.push({id});
}
printf("%lld\n", res);
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
# CodeForces1399E2_WeightsDivision(Hard Version)
# 🔗
# 💡
这个和第一个题差不多,但是难的地方在于操作的花费有的是 有的是
这两者混在一起进行排序非常难做,因为有的地方用了 是浪费,而有的地方必须用 才够贪,并且考虑到最后的结果一定是操作了 次 和操作了 次 ,所以尝试将两者分开处理
分开处理可以得到在光操作需要花费 的边的时候,操作 次后这些边的 最少变成 ,由于每条边花费相同,处理方式和简单版一样
两种花费,处理后得到两个数组 ,枚举“操作需要花费 的边”的次数 ,动态减小“操作需要花费 的边”的次数
在满足 的情况下,维护
# ✅
const int N = 2e5 + 10;
const int M = 4e5 + 10;
struct Edge {
int nxt, to;
int val;
} edge[M];
int head[N], cnt;
inline void add_Edge (int from, int to, int val) {
edge[++cnt] = {head[from], to, val};
head[from] = cnt;
}
ll son_leaves[N];
ll fa_edge[N];
inline void dfs_Son (int u, int fa) {
bool is_leaf = true;
for (int i = head[u]; i; i = edge[i].nxt) {
int v = edge[i].to;
if (v == fa) {
fa_edge[u] = edge[i].val;
continue;
}
dfs_Son(v, u);
is_leaf = false;
son_leaves[u] += son_leaves[v];
}
son_leaves[u] += is_leaf;
}
struct node {
int id;
inline friend bool operator < (node a, node b) {
return (fa_edge[a.id] + 1) / 2 * son_leaves[a.id] < (fa_edge[b.id] + 1) / 2 * son_leaves[b.id];
}
};
int n; ll m;
inline void Solve () {
scanf("%d%lld", &n, &m);
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i ++) head[i] = son_leaves[i] = 0; cnt = 0;
for (int i = 1; i < n; i ++) {
int u, v, w; scanf("%d%d%d", &u, &v, &w);
add_Edge(u, v, w);
add_Edge(v, u, w);
}
dfs_Son(1, 1);
ll sum = 0, res = 0;
priority_queue<node> pque;
for (int i = 2; i <= n; i ++) {
pque.push({i});
sum += fa_edge[i] * son_leaves[i];
}
while (!pque.empty()) {
if (sum <= m) break;
res ++;
int id = pque.top().id; pque.pop();
sum -= (fa_edge[id] + 1) / 2 * son_leaves[id];
fa_edge[id] /= 2;
pque.push({id});
}
printf("%lld\n", res);
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
# CodeForces1443B_SavingTheCity
# 🔗
# 💡
一个贪心问题
如果两个连通'1'之间的'0'的个数*b<=a,那么完全可以连通掉然后一起点燃
否则不可以
那么就是一个模拟题了
我们计算两个连通1之间的'0'个数,如果<=a/b的话,就全更新为'1'
最后再点燃操作
# ✅
#include <iostream>
#include <cstring>
#include <algorithm>
#include <cmath>
#include <vector>
#include <map>
#include <unordered_map>
#define ll long long
using namespace std;
inline void Solve () {
int a, b; cin >> a >> b;
string s; cin >> s;
int res = 0;
// 连通
int canSwp = a / b;
int stt = 0; while ( s[stt] == '0' ) stt ++;
for ( int i = stt; i < s.size() - 1; i ++ )
if ( s[i + 1] == '1' && s[i] == '0' ) {
int ii = i, cnt = 0;
while ( s[ii] == '0' )
cnt ++,
ii --;
if ( cnt <= canSwp )
res += cnt * b,
fill(s.begin() + ii + 1, s.begin() + i + 1, '1');
}
// 点燃
res += (s[0] == '1') * a;
for ( int i = 1; i < s.size(); i ++ )
res += (s[i] == '1' && s[i - 1] != '1' ) * a;
cout << res << endl;
}
int main () {
int cass; cin >> cass; while ( cass -- ) {
Solve();
}
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
# CodeForces1443C_TheDeliveryDilemma
# 🔗
# 💡
本题有一个题意里面待挖掘的性质:如果点了一家外卖,则比这家用时更短的外卖不会花费任何时间
那么就比较明显了,我们可以枚举一下外卖用时的上界,超上界的全自己去买就行
那么按外卖用时排个序
然后维护一下当前外卖用时和自己去买用时的后缀和的最大值的最小值即可
# ✅
#include <vector>
#include <iostream>
#include <algorithm>
#define ll long long
using namespace std;
const ll N = 2e5 + 10;
inline bool cmp ( pair<ll, ll> a, pair<ll, ll> b ) {
return a.first < b.first;
}
inline void Solve () {
ll n; scanf("%lld", &n);
vector<pair<ll, ll> > a; a.push_back({0, 0});
for ( ll i = 1, x; i <= n; i ++ ) scanf("%lld", &x), a.push_back({x, 0});
for ( ll i = 1, x; i <= n; i ++ ) scanf("%lld", &x), a[i].second = x;
sort ( a.begin(), a.end(), cmp );
ll res = 1e18, self_time = 0; // 自己去买的用时和
for ( int i = n; i >= 0; i -- ) {
res = min ( res, max ( self_time, a[i].first ) );
self_time += a[i].second;
}
printf("%lld\n", res);
}
int main () {
ll cass; scanf("%lld", &cass); while ( cass -- ) {
Solve();
}
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
# CodeForces1430E_StringReversal
# 🔗
# 💡
这就是一个从一个串通过交换相邻的转化为目标串的问题
贪心地想,相同的字母不存在交换的情况,即右侧的字母 不会跨越左侧任何一个相同的 达到它要去的位置
那么就可以容易处理出来每一个 应该到的位置
将这个处理出来的数组进行冒泡排序的次数就是我们需要的最少次数,也就是逆序对数
# ✅
const int N = 2e5 + 10;
int n; string a, b;
int id[26][N]; int idx[26];
int t[N << 2];
inline void pushup (int rt) {
t[rt] = t[rt << 1] + t[rt << 1 | 1];
}
inline void update (int id, int l, int r, int rt) {
if (l == r) {
t[rt] ++;
return;
}
int mid = (l + r) >> 1;
if (id <= mid) update(id, l, mid, rt << 1);
else update(id, mid + 1, r, rt << 1 | 1);
pushup(rt);
}
inline int query (int a, int l, int r, int rt) {
if (l >= a) return t[rt];
if (r < a) return 0;
int mid = (l + r) >> 1;
return query(a, l, mid, rt << 1) + query(a, mid + 1, r, rt << 1 | 1);
}
int main() {
cin >> n >> a;
a = "0" + a;
b = a; reverse(b.begin() + 1, b.end());
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i ++) {
id[b[i] - 'a'][++idx[b[i] - 'a']] = i;
}
for (int i = 0; i < 26; i ++) idx[i] = 0;
ll res = 0;
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i ++) {
int x = id[a[i] - 'a'][++idx[a[i] - 'a']];
res += query(x, 1, n, 1);
update(x, 1, n, 1);
}
cout << res << endl;
return 0;
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
# CodeForces1468D_Firecrackers
# 🔗
# 💡
这个题的主要问题就是在于在哪放鞭炮
首先我们肯定不想和警察对着走
这就意味着我们如果走到边界再往回走的话就一定与他对着走了,而对着走明显是很亏的
并且可以注意到如果我们一开始拉响几个鞭炮
那么我们后面会存在足够的时间让其进行燃烧
所以我们的策略就是 先放鞭炮直到警察走到小偷的相邻点,然后一只往边界去跑来争取时间
# ✅
inline void Solve () {
ll n, m, a, b; cin >> n >> m >> a >> b;
vector<ll> s(m); for ( ll &i : s ) cin >> i;
ll dir = abs(a - b);
sort(s.begin(), s.end());
vector<ll> hasrun;
for ( ll i = 0; i < dir - 1 && i < m; i ++ ) {
hasrun.push_back(s[i]);
}
ll runtime;
if ( a < b ) runtime = a - 1;
else runtime = n - a;
vector<ll> leavetime;
for ( ll i = 0; i < hasrun.size(); i ++ ) leavetime.push_back(dir - 1 - i + runtime);
sort(leavetime.begin(), leavetime.end());
ll res = 0;
for ( ll i = 0, j = 0; i < hasrun.size(); i ++ ) {
while ( j < leavetime.size() && leavetime[j] < hasrun[i] ) j ++;
if ( j != leavetime.size() ) {
res ++;
j ++;
}
}
cout << res << endl;
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
# CodeForces1482C_BasicDiplomacy
# 🔗
# 💡
看到这个 就可以往三角形定理上想,我们只用考虑出现次数最多的
但是发现这个次数是可以分配给别人的,并且不存在两个人都超过限制无法选中
即在可选状态下我们要么选第一个要么选第二个
在两个可选条件下不会两个都超过限制
但是存在必选的即这一天只能选一个,我们就要强制先给计入,看看是否成立
不成立的话就直接是 NO
成立的话对空出来的天去看第一个人是否能选,不能选的话就去选第二个
# ✅
const int N = 1e5 + 10;
int day[N]; // day[i]: 第i天用的人
vector<int> chos[N]; // chos[i]: 第i天可以用的人
int use[N]; // use[i]: 第i个人使用的次数
inline void Solve () {
int n, m; cin >> n >> m;
int lim = (m + 1) / 2 + 1;
for ( int i = 1; i <= n; i ++ ) use[i] = 0;
for ( int i = 1; i <= m; i ++ ) chos[i].clear();
bool flag = true;
for ( int i = 1; i <= m; i ++ ) {
day[i] = -1;
int num; cin >> num;
if ( num == 1 ) {
int x; cin >> x;
use[x] ++;
if ( use[x] >= lim ) flag = false;
day[i] = x;
} else {
for ( int j = 1; j <= num; j ++ ) {
int x; cin >> x;
chos[i].push_back(x);
}
}
}
if ( !flag ) { cout << "NO\n"; return; }
for ( int i = 1; i <= m; i ++ ) {
if ( day[i] != -1 ) continue;
if ( use[chos[i][0]] + 1 >= lim ) {
use[chos[i][1]] ++;
day[i] = chos[i][1];
} else {
use[chos[i][0]] ++;
day[i] = chos[i][0];
}
}
cout << "YES\n";
for ( int i = 1; i <= m; i ++ ) cout << day[i] << " ";
cout << "\n";
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
# CodeForces1511B_GCDLength
# 🔗
# 💡
我们想控制gcd的长度为c,
我们知道100和99的gcd为1,100和90的gcd为10,100和1000的gcd为100(100....0和9..90..0是我们可以方便控制gcd长度的数)
所以构造只需分两种情况考虑:
1.c=min(a,b),代表c的长度等于其中一个,那么较大的数可以是较小的数的倍数,所以我们构造出来一个10 ^ a和10 ^ b就行
2.c!=min(a,b),那么我们控制c的长度时,可以将一个数设为99900..0,一个数设为1000...,含9的数所给出来的0的个数+1就是c的长度
# ✅
void solve(){
int a, b, c;
cin >> a >> b >> c;
if(c==min(a,b)){//两个10000....
string rsa="1", rsb="1";
for (int i = 1; i < a; i++)
rsa += "0";
for (int i = 1; i < b; i++)
rsb += "0";
cout << rsa << " " << rsb << endl;
}
else {
string rsa="1", rsb="";
for (int i = 1; i < a; i++)//a为1000....
rsa += "0";
for (int i = 0; i < b - c+1;i++)//b为99900....
rsb += "9";
for (int i = 0; i < c-1; i++)
rsb += "0";
cout << rsa << " " << rsb << endl;
}
}
int main(){
int cass;
each_cass(cass){
solve();
}
return 0;
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
# CodeForces1511C_YetAnotherCardDeck
# 🔗
# 💡
题目中也说了,我们只需要移动id最小的找到的数就行,
所以这个题分两步
1.构造:记录每个数第一次出现的位置
2.移动:我们输入x,将id[x]变成1。在此之前应该先将id比它小的数全后移1(因为插入)
3e5的数据量我们用不到,
因为我们只改变小于id[x]的数的位置,
而我们每个数也就记录了那打头的数的位置,
所以每次循环内只需要从1~50判断一次id[i]的大小即可
# ✅
const int maxn = 3e5 + 10;
void solve()
{
int n, m;
cin >> n >> m;
int id[55];
for (int i = 0; i < 55; i++)
id[i] = -1;//初始化为-1
for (int i = 0, x; i < n; i++)
{
cin >> x;
if (id[x] == -1)
id[x] = i+1;//记录一下位置
}
for (int i = 0, x; i < m; i++){
cin >> x;
cout << id[x] << " ";
for (int j = 1; j <= 50; j++){
if(id[j]<id[x])//小了说明会因本次移动而改变位置
id[j]++;
}
id[x] = 1;
}
}
int main()
{
solve();
return 0;
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
# CodeForces1511D_MinCostString
# 🔗
https://codeforces.com/contest/1511/problem/D
# 💡
问题化简一下:我们要构造出来一个字符串,使得每两个连着的字符形成的长度为2的字符串出现的次数尽量少
那我们就aa,ab,ac,ad,ae...,bb,bc,bd,be,...,......
由于aaa三个同放在开头会直接形成两个同样的长度为2的字符串,那么这里我们删去其中一个a即可
所以构造方式为:
第一个字符x在第一对里面只出现一次,在接下来的对里匹配x+1直到'a'+k-1
# ✅
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int main () {
int n, k; cin >> n >> k;
while ( 1 ) {
for ( char i = 'a'; i < 'a' + k; i ++ ) {
cout << i, n --;
if ( !n ) return 0;
for ( char j = i + 1; j < 'a' + k; j ++ ) {
cout << i, n --;
if ( !n ) return 0;
cout << j, n --;
if ( !n ) return 0;
}
}
}
return 0;
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
# CodeForces1512E_PermutationBySum
# 🔗
# 💡
在[l,r]这个区间内既然每个数都不能被选超过一次,
我们得到S的最小值Min=(1+r-l+1) * (r-l+1)/2(从1到r-l+1),最大值Max=(n+n-r+l+3) * (r-l+1)/2(从n-r+l到n),
若不在这个区间内则输出"-1"
而S可以由Min改变一些数得来,
设cha=S-Min
我们想尽可能的让每一个数都增加相同的数使得这个区间内的数保持连续且cha尽可能减小
这个数就是cha/(r-l+1)
因为这样可以不重复
然后若cha减去这些增加的数还有剩余,
就向前几个最大的数分配1使得cha=0也就是S等于这个集合的和
因为几个最大的数都+1可以防止重复
输出的时候,使用前、中、后三个数组保存,
我们上面求得的[l,r]区间就是"中"数组
并记录vis,使得每个数只能出现过一次
# ✅
void solve()
{
ll n, l, r, s;
cin >> n >> l >> r >> s;
ll Min = (1 + r - l + 1) * (r - l + 1) / 2;
ll Max = (n + n - r + l) * (r - l + 1) / 2;
if (s > Max || s < Min)
{
cout << "-1" << endl;
return;
}
int cha = s - Min;
vector<int> zhong;
vector<int> qian;
vector<int> hou;
int pingduo = cha / (r - l + 1);//代表[1~(r-l+r)]每个数至少要加的数
int len = r - l + 1;
for (int i = 1; i <= len; i++)
zhong.push_back(i+pingduo),cha-=pingduo;
if (cha)//如果cha不为0,就最大的几个数+1直到cha=0
{
for (int i = zhong.size() - 1; cha && i >= 0; i--)
{
zhong[i]++;
cha--;
}
}
int vis[10000] = {0};//记录,防止重复
for (int i = 0; i < zhong.size(); i++)
vis[zhong[i]] = 1;
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++)
{
if (qian.size() == l - 1)//前面的数是(l-1)个
break;
if (!vis[i])
qian.push_back(i), vis[i] = 1;
}
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++)
{
if (hou.size() == n - r)//后面的数是(n-r)个
break;
if (!vis[i])
hou.push_back(i), vis[i] = 1;
}
//输出
for (int i = 0; i < qian.size(); i++)
cout << qian[i] << " ";
for (int i = 0; i < zhong.size(); i++)
cout << zhong[i] << " ";
for (int i = 0; i < hou.size(); i++)
cout << hou[i] << " ";
cout << endl;
}
int main()
{
int cass;
each_cass(cass)
{
solve();
}
return 0;
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
# CodeForces1517C_Fillomino2
# 🔗
https://codeforces.com/problemset/problem/1517/C
# 💡
既想构造满,又想连通
那么绝对不能有一个编号在前面还没构造完时把它封闭起来
如果我们从左上向右下遍历,那么左上是最容易确定的,只需要贴着边向下即可
而我们后面的编号都不能很直接地向下走,那样会封住
所以我们要贴着前面构造过的单元格继续构造
总结一下就是:每个编号默认向左构造,如果左边已经有编号了就向下构造一次,然后继续判断左侧是否构造过
# ✅
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
const int N = 510;
int a[N]; // 按顺序输入的编号
int res[N][N]; // 输出的答案矩阵
int main() {
int n; cin >> n;
for ( int i = 1; i <= n; i ++ ) cin >> a[i];
// 做个边界防止越界
for ( int i = 1; i <= n; i ++ ) res[n + 1][i] = 1;
for ( int i = 1; i <= n; i ++ ) res[i][0] = 1;
for ( int k = 1; k <= n; k ++ ) {
int cnt = a[k], j = k, i = k; // cnt表示还需要摆放的数量,(i, j)
while ( cnt -- ) {
res[i][j] = a[k];
if ( !res[i][j - 1] ) j --; // 默认向左走
else i ++; // 如果被占了就向下走
}
}
for ( int i = 1; i <= n; i ++ ) {
for ( int j = 1; j <= i; j ++ )
cout << res[i][j] << " ";
cout << endl;
}
return 0;
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
# CodeForces1536A_OmkarAndBadStory
# 🔗
# 💡
数据的迷惑性挺强的
稍微看出来点就以为是让GCD出差值然后进行等差数列的构造
但是数据范围只有-100 ~ 100而且如果出现负数就肯定不能用(越添加,差值越大,无法满足)
所以我们就直接构造一个0 ~ 100的差为1的等差数列就行了
# ✅
inline void solve(){
_int(n); _vectorInt(a, n);
sort(ALL(a));
if(a[0] < 0) cout << "NO" << endl;//最小的数为负数
else{
cout << "YES" << endl << 101 << endl;//构造
for(int i = 0; i <= 100; i ++) cout << i << " ";
cout << endl;
}
}
CHIVAS_{
int cass;
EACH_CASE(cass){
solve();
}
_REGAL;
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
# CodeForces1545A_SpecialPermutation
# 🔗
https://codeforces.com/problemset/problem/1454/A
# 💡
签到手速题
每一个数往后错一位就行了
# ✅
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
inline void Solve () {
int n; cin >> n;
for ( int i = 0; i < n; i ++ ) cout << (i + 1) % n + 1 << " ";
puts("");
}
int main () {
int cass;
for ( cin >> cass; cass; cass -- ) Solve();
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
# CodeForces1549B_GregorAndThePawnGame
# 🔗
https://codeforces.com/contest/1549/problem/B
# 💡
我们贪心操作
左边的数不想影响到右边的数取数,所以尽可能向左上走,其次正上,最后右上
那么就是判成立
# ✅
/*
________ _ ________ _
/ ______| | | | __ | | |
/ / | | | |__| | | |
| | | |___ _ _ _ ___ _ _____ | ___| ______ _____ ___ _ | |
| | | __ \ |_| | | | | | _\| | | ____| | |\ \ | __ | | _ | | _\| | | |
| | | | \ | _ | | | | | | \ | | \___ | | \ \ | |_/ _| | |_| | | | \ | | |
\ \______ | | | | | | \ |_| / | |_/ | ___/ | | | \ \ | /_ \__ | | |_/ | | |
Author : \________| |_| |_| |_| \___/ |___/|_| |_____| _________|__| \__\ |______| | | |___/|_| |_|
____| |
\_____/
*/
//#include <unordered_map>
#include <algorithm>
#include <iostream>
#include <cstring>
#include <utility>
#include <string>
#include <vector>
#include <cstdio>
#include <stack>
#include <queue>
#include <cmath>
#include <map>
#include <set>
#define G 10.0
#define LNF 1e18
#define EPS 1e-6
#define PI acos(-1.0)
#define INF 0x7FFFFFFF
#define ll long long
#define ull unsigned long long
#define INT __int128
#define LOWBIT(x) ((x) & (-x))
#define LOWBD(a, x) lower_bound(a.begin(), a.end(), x) - a.begin()
#define UPPBD(a, x) upper_bound(a.begin(), a.end(), x) - a.begin()
#define TEST(a) cout << "---------" << a << "---------" << endl
#define CHIVAS_ int main()
#define _REGAL exit(0)
#define SP system("pause")
#define IOS ios::sync_with_stdio(false)
//#define map unordered_map
#define _int(a) int a; cin >> a
#define _ll(a) ll a; cin >> a
#define _char(a) char a; cin >> a
#define _string(a) string a; cin >> a
#define _vectorInt(a, n) vector<int>a(n); cin >> a
#define _vectorLL(a, b) vector<ll>a(n); cin >> a
#define PB(x) push_back(x)
#define ALL(a) a.begin(),a.end()
#define MEM(a, b) memset(a, b, sizeof(a))
#define EACH_CASE(cass) for (cass = inputInt(); cass; cass--)
#define LS l, mid, rt << 1
#define RS mid + 1, r, rt << 1 | 1
#define GETMID (l + r) >> 1
using namespace std;
template<typename T> inline T MAX(T a, T b){return a > b? a : b;}
template<typename T> inline T MIN(T a, T b){return a > b? b : a;}
template<typename T> inline void SWAP(T &a, T &b){T tp = a; a = b; b = tp;}
template<typename T> inline T GCD(T a, T b){return b > 0? GCD(b, a % b) : a;}
template<typename T> inline void ADD_TO_VEC_int(T &n, vector<T> &vec){vec.clear(); cin >> n; for(int i = 0; i < n; i ++){T x; cin >> x, vec.PB(x);}}
template<typename T> inline pair<T, T> MaxInVector_ll(vector<T> vec){T MaxVal = -LNF, MaxId = 0;for(int i = 0; i < (int)vec.size(); i ++) if(MaxVal < vec[i]) MaxVal = vec[i], MaxId = i; return make_pair(MaxVal, MaxId);}
template<typename T> inline pair<T, T> MinInVector_ll(vector<T> vec){T MinVal = LNF, MinId = 0;for(int i = 0; i < (int)vec.size(); i ++) if(MinVal > vec[i]) MinVal = vec[i], MinId = i; return make_pair(MinVal, MinId);}
template<typename T> inline pair<T, T> MaxInVector_int(vector<T> vec){T MaxVal = -INF, MaxId = 0;for(int i = 0; i < (int)vec.size(); i ++) if(MaxVal < vec[i]) MaxVal = vec[i], MaxId = i; return make_pair(MaxVal, MaxId);}
template<typename T> inline pair<T, T> MinInVector_int(vector<T> vec){T MinVal = INF, MinId = 0;for(int i = 0; i < (int)vec.size(); i ++) if(MinVal > vec[i]) MinVal = vec[i], MinId = i; return make_pair(MinVal, MinId);}
template<typename T> inline pair<map<T, T>, vector<T> > DIV(T n){T nn = n;map<T, T> cnt;vector<T> div;for(ll i = 2; i * i <= nn; i ++){while(n % i == 0){if(!cnt[i]) div.push_back(i);cnt[i] ++;n /= i;}}if(n != 1){if(!cnt[n]) div.push_back(n);cnt[n] ++;n /= n;}return make_pair(cnt, div);}
inline int inputInt(){int X=0; bool flag=1; char ch=getchar();while(ch<'0'||ch>'9') {if(ch=='-') flag=0; ch=getchar();}while(ch>='0'&&ch<='9') {X=(X<<1)+(X<<3)+ch-'0'; ch=getchar();}if(flag) return X;return ~(X-1);}
inline void outInt(int X){if(X<0) {putchar('-'); X=~(X-1);}int s[20],top=0;while(X) {s[++top]=X%10; X/=10;}if(!top) s[++top]=0;while(top) putchar(s[top--]+'0');}
inline ll inputLL(){ll X=0; bool flag=1; char ch=getchar();while(ch<'0'||ch>'9') {if(ch=='-') flag=0; ch=getchar();}while(ch>='0'&&ch<='9') {X=(X<<1)+(X<<3)+ch-'0'; ch=getchar();}if(flag) return X;return ~(X-1); }
inline void outLL(ll X){if(X<0) {putchar('-'); X=~(X-1);}ll s[20],top=0;while(X) {s[++top]=X%10; X/=10;}if(!top) s[++top]=0;while(top) putchar(s[top--]+'0');}
inline void solve ( ) {
int n; cin >> n;
string a, b; cin >> a >> b;
int res = 0;
for ( int i = 0; i < n; i ++ ) {
if ( b[i] == '1' ) {
if ( i == 0 ) {
if ( a[i] == '0' ) a[i] = '2', res ++;
else if ( a[i + 1] == '1' ) a[i + 1] = '2', res ++;
} else {
if ( a[i - 1] == '1' ) a[i - 1] = '2', res ++;
else if ( a[i] == '0' ) a[i] = '2', res ++;
else if ( a[i + 1] == '1' ) a[i + 1] = '2', res ++;
}
}
}cout << res << endl;
}
CHIVAS_{
int cass;
for ( cin >> cass; cass; cass -- ) {
solve();
}
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
99
100
101
102
103
104
105
106
107
# CodeForces1555A_PizzaForces
# 🔗
https://codeforces.com/contest/1555/problem/A
# 💡
通过分析数据来获得贪心策略的题
首先发现性价比相同,但6是个更灵活的数,可以拼接别的数保证不会亏太多片披萨, 所以优先造6
1.是6的倍数:那么直接 n / 6 * 15
2.离6的倍数差1: 那么多买一片披萨,补上去即可 n / 6 * 15 + 15
3.离6的倍数差4或5: 那么把最后一块小披萨换成中披萨 ( n / 6 - 1 ) * 15 + 20
4.离6的倍数差2或3: 那么把最后一块小披萨换成大披萨 ( n / 6 - 1 ) * 15 + 25
# ✅
/*
________ _ ________ _
/ ______| | | | __ | | |
/ / | | | |__| | | |
| | | |___ _ _ _ ___ _ _____ | ___| ______ _____ ___ _ | |
| | | __ \ |_| | | | | | _\| | | ____| | |\ \ | __ | | _ | | _\| | | |
| | | | \ | _ | | | | | | \ | | \___ | | \ \ | |_/ _| | |_| | | | \ | | |
\ \______ | | | | | | \ |_| / | |_/ | ___/ | | | \ \ | /_ \__ | | |_/ | | |
Author : \________| |_| |_| |_| \___/ |___/|_| |_____| _________|__| \__\ |______| | | |___/|_| |_|
____| |
\_____/
*/
//#include <unordered_map>
#include <algorithm>
#include <iostream>
#include <cstring>
#include <utility>
#include <string>
#include <vector>
#include <cstdio>
#include <stack>
#include <queue>
#include <cmath>
#include <map>
#include <set>
#define G 10.0
#define LNF 1e18
#define EPS 1e-6
#define PI acos(-1.0)
#define INF 0x7FFFFFFF
#define ll long long
#define ull unsigned long long
#define INT __int128
#define LOWBIT(x) ((x) & (-x))
#define LOWBD(a, x) lower_bound(a.begin(), a.end(), x) - a.begin()
#define UPPBD(a, x) upper_bound(a.begin(), a.end(), x) - a.begin()
#define TEST(a) cout << "---------" << a << "---------" << '<br>'
#define CHIVAS_ int main()
#define _REGAL exit(0)
#define SP system("pause")
#define IOS ios::sync_with_stdio(false)
//#define map unordered_map
#define _int(a) int a; cin >> a
#define _ll(a) ll a; cin >> a
#define _char(a) char a; cin >> a
#define _string(a) string a; cin >> a
#define _vectorInt(a, n) vector<int>a(n); cin >> a
#define _vectorLL(a, b) vector<ll>a(n); cin >> a
#define PB(x) push_back(x)
#define ALL(a) a.begin(),a.end()
#define MEM(a, b) memset(a, b, sizeof(a))
#define EACH_CASE(cass) for (cass = inputInt(); cass; cass--)
#define LS l, mid, rt << 1
#define RS mid + 1, r, rt << 1 | 1
#define GETMID (l + r) >> 1
using namespace std;
template<typename T> inline T MAX(T a, T b){return a > b? a : b;}
template<typename T> inline T MIN(T a, T b){return a > b? b : a;}
template<typename T> inline void SWAP(T &a, T &b){T tp = a; a = b; b = tp;}
template<typename T> inline T GCD(T a, T b){return b > 0? GCD(b, a % b) : a;}
template<typename T> inline void ADD_TO_VEC_int(T &n, vector<T> &vec){vec.clear(); cin >> n; for(int i = 0; i < n; i ++){T x; cin >> x, vec.PB(x);}}
template<typename T> inline pair<T, T> MaxInVector_ll(vector<T> vec){T MaxVal = -LNF, MaxId = 0;for(int i = 0; i < (int)vec.size(); i ++) if(MaxVal < vec[i]) MaxVal = vec[i], MaxId = i; return make_pair(MaxVal, MaxId);}
template<typename T> inline pair<T, T> MinInVector_ll(vector<T> vec){T MinVal = LNF, MinId = 0;for(int i = 0; i < (int)vec.size(); i ++) if(MinVal > vec[i]) MinVal = vec[i], MinId = i; return make_pair(MinVal, MinId);}
template<typename T> inline pair<T, T> MaxInVector_int(vector<T> vec){T MaxVal = -INF, MaxId = 0;for(int i = 0; i < (int)vec.size(); i ++) if(MaxVal < vec[i]) MaxVal = vec[i], MaxId = i; return make_pair(MaxVal, MaxId);}
template<typename T> inline pair<T, T> MinInVector_int(vector<T> vec){T MinVal = INF, MinId = 0;for(int i = 0; i < (int)vec.size(); i ++) if(MinVal > vec[i]) MinVal = vec[i], MinId = i; return make_pair(MinVal, MinId);}
template<typename T> inline pair<map<T, T>, vector<T> > DIV(T n){T nn = n;map<T, T> cnt;vector<T> div;for(ll i = 2; i * i <= nn; i ++){while(n % i == 0){if(!cnt[i]) div.push_back(i);cnt[i] ++;n /= i;}}if(n != 1){if(!cnt[n]) div.push_back(n);cnt[n] ++;n /= n;}return make_pair(cnt, div);}
inline int inputInt(){int X=0; bool flag=1; char ch=getchar();while(ch<'0'||ch>'9') {if(ch=='-') flag=0; ch=getchar();}while(ch>='0'&&ch<='9') {X=(X<<1)+(X<<3)+ch-'0'; ch=getchar();}if(flag) return X;return ~(X-1);}
inline void outInt(int X){if(X<0) {putchar('-'); X=~(X-1);}int s[20],top=0;while(X) {s[++top]=X%10; X/=10;}if(!top) s[++top]=0;while(top) putchar(s[top--]+'0');}
inline ll inputLL(){ll X=0; bool flag=1; char ch=getchar();while(ch<'0'||ch>'9') {if(ch=='-') flag=0; ch=getchar();}while(ch>='0'&&ch<='9') {X=(X<<1)+(X<<3)+ch-'0'; ch=getchar();}if(flag) return X;return ~(X-1); }
inline void outLL(ll X){if(X<0) {putchar('-'); X=~(X-1);}ll s[20],top=0;while(X) {s[++top]=X%10; X/=10;}if(!top) s[++top]=0;while(top) putchar(s[top--]+'0');}
inline void solve ( ){
ll n; cin >> n;
if ( n % 6 == 0 ) {
cout << n / 6 * 15 << endl;
} else if ( n % 6 == 5 || n <= 5 ) {
cout << n / 6 * 15 + 15 << endl;
} else if( n % 6 == 2 || n % 6 == 1 ) {
cout << (n / 6 - 1) * 15 + 20 << endl;
} else if( n % 6 == 4 || n % 6 == 3 ){
cout << (n / 6 - 1) * 15 + 25 << endl;
}
}
CHIVAS_{
int cass;
for ( cin >> cass; cass; cass -- ){
solve();
}
_REGAL;
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
99
100
101
102
103
# CodeForces1555C_CoinRows
# 🔗
https://codeforces.com/contest/1555/problem/C
# 💡
我们贪心一下Bob,即Bob只有通过 “下->右“ 或者 “右->下” 才能吃得最大,那么我们设立两个路线的值step1,step2
那么我们模拟 Alice 的所有走法即可(即在哪拐弯)
每一次更改拐弯其实就是抛掉折角右上块,选择折角左下块
在所有的Alice走法中,Bob需要使自己更大,所以会走那个最大的路线
同时Alice想让Bob更小,所以走无论Bob走哪条路线都很小的走法
即我们枚举Alice的走法,维护一下 “Bob选最大路线” 的情况下所获得的最小的值
# ✅
/*
________ _ ________ _
/ ______| | | | __ | | |
/ / | | | |__| | | |
| | | |___ _ _ _ ___ _ _____ | ___| ______ _____ ___ _ | |
| | | __ \ |_| | | | | | _\| | | ____| | |\ \ | __ | | _ | | _\| | | |
| | | | \ | _ | | | | | | \ | | \___ | | \ \ | |_/ _| | |_| | | | \ | | |
\ \______ | | | | | | \ |_| / | |_/ | ___/ | | | \ \ | /_ \__ | | |_/ | | |
Author : \________| |_| |_| |_| \___/ |___/|_| |_____| _________|__| \__\ |______| | | |___/|_| |_|
____| |
\_____/
*/
//#include <unordered_map>
#include <algorithm>
#include <iostream>
#include <cstring>
#include <utility>
#include <string>
#include <vector>
#include <cstdio>
#include <stack>
#include <queue>
#include <cmath>
#include <map>
#include <set>
#define G 10.0
#define LNF 1e18
#define EPS 1e-6
#define PI acos(-1.0)
#define INF 0x7FFFFFFF
#define ll long long
#define ull unsigned long long
#define INT __int128
#define LOWBIT(x) ((x) & (-x))
#define LOWBD(a, x) lower_bound(a.begin(), a.end(), x) - a.begin()
#define UPPBD(a, x) upper_bound(a.begin(), a.end(), x) - a.begin()
#define TEST(a) cout << "---------" << a << "---------" << '<br>'
#define CHIVAS_ int main()
#define _REGAL exit(0)
#define SP system("pause")
#define IOS ios::sync_with_stdio(false)
//#define map unordered_map
#define _int(a) int a; cin >> a
#define _ll(a) ll a; cin >> a
#define _char(a) char a; cin >> a
#define _string(a) string a; cin >> a
#define _vectorInt(a, n) vector<int>a(n); cin >> a
#define _vectorLL(a, b) vector<ll>a(n); cin >> a
#define PB(x) push_back(x)
#define ALL(a) a.begin(),a.end()
#define MEM(a, b) memset(a, b, sizeof(a))
#define EACH_CASE(cass) for (cass = inputInt(); cass; cass--)
#define LS l, mid, rt << 1
#define RS mid + 1, r, rt << 1 | 1
#define GETMID (l + r) >> 1
using namespace std;
template<typename T> inline T MAX(T a, T b){return a > b? a : b;}
template<typename T> inline T MIN(T a, T b){return a > b? b : a;}
template<typename T> inline void SWAP(T &a, T &b){T tp = a; a = b; b = tp;}
template<typename T> inline T GCD(T a, T b){return b > 0? GCD(b, a % b) : a;}
template<typename T> inline void ADD_TO_VEC_int(T &n, vector<T> &vec){vec.clear(); cin >> n; for(int i = 0; i < n; i ++){T x; cin >> x, vec.PB(x);}}
template<typename T> inline pair<T, T> MaxInVector_ll(vector<T> vec){T MaxVal = -LNF, MaxId = 0;for(int i = 0; i < (int)vec.size(); i ++) if(MaxVal < vec[i]) MaxVal = vec[i], MaxId = i; return make_pair(MaxVal, MaxId);}
template<typename T> inline pair<T, T> MinInVector_ll(vector<T> vec){T MinVal = LNF, MinId = 0;for(int i = 0; i < (int)vec.size(); i ++) if(MinVal > vec[i]) MinVal = vec[i], MinId = i; return make_pair(MinVal, MinId);}
template<typename T> inline pair<T, T> MaxInVector_int(vector<T> vec){T MaxVal = -INF, MaxId = 0;for(int i = 0; i < (int)vec.size(); i ++) if(MaxVal < vec[i]) MaxVal = vec[i], MaxId = i; return make_pair(MaxVal, MaxId);}
template<typename T> inline pair<T, T> MinInVector_int(vector<T> vec){T MinVal = INF, MinId = 0;for(int i = 0; i < (int)vec.size(); i ++) if(MinVal > vec[i]) MinVal = vec[i], MinId = i; return make_pair(MinVal, MinId);}
template<typename T> inline pair<map<T, T>, vector<T> > DIV(T n){T nn = n;map<T, T> cnt;vector<T> div;for(ll i = 2; i * i <= nn; i ++){while(n % i == 0){if(!cnt[i]) div.push_back(i);cnt[i] ++;n /= i;}}if(n != 1){if(!cnt[n]) div.push_back(n);cnt[n] ++;n /= n;}return make_pair(cnt, div);}
inline int inputInt(){int X=0; bool flag=1; char ch=getchar();while(ch<'0'||ch>'9') {if(ch=='-') flag=0; ch=getchar();}while(ch>='0'&&ch<='9') {X=(X<<1)+(X<<3)+ch-'0'; ch=getchar();}if(flag) return X;return ~(X-1);}
inline void outInt(int X){if(X<0) {putchar('-'); X=~(X-1);}int s[20],top=0;while(X) {s[++top]=X%10; X/=10;}if(!top) s[++top]=0;while(top) putchar(s[top--]+'0');}
inline ll inputLL(){ll X=0; bool flag=1; char ch=getchar();while(ch<'0'||ch>'9') {if(ch=='-') flag=0; ch=getchar();}while(ch>='0'&&ch<='9') {X=(X<<1)+(X<<3)+ch-'0'; ch=getchar();}if(flag) return X;return ~(X-1); }
inline void outLL(ll X){if(X<0) {putchar('-'); X=~(X-1);}ll s[20],top=0;while(X) {s[++top]=X%10; X/=10;}if(!top) s[++top]=0;while(top) putchar(s[top--]+'0');}
inline void solve ( ) {
ll res = LNF;
ll step1 = 0, step2 = 0;
ll n; cin >> n;
ll a[2][n];
// 首先在输入的时候我们就可以构造出Bob的“右下路线(初始和Alice重叠,为0)” 和 “下右路线(开始Alice把下右全放出来,累加)”
for ( int i = 0; i < 2; i ++ ) {
for (int j = 0; j < n; j ++ ) {
cin >> a[i][j];
if ( i == 1 && j != n - 1 ) step2 += a[i][j];
}
}
// 开始维护最大路线的最小值
res = MIN(MAX(step1, step2), res);
for ( int i = n - 1; i >= 1; i -- ) {
step1 += a[0][i]; // “下右”被放出来一个拐角块
step2 -= a[1][i - 1];// “右下”被吃掉了一个拐角块
res = MIN(MAX(step1, step2), res);
}cout << res << endl;
}
CHIVAS_{IOS;
int cass;
for ( cin >> cass; cass; cass -- ) {
solve();
}
_REGAL;
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
99
100
101
102
103
104
105
106
107
108
109
110
111
112
113
# CodeForces1555D_SayNoToPalindromes
# 🔗
https://codeforces.com/contest/1555/problem/D
# 💡
由于不能出现长度至少为2的回文子串,意味着两个同样的字符挨着就不成立
那么分析一个较长的字符串,要想成立,在纸上模拟后发现只有六种构造方式,即以 a b c 为元素的六个排列作为循环节
那么我们对每次裁出来的字符串求得这六种循环节所花费的最小值即可
但是无疑每次循环一遍会超时,同时我们知道由于是排列,所以循环节一起从哪开始都无所谓,所以我们可以设立一个前缀和进行预处理,在求的时候计算它们差分的最小值即可
同时观测数据还有两个特点:
- r = l,必定为0
- r - l + 1 = 2,此时要看一下前后是否相等
- r - l + 1 > 2,那么就是我们上面说到的构造方式之间的比较
# ✅
/*
________ _ ________ _
/ ______| | | | __ | | |
/ / | | | |__| | | |
| | | |___ _ _ _ ___ _ _____ | ___| ______ _____ ___ _ | |
| | | __ \ |_| | | | | | _\| | | ____| | |\ \ | __ | | _ | | _\| | | |
| | | | \ | _ | | | | | | \ | | \___ | | \ \ | |_/ _| | |_| | | | \ | | |
\ \______ | | | | | | \ |_| / | |_/ | ___/ | | | \ \ | /_ \__ | | |_/ | | |
Author : \________| |_| |_| |_| \___/ |___/|_| |_____| _________|__| \__\ |______| | | |___/|_| |_|
____| |
\_____/
*/
//#include <unordered_map>
#include <algorithm>
#include <iostream>
#include <cstring>
#include <utility>
#include <string>
#include <vector>
#include <cstdio>
#include <stack>
#include <queue>
#include <cmath>
#include <map>
#include <set>
#define G 10.0
#define LNF 1e18
#define EPS 1e-6
#define PI acos(-1.0)
#define INF 0x7FFFFFFF
#define ll long long
#define ull unsigned long long
#define INT __int128
#define LOWBIT(x) ((x) & (-x))
#define LOWBD(a, x) lower_bound(a.begin(), a.end(), x) - a.begin()
#define UPPBD(a, x) upper_bound(a.begin(), a.end(), x) - a.begin()
#define TEST(a) cout << "---------" << a << "---------" << '<br>'
#define CHIVAS_ int main()
#define _REGAL exit(0)
#define SP system("pause")
#define IOS ios::sync_with_stdio(false)
//#define map unordered_map
#define _int(a) int a; cin >> a
#define _ll(a) ll a; cin >> a
#define _char(a) char a; cin >> a
#define _string(a) string a; cin >> a
#define _vectorInt(a, n) vector<int>a(n); cin >> a
#define _vectorLL(a, b) vector<ll>a(n); cin >> a
#define PB(x) push_back(x)
#define ALL(a) a.begin(),a.end()
#define MEM(a, b) memset(a, b, sizeof(a))
#define EACH_CASE(cass) for (cass = inputInt(); cass; cass--)
#define LS l, mid, rt << 1
#define RS mid + 1, r, rt << 1 | 1
#define GETMID (l + r) >> 1
using namespace std;
template<typename T> inline T MAX(T a, T b){return a > b? a : b;}
template<typename T> inline T MIN(T a, T b){return a > b? b : a;}
template<typename T> inline void SWAP(T &a, T &b){T tp = a; a = b; b = tp;}
template<typename T> inline T GCD(T a, T b){return b > 0? GCD(b, a % b) : a;}
template<typename T> inline void ADD_TO_VEC_int(T &n, vector<T> &vec){vec.clear(); cin >> n; for(int i = 0; i < n; i ++){T x; cin >> x, vec.PB(x);}}
template<typename T> inline pair<T, T> MaxInVector_ll(vector<T> vec){T MaxVal = -LNF, MaxId = 0;for(int i = 0; i < (int)vec.size(); i ++) if(MaxVal < vec[i]) MaxVal = vec[i], MaxId = i; return make_pair(MaxVal, MaxId);}
template<typename T> inline pair<T, T> MinInVector_ll(vector<T> vec){T MinVal = LNF, MinId = 0;for(int i = 0; i < (int)vec.size(); i ++) if(MinVal > vec[i]) MinVal = vec[i], MinId = i; return make_pair(MinVal, MinId);}
template<typename T> inline pair<T, T> MaxInVector_int(vector<T> vec){T MaxVal = -INF, MaxId = 0;for(int i = 0; i < (int)vec.size(); i ++) if(MaxVal < vec[i]) MaxVal = vec[i], MaxId = i; return make_pair(MaxVal, MaxId);}
template<typename T> inline pair<T, T> MinInVector_int(vector<T> vec){T MinVal = INF, MinId = 0;for(int i = 0; i < (int)vec.size(); i ++) if(MinVal > vec[i]) MinVal = vec[i], MinId = i; return make_pair(MinVal, MinId);}
template<typename T> inline pair<map<T, T>, vector<T> > DIV(T n){T nn = n;map<T, T> cnt;vector<T> div;for(ll i = 2; i * i <= nn; i ++){while(n % i == 0){if(!cnt[i]) div.push_back(i);cnt[i] ++;n /= i;}}if(n != 1){if(!cnt[n]) div.push_back(n);cnt[n] ++;n /= n;}return make_pair(cnt, div);}
inline int inputInt(){int X=0; bool flag=1; char ch=getchar();while(ch<'0'||ch>'9') {if(ch=='-') flag=0; ch=getchar();}while(ch>='0'&&ch<='9') {X=(X<<1)+(X<<3)+ch-'0'; ch=getchar();}if(flag) return X;return ~(X-1);}
inline void outInt(int X){if(X<0) {putchar('-'); X=~(X-1);}int s[20],top=0;while(X) {s[++top]=X%10; X/=10;}if(!top) s[++top]=0;while(top) putchar(s[top--]+'0');}
inline ll inputLL(){ll X=0; bool flag=1; char ch=getchar();while(ch<'0'||ch>'9') {if(ch=='-') flag=0; ch=getchar();}while(ch>='0'&&ch<='9') {X=(X<<1)+(X<<3)+ch-'0'; ch=getchar();}if(flag) return X;return ~(X-1); }
inline void outLL(ll X){if(X<0) {putchar('-'); X=~(X-1);}ll s[20],top=0;while(X) {s[++top]=X%10; X/=10;}if(!top) s[++top]=0;while(top) putchar(s[top--]+'0');}
const int N = 2e5 + 10;
int res1[N], res2[N], res3[N], res4[N], res5[N], res6[N];
inline void solve ( ){
int n; cin >> n;
int m; cin >> m;
string s; cin >> s; s = "0" + s;
for (int i = 1; i < s.size(); i ++ ) { // 六种排列的预处理
if (i % 3 == 0){
res1[i] = res1[i - 1] + (s[i] != 'a');
res2[i] = res2[i - 1] + (s[i] != 'a');
res3[i] = res3[i - 1] + (s[i] != 'b');
res4[i] = res4[i - 1] + (s[i] != 'b');
res5[i] = res5[i - 1] + (s[i] != 'c');
res6[i] = res6[i - 1] + (s[i] != 'c');
} else if (i % 3 == 1) {
res1[i] = res1[i - 1] + (s[i] != 'b');
res2[i] = res2[i - 1] + (s[i] != 'c');
res3[i] = res3[i - 1] + (s[i] != 'c');
res4[i] = res4[i - 1] + (s[i] != 'a');
res5[i] = res5[i - 1] + (s[i] != 'a');
res6[i] = res6[i - 1] + (s[i] != 'b');
} else {
res1[i] = res1[i - 1] + (s[i] != 'c');
res2[i] = res2[i - 1] + (s[i] != 'b');
res3[i] = res3[i - 1] + (s[i] != 'a');
res4[i] = res4[i - 1] + (s[i] != 'c');
res5[i] = res5[i - 1] + (s[i] != 'b');
res6[i] = res6[i - 1] + (s[i] != 'a');
}
}
while ( m -- ) {
int l, r; cin >> l >> r;
if(l == r){ // 特判
cout << 0 << endl;
} else if ( r == l + 1 ) { // 特判
if ( s[r] == s[l] ) cout << 1 << endl;
else cout << 0 << endl;
} else { // 对前缀和差分求得区间和,进行查找最小值
cout << MIN(
MIN(
MIN(res1[r] - res1[l - 1], res2[r] - res2[l - 1]),
MIN(res3[r] - res3[l - 1], res4[r] - res4[l - 1])),
MIN(res5[r] - res5[l - 1], res6[r] - res6[l - 1]) ) << endl;
}
}
}
CHIVAS_{IOS;
solve();
_REGAL;
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
99
100
101
102
103
104
105
106
107
108
109
110
111
112
113
114
115
116
117
118
119
120
121
122
123
124
125
126
127
128
129
130
131
132
133
134
135
136
137
138
139
140
141
# CodeForces1556D_TakeAGuess
# 🔗
# 💡
本题我们可以把原数组构造出来,所以重在发现一个公式关系
对于每一位,我们可以用或运算求出这一位是否存在1,同时加上与运算求出这一位有几个1
则公式为:
同时可以推出一组方程组运算关系:
然后直接:即可
# ✅
#include <iostream>
#include <algorithm>
#include <cstring>
#include <vector>
#define ll long long
using namespace std;
int main () {
#ifndef ONLINE_JUDGE
freopen("../in.in", "r", stdin);
freopen("../out.out", "w", stdout);
#endif
auto And = [&](int a, int b) { // 放出询问,返回给定值
cout << "and " << a << " " << b << endl;
int ord;
cin >> ord;
return ord;
};
auto Or = [&](int a, int b) { // 放出询问,返回给定值
cout << "or " << a << " " << b << endl;
int ord;
cin >> ord;
return ord;
};
int n, k;
cin >> n >> k;
int a12 = And(1, 2) + Or(1, 2),
a13 = And(1, 3) + Or(1, 3),
a23 = And(2, 3) + Or(2, 3);
vector<int> vec;
vec.push_back((a12 - a23 + a13) / 2);
vec.push_back((a12 + a23 - a13) / 2);
vec.push_back((a23 + a13 - a12) / 2); // 前三个先造好
while ( vec.size() < n ) {
int aa = And(vec.size(), vec.size() + 1) + Or(vec.size(), vec.size() + 1);
vec.push_back(aa - vec.back());
}
sort ( vec.begin(), vec.end() );
cout << "finish " << vec[k - 1] << endl;
return 0;
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
# CodeForces1569B_ChessTournament
# 🔗
# 💡
一道比较细节的贪心构造题
首先有两种人
1号因为不输,我们也不想影响到与他比赛的所有1号,所以直接构造成平局即可
2号因为有赢,所以他在赢了一场之后都要把没比的设置为输,这样可以为其他的2号提供贡献
在构造的过程中进行判断"NO",即1号有输,2号出不来赢
其次就是对细节的把控即可
# ✅
#include <iostream>
#include <algorithm>
#include <map>
#include <cmath>
#include <vector>
#include <cstring>
#include <list>
using namespace std;
#define ll long long
const int N = 100;
char res[N][N]; // 答案图
int won[N]; // 第i个人赢过没
inline void solve () {
int n; cin >> n;
string s; cin >> s;
memset(won, 0, sizeof won);
memset(res, 0, sizeof res);
for ( int i = 0; i < n; i ++ ) {
if ( s[i] == '2' ) { // 有赢:贪法--赢过之后一直输
for ( int j = 0; j < n; j ++ ) {
if ( i == j || res[i][j] ) continue;
if ( s[j] == '1' ) // 有赢vs不输
res[i][j] = '=', // 贪一下,这类也不让那个不输的赢,让平局
res[j][i] = '=';
else { // 有赢vs有赢
if ( !won[i] ) // 如果i没赢过,那么这把赶紧让他赢了
res[i][j] = '+',
res[j][i] = '-',
won[i] = 1;
else // 如果赢过了,就可以贪心地后面的全让他输
res[i][j] = '-',
res[j][i] = '+',
won[j] = 1;
}
}
if ( !won[i] ) { // 没赢过肯定不行
cout << "NO" << endl;
return ;
}
} else { // 不输:贪法--都平局
for ( int j = 0; j < n; j ++ ) {
if ( res[i][j] == '-' ) { // 输了肯定不行
cout << "NO" << endl;
return;
}
if ( i == j || res[i][j] ) continue;
res[i][j] = '=',
res[j][i] = '=';
}
}
}
cout << "YES" << endl;
for ( int i = 0; i < n; i ++ ) {
for ( int j = 0; j < n; j ++ ) {
if ( i == j ) cout << "X";
else cout << res[i][j];
}cout << endl;
}
}
int main () {
#ifndef ONLINE_JUDGE
freopen("in.in", "r", stdin);
freopen("out.out", "w", stdout);
#endif
int cass;
cin >> cass;
while ( cass -- ) {
solve();
}
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
# CodeForces1593C_SaveMoreMice
# 🔗
# 💡
首先我们想让尽可能多的老鼠进洞,除了从最后面的往后走之外没有别的办法
因为把几个老鼠挪进去的总耗时是一定的
那么从最后开始挪肯定是性价比最高的
# ✅
const int N = 4e5 + 10;
ll n, k;
ll a[N];
inline void Solve() {
cin >> n >> k;
ll res = 0;
for ( ll i = 0; i < k; i ++ ) cin >> a[i];
sort ( a, a + n, greater<ll>());
ll catid = 0;
for ( ll i = 0; i < k; i ++ ) {
if ( a[i] <= catid ) break;
catid += n - a[i];
res ++;
}
cout << res << endl;
}
int main () {
ios::sync_with_stdio(false);
ll cass; cin >> cass; while ( cass -- ) {
Solve();
}
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
# CodeForces1611D_WeightsAssignmentForTreeEdges
# 🔗
# 💡
想半天以为这道题难点在找根...,然后发现我真是个憨憨
# 找根
如果一个点的父节点是自己,那它就是根...(不会就我一个人这地方看半天吧
# 检查
由于 表示先后顺序,我们设 表示 是 中第几个
int pr[N];
int rp[N];
for ( int i = 1; i <= n; i ++ )
scanf("%d", &pr[i]),
rp[pr[i]] = i;
2
3
4
5
一条链上的 必定越来越大, 同样
那么可以知道的是,如果一堆父子关系中, 那么一定不行
这个跑一遍点就可以实现了,也要在输入 的时候记录一下父子关系
记录
for ( int i = 1, x; i <= n; i ++ ) {
scanf("%d", &x); b[i] = { x, i };
}
2
3
检查
inline bool check() {
for ( int i = 1; i <= n; i ++ ) {
if ( rp[b[i].first] > rp[b[i].second] ) return false;
}
return true;
}
if ( !check() ) { printf("-1\n"); return;};
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
# 边权
我们不想影响他们的先后顺序
那么可以让
这样的话一条边 的边权就是
for ( int i = 1; i <= n; i ++ ) {
printf("%d ", rp[b[i].second] - rp[b[i].first]);
} printf("\n");
2
3
# ✅
#include <iostream>
#include <queue>
#define ll long long
using namespace std;
const int N = 2e5 + 10;
int n;
pair<int, int> b[N]; // first: fath, second: son
int pr[N]; // 正p数组
int rp[N]; // 反p数组
inline bool check() {
for ( int i = 1; i <= n; i ++ ) {
if ( rp[b[i].first] > rp[b[i].second] ) return false;
}
return true;
}
inline void Solve () {
scanf("%d", &n);
for ( int i = 1, x; i <= n; i ++ ) {
scanf("%d", &x); b[i] = { x, i };
}
for ( int i = 1; i <= n; i ++ )
scanf("%d", &pr[i]),
rp[pr[i]] = i;
if ( !check() ) { printf("-1\n"); return;};
for ( int i = 1; i <= n; i ++ ) {
printf("%d ", rp[b[i].second] - rp[b[i].first]);
} printf("\n");
}
int main () {
int cass; scanf("%d", &cass); while ( cass -- ) {
Solve ();
}
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
# CodeForces1618D_ArrayAndOperations
# 🔗
# 💡
注意到我们可以将 个最大的通过前除后降到
但是存在降不到零的情况,即相同的数过多的时候,我们肯定有一部分只能两两匹配而不能将其分配给别人
这也是三角形定理中的,我们统计出来相同的个数最多的数量 ,如果它大于 就只能用
前面的数是一定被统计的
# ✅
int a[110];
inline void Solve () {
int n, k; cin >> n >> k;
for ( int i = 1; i <= n; i ++ ) cin >> a[i];
sort(a + 1, a + 1 + n);
int res = 0;
for ( int i = 1; i <= n - k * 2; i ++ ) res += a[i];
map<int, int> num;
int mxnum = 0;
for ( int i = n - k * 2 + 1; i <= n; i ++ ) {
num[a[i]] ++;
mxnum = max(mxnum, num[a[i]]);
}
int elnum = k * 2 - mxnum;
res += max(0, (mxnum - elnum) / 2);
cout << res << endl;
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
# CodeForces1620D_ExactChange
# 🔗
# 💡
首先注意到, 的个数和 的个数一定不会超过两个,因为三个 可以用一个 代替, 同理
而 的个数的范围也是在三个,即
那么我们可以暴力检查这三个硬币各用多少个
再检查一个数是否能被构造出来的时候,由于我们枚举出来了前两种硬币的上界了,这里就直接再暴力这两种硬币看看它们各自用多少个来构造这一个数
由于有了这两个硬币的数量了,第三种硬币需要多少个也可以直接算出来了,就可以检查出来这个数是否能被这些硬币构造出来
对于枚举的上界,这一套数都被构造出来才算成功
如果成功的话,维护使用硬币个数的最小值即可
# ✅
int n;
vector<ll> a;
inline bool Joint (ll c1, ll c2, ll c3, ll v) {
for (ll i = 0; i <= c1; i ++) {
for (ll j = 0; j <= c2; j ++) {
if (i + j * 2 > v) continue;
if ((v - i - j * 2) % 3 != 0) continue;
if ((v - i - j * 2) / 3 <= c3) return true;
}
}
return false;
}
inline bool Check (ll c1, ll c2, ll c3) {
for (ll v : a) {
if (!Joint(c1, c2, c3, v)) return false;
}
return true;
}
inline void Solve () {
cin >> n;
a.resize(n); for (ll &i : a) cin >> i;
sort(a.begin(), a.end(), greater<ll>());
ll up12 = 3;
ll up3 = a[0] / 3 + 1;
ll res = 1e18;
for (ll c1 = 0; c1 <= up12; c1 ++) {
for (ll c2 = 0; c2 <= up12; c2 ++) {
for (ll c3 = max(0ll, up3 - 3); c3 <= up3; c3 ++) {
if (Check(c1, c2, c3)) {
res = min(res, c1 + c2 + c3);
}
}
}
}
cout << res << endl;
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
# CodeForces1621B_IntegersShop
# 🔗
# 💡
根据题意我们容易知道,其实就是让你选能覆盖已知全局的 和
这个 和 可能会在一个段里也可能会在两个段里

所以我们维护一个只会扩展的单段,维护这个单段在两端都最边界的情况下价值最小
如果枚举到的段两端都比这个单段靠边 或者 等于这个单段的两端(彻底包含它)并且可以让它的价值更小,就替换这个单段
和一套双段,一个左段一个右段,维护这两个双段分别左侧和右侧都最边界的情况下价值最小
对于左段,如果枚举到的段左侧比这个左段靠边 或者 等于这个左段的左侧并且可以让它的价值更小,就替换这个左段
右段同理
在求最小价值的时候
如果这个单段包含这套双段,那么就要比价值了,肯定是选 双段价值和 与 单段价值 的最小值
如果不包含,那么肯定是双段覆盖的点最多,就必选双段价值和了
# ✅
struct node {
ll a, b, v;
}nd[100005];
inline void Solve () {
ll n; scanf("%lld", &n);
for ( ll i = 0; i < n; i ++ ) scanf("%lld%lld%lld", &nd[i].a, &nd[i].b, &nd[i].v);
node l = nd[0], r = nd[0]; // 左段,右段
node allin = nd[0]; // 单段
for ( ll i = 0; i < n; i ++ ) {
if ( nd[i].b > r.b ) r = nd[i];
else if ( nd[i].b == r.b && nd[i].v < r.v ) r = nd[i];
if ( nd[i].a < l.a ) l = nd[i];
else if ( nd[i].a == l.a && nd[i].v < l.v ) l = nd[i];
if ( (nd[i].a <= allin.a && nd[i].b > allin.b) || (nd[i].a < allin.a && nd[i].b >= allin.b) ) allin = nd[i];
else if ( nd[i].a == allin.a && nd[i].b == allin.b && nd[i].v < allin.v ) allin = nd[i];
if ( allin.a <= l.a && allin.b >= r.b ) {
printf("%lld\n", min(allin.v, r.v + l.v));
} else printf("%lld\n", r.v + l.v);
}
}
int main () {
ll cass; scanf("%lld", &cass); while ( cass -- ) {
Solve();
}
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
# CodeForces1624D_PalindromesColoring
# 🔗
# 💡
由于分配后的最小值最大,所以我们肯定是希望均分
根据回文串的性质,如果我们能找出来一对一对的相同字符,那么我们可以把它分到每个字符串两侧
所以我们拿出来成对的字符,即偶数个字符
把它们分给 个人
先记为分成了 轮
那么一定会有 比 少了两个,我们尽可能均分,让那 个人每个人拿出来一个字符,此时和它配对的字符落单放到中间,然后在总字符串内的所有落单的字符个数中加进这些字符,设加后总共有 个单字符,这些单字符可以拼给那 个人,如果给的完,答案就是 ,否则就是
# ✅
inline void Solve () {
int n, k; cin >> n >> k;
string s; cin >> s;
int cnt[400]; memset(cnt, -1, sizeof cnt);
int vis[200005] = {0};
int num2 = 0;
for ( int i = 0; i < n; i ++ ) {
if ( ~cnt[s[i]] ) {
vis[i] = 1;
vis[cnt[s[i]]] = 1;
cnt[s[i]] = -1;
num2 ++;
} else {
cnt[s[i]] = i;
}
}
int num1 = n - num2 * 2;
int lft_ppl = k - num2 % k;
num1 += num2 % k;
if ( num1 >= lft_ppl ) cout << num2 / k * 2 + 1 << endl;
else cout << num2 / k * 2 << endl;
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
# CodeForces1626C_MonstersAndSpells
# 🔗
# 💡
建立一个这样的模型 
我们可以从 中得出,我们至少要从 这个时刻开始释放 的攻击
才能安全地在 时释放出 的攻击
为了贪心,我们得出开始时间 ,结束时间
而需要更早蓄力更晚触发的中途就可以将晚蓄力早触发的怪消灭
那么我们要保证蓄力是一个严格单调递增的序列即可
但是要考虑到三角形部分重叠的情况
这种就要在之前蓄力的基础上消灭该怪兽后不停止继续蓄力
才可以安全消灭后面那只怪兽
所以要合并一下区间
对于每个 ,如果存在 并且满足上面条件( ),那么合并区间操作为
然后我们就可以用单调栈求上升序列了
对于每个序列累加 的和
# ✅
inline void Solve () {
ll n; cin >> n;
ll k[n + 10], h[n + 10];
ll beg[n + 10];
for ( ll i = 0; i < n; i ++ ) cin >> k[i];
for ( ll i = 0; i < n; i ++ ) cin >> h[i];
for ( ll i = 0; i < n; i ++ ) beg[i] = k[i] - h[i] + 1;
for ( ll i = 0; i < n; i ++ ) {
for ( int j = i; j >= 0; j -- ) {
if ( beg[i] >= beg[j] && beg[i] <= k[j] ) beg[i] = beg[j];
}
}
stack<pair<ll, ll> > stk;
for ( ll i = 0; i < n; i ++ ) {
ll x = beg[i];
while ( stk.size() && stk.top().second >= x ) stk.pop();
stk.push({x, k[i]});
}
ll res = 0;
while ( stk.size() ) {
ll fir = stk.top().first, sec = stk.top().second; stk.pop();
res += (1 + sec - fir + 1) * (sec - fir + 1) / 2;
}
cout << res << endl;
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
# CodeForces1626D_MartialArtsTournament
# 🔗
# 💡
我们对 的所有体重记录一个出现的次数
然后枚举第一段和第二段的期望长度
遍历 到 看看每段在不超过自身预期的前提下,最多能存在多少个运动员
预期和实际的差即是我们要扩招的人数
对于第三段,我们看看枚举完 后面的人中,向上的第一个 的整数幂,就是第三段预期的人数
这三个相加,对于每一个枚举的前两段长度,我们维护一下我们要扩招的人的最小值即可
# ✅
int cnt[200005];
int n;
inline int calc ( int L1, int L2 ) { int L3 = 1; // 预期人数
int res = 0;
int i = 1, sum; // 实际人数
sum = 0;
for (; i <= n; i ++ ) {
if ( sum + cnt[i] > L1 ) break;
sum += cnt[i];
}
res += L1 - sum;
sum = 0;
for (; i <= n; i ++ ) {
if ( sum + cnt[i] > L2 ) break;
sum += cnt[i];
}
res += L2 - sum;
sum = 0;
for (; i <= n; i ++ ) sum += cnt[i];
while ( L3 < sum ) L3 <<= 1;
res += L3 - sum;
return res;
}
inline void Solve () {
scanf("%d", &n);
for ( int i = 1; i <= n; i ++ ) cnt[i] = 0;
for ( int i = 0; i < n; i ++ ) {
int x; scanf("%d", &x);
cnt[x] ++;
}
int res = 0x3f3f3f3f;
for ( int len1 = 1; len1 <= n; len1 <<= 1 ) {
for ( int len2 = 1; len2 <= n; len2 <<= 1 ) {
res = min(res, calc(len1, len2));
}
}
printf("%d\n", res);
}
int main () {
int cass; scanf("%d", &cass); while ( cass -- ) {
Solve ();
}
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
# CodeForces1629E_GridXor
# 🔗
# 💡
本题的关键还是在于模型的建立,还有注意 是偶数,不然会像我赛时疯狂画 的情况怎么也造不出来
画图中可以考虑到两个相邻单元格的操作

图中标 为操作,标 为改变
把它看作一个拼图的块,那么题目问的就是我们如何拼才能把这个图拼满(可以拼出界外
可以画几个试试,发现这些拼图块是互补的

就意味着我们可以把它拼出来
遍历一遍,每次看操作一个位置和它左侧形成的拼图是否可以完美拼上(操作区域全为 ),再看和它下侧是否可以拼上
但是要考虑到一种情况,就是一个拼图方向顺序
可以看到这个拼图竖着放和横着放是两种不同的情况
这里先遍历的是行,内重按列
我们先考虑竖着放的话,它会过长,在第一行检查时就有可能造成上下连着两个最右侧为空的情况( 时)
这种我们就无法塞入拼图了
所以我们优先考虑横着放
# ✅
const int N = 1e3 + 10;
bool vis[N][N]; // 记录是否被放过拼图了
int a[N][N];
int n;
inline bool Is_1 ( int x, int y, int op = 0 ) { // op=0:检查,op=1:修改
if ( x < 1 || x > n || y < 1 || y > n ) return 1;
if ( op ) return vis[x][y] = 1;
return !vis[x][y];
}
inline bool Check ( int x, int y, int op = 0 ) {
return Is_1(x, y - 1, op) && Is_1(x, y + 1, op) && Is_1(x + 1, y, op) && Is_1(x - 1, y, op);
}
inline void Solve () {
cin >> n;
for ( int i = 1; i <= n; i ++ ) for ( int j = 1; j <= n; j ++ ) vis[i][j] = 0;
for ( int i = 1; i <= n; i ++ ) for ( int j = 1; j <= n; j ++ ) cin >> a[i][j];
int res = 0;
for ( int i = 1; i <= n; i ++ ) for ( int j = 1; j <= n; j ++ ) {
if ( j < n && Check(i, j) && Check(i, j + 1) ) { // 横着放
Check(i, j, 1);
Check(i, j + 1, 1);
res ^= a[i][j] ^ a[i][j + 1];
}
if ( i < n && Check(i, j) && Check(i + 1, j) ) { // 竖着放
Check(i, j, 1);
Check(i + 1, j, 1);
res ^= a[i][j] ^ a[i + 1][j];
}
}
cout << res << endl;
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
# CodeForces1632B_RoofConstruction
# 🔗
# 💡
由于两个数异或,在位数不同的情况下,最高位的 一定会被保留下来
所以 一定会有 小于 的最高二的幂,设为
那么考虑可不可以让别的都小于
由于 ,那么我们让 的都放在 的前面
那么就剩下和 同位数的数了
全放在 的后面就可以让他们最高位消掉来保证
那么构造方法就是
# ✅
inline void Solve () {
int n; cin >> n;
ll mx = 1;
while ( mx * 2 < n ) mx *= 2;
for ( int i = 1; i < mx; i ++ ) cout << i << " ";
cout << 0 << " " << mx << " ";
for ( int i = mx + 1; i < n; i ++ ) cout << i << ' '; cout << endl;
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
# CodeForces1634C_OKEA
# 🔗
# 💡
注意每一行只能是连续的奇数或者是连续的偶数,否则奇偶相间则这一对相邻的平均数不为整数
那么我们就构造,如果奇数不够或者是偶数不够就 NO
否则输出 YES 和构造后的数组即可
# ✅
int res[505][505];
inline void Solve () {
ll n, k; cin >> n >> k;
vector<ll> odd, eve;
for ( int i = n * k; i >= 1; i -- ) {
if ( i & 1 ) odd.push_back(i);
else eve.push_back(i);
}
for ( int i = 1; i <= n; i ++ ) {
if ( i & 1 ) {
for ( int j = 1; j <= k; j ++ ) {
if ( !odd.size() ) {
cout << "NO" << endl;
return;
}
res[i][j] = odd.back(); odd.pop_back();
}
} else {
for ( int j = 1; j <= k; j ++ ) {
if ( !eve.size() ) {
cout << "NO" << endl;
return;
}
res[i][j] = eve.back(); eve.pop_back();
}
}
}
cout << "YES" << endl;
for ( int i = 1; i <= n; i ++ ) {
for ( int j = 1; j <= k; j ++ ) cout << res[i][j] << ' ';
cout << endl;
}
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
# CodeForces1634D_FindZero
# 🔗
# 💡
我们每次可以获得
在所有的三元组中,若这个值最大
那么 和 一定存在于这个三元组中
所以我们可以先固定 ,然后遍历两遍,在维护 的最大值时更新 和
那么我们就会获得一个包含 最大值 和 的三元组,且一共询问了 次
然后我们就要判断 和 在哪两个里面
找一个 满足
分别用 替换
若替换后查询结果还是最大值,那么 和 一定在另外两个里面,输出就行了
# ✅
inline int query ( int x, int y, int z ) {
cout << "? " << x << " " << y << " " << z << endl; cout.flush();
int res; cin >> res;
return res;
}
inline void answer ( int x, int y ) {
cout << "! " << x << ' ' << y << endl; cout.flush();
}
inline void Solve () {
int n; cin >> n;
int a = 1, b = 2, c = 3;
int mx = query(a, b, c);
for ( int i = 4; i <= n; i ++ ) {
int abi = query(a, b, i);
if ( mx < abi )
mx = abi,
c = i;
}
for ( int i = 1; i <= n; i ++ ) {
if ( i == a || i == b || i == c ) continue;
int aic = query(a, i, c);
if ( mx < aic )
mx = aic,
b = i;
}
int id = 1; while ( id == a || id == b || id == c ) id ++;
int tst1 = query(id, b, c);
int tst2 = query(a, id, c);
if ( tst1 == mx ) answer(b, c);
else if ( tst2 == mx ) answer(a, c);
else answer(a, b);
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
# CodeForces1637F_Towers
# 🔗
# 💡
先考虑 最大的点 ,先让它找到两个路径两个端点
这样的话别的点都可以白嫖其中一个或两个端点
那么我们令 作为根节点,其要构造出来的两个塔高度一定是 ,由于经过叶子结点的路径必然有一个端点在叶子结点上,所以我们让两个塔位于两个叶子结点上
那么对于一个节点 ,其向上经过根节点肯定可以到达一个塔高度为 的叶子结点,所以我们只需要考虑在其子树内构造出一棵高度不小于 的塔,如果已经存在这样的塔那么就不用管了
具体实现我们可以采用回溯的方式,向上维护子树中建过的塔的最大值
按上面所说:
- 对于非根节点 ,我们要找到一个子树最大值,如果 需要将其补到
- 对于根节点 ,我们要找到两个子树最大值,同样如果 也是需要将其补到
# ✅
const int N = 2e5 + 10;
const int M = 4e5 + 10;
struct Edge {
int nxt, to;
} edge[M];
int head[N], cnt;
inline void add_Edge ( int from, int to ) {
edge[++cnt] = { head[from], to };
head[from] = cnt;
}
int n, h[N], root;
ll e[N];
ll res;
inline int DFS ( int x, int fa ) {
bool leaf = true;
for ( int i = head[x]; i; i = edge[i].nxt ) {
if ( edge[i].to == fa ) continue;
leaf = false;
}
if ( leaf ) { // 叶子结点建塔为 h[x] 即可
res += h[x];
return h[x];
} else {
if ( x == root ) { // 根节点找两个
int firmx = 0, secmx = 0;
for ( int i = head[x]; i; i = edge[i].nxt ) {
int to = edge[i].to;
if ( to == fa ) continue;
int sonmx = DFS(to, x);
if ( sonmx >= firmx ) {
secmx = firmx;
firmx = sonmx;
} else if ( sonmx >= secmx )
secmx = sonmx;
}
res += (ll)max(0, h[x] - firmx) + max(0, h[x] - secmx);
return 0;
} else { // 非根节点找一个
int mx = 0;
for ( int i = head[x]; i; i = edge[i].nxt ) {
int to = edge[i].to;
if ( to == fa ) continue;
int sonmx = DFS(to, x);
mx = max(mx, sonmx);
}
res += (ll)max(0, h[x] - mx); // 取 max(0, h[x] - mx) 是因为子树中的 mx 有可能比 h[x] 大
return max(mx, h[x]);
}
}
}
int main () {
scanf("%d", &n);
for ( int i = 1; i <= n; i ++ ) {
scanf("%d", &h[i]);
if ( h[i] > h[root] ) root = i;
}
for ( int i = 1; i < n; i ++ ) {
int a, b; scanf("%d%d", &a, &b);
add_Edge(a, b);
add_Edge(b, a);
}
DFS(root, root);
printf("%lld\n", res);
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
# CodeForces1649B_GameOfPassing
# 🔗
# 💡
如果出现一个 这种情况的传球
那么就只考虑最大的数额外分配需要的次数
所以我们定义一轮为以最大的数开始,向别的数传球
那么一轮我们可以让最大的数减 ,其余的任选几个减 ,注意最后可以让最大的再额外传出一个球
如果最大的大于其余的,那么剩下的我们就要单独给最大的分配次数,也就是需要
如果小于等于,那么就只需要一个球
特判一下 即可
# ✅
inline void Solve () {
int n; cin >> n;
ll mx = 0;
ll sum = 0;
for ( int i = 0; i < n; i ++ ) {
ll x; cin >> x;
mx = max(mx, x);
sum = sum + x;
}
sum -= mx;
if ( mx == 0 ) {
cout << 0 << endl;
} else if ( mx <= sum ) {
cout << 1 << endl;
} else {
cout << mx - sum << endl;
}
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
# CodeForces1647D_MadokaAndChildishPranks
# 🔗
# 💡
样例中一个构造方式就很明显了
一次选一个面积为 的片,然后贴上去,横片的右侧为黑,竖片的下侧为黑
但是考虑到一次覆盖会有部分变白的因素,所以我们贴横片从右往左,贴竖片从下往上
横片可在从第二列开始的右侧进行贴,竖片则是去补第一列的
# ✅
struct node { int a, b, c, d; };
inline void Solve () {
int n, m; cin >> n >> m;
vector<string> s(n);
for ( int i = 0; i < n; i ++ ) cin >> s[i];
if ( s[0][0] == '1' ) { cout << "-1\n"; return;}
vector<node> res;
for ( int i = n - 1; i >= 0; i -- ) {
for ( int j = m - 1; j >= 1; j -- ) {
if ( s[i][j] == '1' ) res.push_back({i, j - 1, i, j});
}
}
for ( int i = n - 1; i >= 1; i -- ) {
if ( s[i][0] == '1' ) {
res.push_back({i - 1, 0, i, 0});
}
}
cout << res.size() << "\n";
for ( auto [a, b, c, d] : res ) {
cout << a << " " << b << " " << c << " " << d << "\n";
}
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
# CodeForces1656D_K-good
# 🔗
# 💡
我们做一下公式 得到 且
若 为偶数
令 ,则
得
即 是 的倍数但 不是 的倍数
让 最小 ,令
那么 便是满足第一个条件,令
若 为奇数
注意到我们最后剩了一个 ,尝试利用一下
令
因为 是 的因数
则
满足
考虑他们俩是否可以选一个
若 不满足第二个条件
则
满足
# ✅
inline void Solve () {
ll n; cin >> n;
ll d = 1, x = n;
while ( !(x & 1) ) x >>= 1, d <<= 1;
if ( x == 1 ) cout << "-1\n";
else cout << min(d << 1, x) << endl;
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
# CodeForces1659D_ReverseSortSum
# 🔗
# 💡
首先设置 表示第 位之前(包含第 位) 的数量
分类讨论一下
如果 ,那么在 位之前,这一位都是
那么 为什么可以大于 ,就是因为在 中存在一些
由于 不断变大,很明显就是从 开始 个 小于 ,即区间
也就是说从 开始 ,即
如果 ,那么在 位之前,这一位都是
所以我们必须要让
换到上一位上也就是
由于这些操作都是赋值 的,所以我们让 首先全为 即可
当然要注意如果 则 一定为
# ✅
int b[200005];
int a[200005];
inline void Solve () {
int n; cin >> n;
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i ++) cin >> b[i];
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i ++) a[i] = 1;
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i ++) {
if (b[i] == 0) {
a[i] = 0;
continue;
}
if (a[i]) a[b[i] + 1] = 0;
else a[b[i] + i] = 0;
}
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i ++) cout << a[i] << " "; cout << endl;
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
# CodeForces1691C_SumOfSubstrings
# 🔗
# 💡
注意到如果 不在首尾的话,每一个都会作为 算一次 ,作为 算一次
那么题目就是想让我们将 填在首尾
并且注意到如果填在首位的话是会算一次 ,但填在尾部就只会算一次 ,所以肯定是优先希望填在尾部的
那么就先判断尾部,如果尾部不是 并且最后一个 可以移动过去,就移动过去,并扣掉 移动的花费
然后用剩下的 去将第一个 移动到首位
# ✅
inline void Solve () {
int n, k; cin >> n >> k;
string s; cin >> s;
int cnt0 = 0, cnt1 = 0;
for (char c : s) cnt0 += c == '0', cnt1 += c == '1';
if (cnt0 == n) {
cout << "0\n";
return;
}
int lsid = n - 1; // 最后一个 1
while (s[lsid] == '0') lsid --;
if (cnt1 == 1) {
if (n - 1 - lsid <= k) cout << 1 << endl;
else if (lsid <= k) cout << 10 << endl;
else cout << 11 << endl;
return;
}
int len2 = n - 1 - lsid; // 最后一个 1 移动到末尾需要的花费
int bgid = 0; // 第一个 1
while (s[bgid] == '0') bgid ++;
int len1 = bgid; // 第一个 1 移动到首位需要的花费
if (len2 <= k && s[n - 1] != '1') {
swap(s[lsid], s[n - 1]);
k -= len2;
}
if (len1 <= k && s[0] != '1') {
swap(s[0], s[bgid]);
}
int res = 0;
for (int i = 1; i < n; i ++) {
res += stoi(s.substr(i - 1, 2));
}
cout << res << endl;
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
# CodeForces1702C_TrainAndQueries
# 🔗
# 💡
从询问入手,问的两个数的意思是:如果有一个 出现在一个 的前面,就一定可以到达
那么 一定想要最靠前的, 一定想要最靠后的
就维护每一个数的最小出现下标与一个数的最大出现下标
对于 用这两者进行比较即可
# ✅
inline void Solve () {
int n, m; cin >> n >> m;
map<int, int> minid, maxid;
vector<int> a(n);
for (int i = 0; i < n; i ++) {
cin >> a[i];
if (!minid.count(a[i])) minid[a[i]] = i;
}
for (int i = n - 1; i >= 0; i --) {
if (!maxid.count(a[i])) maxid[a[i]] = i;
}
while (m --) {
int x, y; cin >> x >> y;
if (!minid.count(x) || !maxid.count(y)) {
cout << "NO\n";
continue;
}
if (minid[x] < maxid[y]) {
cout << "YES\n";
} else cout << "NO\n";
}
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
# CodeForces1702F_EquateMultisets
# 🔗
# 💡
需要注意到的点是:对于 ,如果 能通过除二变成 ,那么 所覆盖的内容一定是 的子集
所以 覆盖的点的量一定是少于 的,匹配的时候 优先进行匹配。不然会出现 只能匹配上一个点但是 可以匹配上多个点,但是匹配完 后把 匹配的点占了, 就无法匹配的问题。
那么首先在读入 时,先存一下每一个数出现的次数
然后对 排一个序,对于每一个 遍历它能变成的所有点(每次除二后不断乘二直到超过 ),遇到第一个匹配上的点就退出并对这个点出现次数减一。如果遇不到匹配的数,就说明这个点没有可以匹配的点了,就输出 NO 即可
# ✅
inline void Solve () {
int n; cin >> n;
map<int, int> mp;
for (int i = 0; i < n; i ++) {
int x; cin >> x;
while (x % 2 == 0) x /= 2;
mp[x] ++;
}
vector<int> v;
for (int i = 0; i < n; i ++) {
int x; cin >> x;
while (x % 2 == 0) x /= 2;
v.push_back(x);
}
sort(v.begin(), v.end());
for (int x : v) {
int flag = false;
while (1) {
for (int tmpx = x; tmpx <= 1000000000; tmpx *= 2) {
if (mp.count(tmpx)) {
mp[tmpx] --;
if (!mp[tmpx]) mp.erase(tmpx);
flag = true;
goto end;
}
}
if (x == 1) break;
x /= 2;
}
end:;
if (!flag) {
cout << "NO\n";
return;
}
}
if (mp.size() == 0) cout << "YES\n";
else cout << "NO\n";
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
# CodeForces1713D_TournamentCountdown
# 🔗
# 💡
发现询问次数甚至会小于人数,所以必须跳过一些过程。
注意在第一轮 的比赛中,在最后一层和倒数第二层赢的次数有
一共两组比赛,我们直接用一组比赛去得到另一组比赛的结果,即询问 赢的数量的比较
如果赢的次数相同,则他们都是输的,直接比 就行
如果一个人赢的次数多,那么他在第一轮是赢的,另一个人在第一轮是输的,那么再比这个人和另一组的另一个没比的人
例如 赢,就比
如果 赢,就比
这样四个四个讨论能把 次确定结果化简为 次
开一个滚动数组,意味着每次往上跳两层,四个四个进行比较就可以得到答案了。
# ✅
inline int ask (int a, int b) { // 1:a>b
printf("? %d %d\n", a, b); fflush(stdout);
int x; scanf("%d", &x);
return x;
}
int a[2][1000006];
int cnt[2];
inline int getWin (int l, int r, int op) {
int ask1 = ask(a[op][l], a[op][l + 2]);
if (ask1 == 0) {
int ask2 = ask(a[op][l + 1], a[op][l + 3]);
if (ask2 == 1) return a[op][l + 1];
else return a[op][l + 3];
} else if (ask1 == 1) {
int ask2 = ask(a[op][l], a[op][l + 3]);
if (ask2 == 1) return a[op][l];
else return a[op][l + 3];
} else {
int ask2 = ask(a[op][l + 1], a[op][l + 2]);
if (ask2 == 1) return a[op][l + 1];
else return a[op][l + 2];
}
}
inline void Solve () {
int n; scanf("%d", &n);
n = 1 << n;
int idx = 0;
cnt[0] = cnt[1] = 0;
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i ++) a[!idx][cnt[!idx] ++] = i;
while (cnt[!idx] > 2) {
cnt[idx] = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < cnt[!idx]; i += 4) {
a[idx][cnt[idx] ++] = getWin(i, i + 3, !idx);
}
idx = !idx;
}
if (cnt[!idx] == 2) {
int ask1 = ask(a[!idx][0], a[!idx][1]);
if (ask1 == 1) printf("! %d\n", a[!idx][0]);
else printf("! %d\n", a[!idx][1]);
fflush(stdout);
} else {
printf("! %d\n", a[!idx][0]);
fflush(stdout);
}
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
# GYM102174F_风王之瞳
# 🔗
https://codeforces.com/gym/102174/problem/F
# 💡
本题要开始就考虑到一个矩形内满大(点均在边界上)的几个"歪正方形"如何构造
 如图一个 4 * 4 的正方形,其内部带上自己可以构造出 3 + 1 个满大正方形
如图一个 4 * 4 的正方形,其内部带上自己可以构造出 3 + 1 个满大正方形
于是得知:一个边长为 a 的正方形,可以构造出 a 个满大矩形
所以我们枚举正方形边长,每次累加 (a - i + 1) * (b - i + 1) * i 即可
# ✅
/*
________ _ ________ _
/ ______| | | | __ | | |
/ / | | | |__| | | |
| | | |___ _ _ _ ___ _ _____ | ___| ______ _____ ___ _ | |
| | | __ \ |_| | | | | | _\| | | ____| | |\ \ | __ | | _ | | _\| | | |
| | | | \ | _ | | | | | | \ | | \___ | | \ \ | |_/ _| | |_| | | | \ | | |
\ \______ | | | | | | \ |_| / | |_/ | ___/ | | | \ \ | /_ \__ | | |_/ | | |
Author : \________| |_| |_| |_| \___/ |___/|_| |_____| _________|__| \__\ |______| | | |___/|_| |_|
____| |
\_____/
*/
//#include <unordered_map>
#include <algorithm>
#include <iostream>
#include <cstring>
#include <utility>
#include <string>
#include <vector>
#include <cstdio>
#include <stack>
#include <queue>
#include <cmath>
#include <map>
#include <set>
#define G 10.0
#define LNF 1e18
#define EPS 1e-6
#define PI acos(-1.0)
#define INF 0x7FFFFFFF
#define ll long long
#define ull unsigned long long
#define LOWBIT(x) ((x) & (-x))
#define LOWBD(a, x) lower_bound(a.begin(), a.end(), x) - a.begin()
#define UPPBD(a, x) upper_bound(a.begin(), a.end(), x) - a.begin()
#define TEST(a) cout << "---------" << a << "---------" << '<br>'
#define CHIVAS_ int main()
#define _REGAL exit(0)
#define SP system("pause")
#define IOS ios::sync_with_stdio(false)
//#define map unordered_map
#define PB(x) push_back(x)
#define ALL(a) a.begin(),a.end()
#define MEM(a, b) memset(a, b, sizeof(a))
#define EACH_CASE(cass) for (cass = inputInt(); cass; cass--)
#define LS l, mid, rt << 1
#define RS mid + 1, r, rt << 1 | 1
#define GETMID (l + r) >> 1
using namespace std;
template<typename T> inline T MAX(T a, T b){return a > b? a : b;}
template<typename T> inline T MIN(T a, T b){return a > b? b : a;}
template<typename T> inline void SWAP(T &a, T &b){T tp = a; a = b; b = tp;}
template<typename T> inline T GCD(T a, T b){return b > 0? GCD(b, a % b) : a;}
template<typename T> inline void ADD_TO_VEC_int(T &n, vector<T> &vec){vec.clear(); cin >> n; for(int i = 0; i < n; i ++){T x; cin >> x, vec.PB(x);}}
template<typename T> inline pair<T, T> MaxInVector_ll(vector<T> vec){T MaxVal = -LNF, MaxId = 0;for(int i = 0; i < (int)vec.size(); i ++) if(MaxVal <vec[i]) MaxVal = vec[i], MaxId = i; return {MaxVal, MaxId};}
template<typename T> inline pair<T, T> MinInVector_ll(vector<T> vec){T MinVal = LNF, MinId = 0;for(int i = 0; i < (int)vec.size(); i ++) if(MinVal > vec[i])MinVal = vec[i], MinId = i; return {MinVal, MinId};}
template<typename T> inline pair<T, T> MaxInVector_int(vector<T> vec){T MaxVal = -INF, MaxId = 0;for(int i = 0; i < (int)vec.size(); i ++) if(MaxVal <vec[i]) MaxVal = vec[i], MaxId = i; return {MaxVal, MaxId};}
template<typename T> inline pair<T, T> MinInVector_int(vector<T> vec){T MinVal = INF, MinId = 0;for(int i = 0; i < (int)vec.size(); i ++) if(MinVal > vec[i])MinVal = vec[i], MinId = i; return {MinVal, MinId};}
template<typename T> inline pair<map<T, T>, vector<T> > DIV(T n){T nn = n;map<T, T> cnt;vector<T> div;for(ll i = 2; i * i <= nn; i ++){while(n % i == 0){if(!cnt[i]) div.push_back(i);cnt[i] ++;n /= i;}}if(n != 1){if(!cnt[n]) div.push_back(n);cnt[n] ++;n /= n;}return {cnt, div};}
template<typename T> vector<T>& operator-- (vector<T> &v){for (auto& i : v) --i; return v;}
template<typename T> vector<T>& operator++ (vector<T> &v){for (auto& i : v) ++i; return v;}
template<typename T> istream& operator>>(istream& is, vector<T> &v){for (auto& i : v) is >> i; return is;}
template<typename T> ostream& operator<<(ostream& os, vector<T> v){for (auto& i : v) os << i << ' '; return os;}
inline int inputInt(){int X=0; bool flag=1; char ch=getchar();while(ch<'0'||ch>'9') {if(ch=='-') flag=0; ch=getchar();}while(ch>='0'&&ch<='9') {X=(X<<1)+(X<<3)+ch-'0'; ch=getchar();}if(flag) return X;return ~(X-1);}
inline void outInt(int X){if(X<0) {putchar('-'); X=~(X-1);}int s[20],top=0;while(X) {s[++top]=X%10; X/=10;}if(!top) s[++top]=0;while(top) putchar(s[top--]+'0');}
inline ll inputLL(){ll X=0; bool flag=1; char ch=getchar();while(ch<'0'||ch>'9') {if(ch=='-') flag=0; ch=getchar();}while(ch>='0'&&ch<='9') {X=(X<<1)+(X<<3)+ch-'0'; ch=getchar();}if(flag) return X;return ~(X-1); }
inline void outLL(ll X){if(X<0) {putchar('-'); X=~(X-1);}ll s[20],top=0;while(X) {s[++top]=X%10; X/=10;}if(!top) s[++top]=0;while(top) putchar(s[top--]+'0');}
inline void solve ( ) {
ll a = inputLL(), b = inputLL(), res = 0;
for ( ll i = 1; i <= MIN(a, b); i ++ ) res += (a - i + 1) * (b - i + 1) * i;
outLL(res); puts("");
}
CHIVAS_{
int cass;
EACH_CASE ( cass ) {
solve();
}
};
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
# HDU2021多校(1)5_MinimumSpanningTree
# 🔗
https://acm.hdu.edu.cn/showproblem.php?pid=6954
# 💡
模拟找到构造这么一棵最小生成树:所有质数和2连,不是质数就是自己
所造成的贡献会使这一位的差分值是这个贡献
然后预处理一下前缀和to差分即可
# ✅
/*
________ _ ________ _
/ ______| | | | __ | | |
/ / | | | |__| | | |
| | | |___ _ _ _ ___ _ _____ | ___| ______ _____ ___ _ | |
| | | __ \ |_| | | | | | _\| | | ____| | |\ \ | __ | | _ | | _\| | | |
| | | | \ | _ | | | | | | \ | | \___ | | \ \ | |_/ _| | |_| | | | \ | | |
\ \______ | | | | | | \ |_| / | |_/ | ___/ | | | \ \ | /_ \__ | | |_/ | | |
Author : \________| |_| |_| |_| \___/ |___/|_| |_____| _________|__| \__\ |______| | | |___/|_| |_|
____| |
\_____/
*/
//#include <unordered_map>
#include <algorithm>
#include <iostream>
#include <cstring>
#include <utility>
#include <string>
#include <vector>
#include <cstdio>
#include <stack>
#include <queue>
#include <ctime>
#include <cmath>
#include <map>
#include <set>
#define G 10.0
#define LNF 1e18
#define EPS 1e-6
#define PI acos(-1.0)
#define INF 0x7FFFFFFF
#define ll long long
#define ull unsigned long long
#define LOWBIT(x) ((x) & (-x))
#define LOWBD(a, x) lower_bound(a.begin(), a.end(), x) - a.begin()
#define UPPBD(a, x) upper_bound(a.begin(), a.end(), x) - a.begin()
#define TEST(a) cout << "---------" << a << "---------" << '<br>'
#define CHIVAS_ int main()
#define _REGAL exit(0)
#define SP system("pause")
#define IOS ios::sync_with_stdio(false)
#define beginTime clock_t startTime, toTime;startTime=clock();
#define endTime toTime=clock();cout << "The run time is:" << (double)(toTime - startTime)/CLOCKS_PER_SEC<<"s"<<endl;
//#define map unordered_map
#define _int(a) int a; cin >> a
#define _ll(a) ll a; cin >> a
#define _char(a) char a; cin >> a
#define _string(a) string a; cin >> a
#define _vectorInt(a, n) vector<int>a(n); cin >> a
#define _vectorLL(a, b) vector<ll>a(n); cin >> a
#define PB(x) push_back(x)
#define ALL(a) a.begin(),a.end()
#define MEM(a, b) memset(a, b, sizeof(a))
#define EACH_CASE(cass) for (cass = inputInt(); cass; cass--)
#define LS l, mid, rt << 1
#define RS mid + 1, r, rt << 1 | 1
#define GETMID (l + r) >> 1
using namespace std;
template<typename T> inline T MAX(T a, T b){return a > b? a : b;}
template<typename T> inline T MIN(T a, T b){return a > b? b : a;}
template<typename T> inline void SWAP(T &a, T &b){T tp = a; a = b; b = tp;}
template<typename T> inline T GCD(T a, T b){return b > 0? GCD(b, a % b) : a;}
template<typename T> inline void ADD_TO_VEC_int(T &n, vector<T> &vec){vec.clear(); cin >> n; for(int i = 0; i < n; i ++){T x; cin >> x, vec.PB(x);}}
template<typename T> inline pair<T, T> MaxInVector_ll(vector<T> vec){T MaxVal = -LNF, MaxId = 0;for(int i = 0; i < (int)vec.size(); i ++) if(MaxVal < vec[i]) MaxVal = vec[i], MaxId = i; return {MaxVal, MaxId};}
template<typename T> inline pair<T, T> MinInVector_ll(vector<T> vec){T MinVal = LNF, MinId = 0;for(int i = 0; i < (int)vec.size(); i ++) if(MinVal > vec[i]) MinVal = vec[i], MinId = i; return {MinVal, MinId};}
template<typename T> inline pair<T, T> MaxInVector_int(vector<T> vec){T MaxVal = -INF, MaxId = 0;for(int i = 0; i < (int)vec.size(); i ++) if(MaxVal < vec[i]) MaxVal = vec[i], MaxId = i; return {MaxVal, MaxId};}
template<typename T> inline pair<T, T> MinInVector_int(vector<T> vec){T MinVal = INF, MinId = 0;for(int i = 0; i < (int)vec.size(); i ++) if(MinVal > vec[i]) MinVal = vec[i], MinId = i; return {MinVal, MinId};}
template<typename T> inline pair<map<T, T>, vector<T> > DIV(T n){T nn = n;map<T, T> cnt;vector<T> div;for(ll i = 2; i * i <= nn; i ++){while(n % i == 0){if(!cnt[i]) div.push_back(i);cnt[i] ++;n /= i;}}if(n != 1){if(!cnt[n]) div.push_back(n);cnt[n] ++;n /= n;}return {cnt, div};}
template<typename T> vector<T>& operator-- (vector<T> &v){for (auto& i : v) --i; return v;}
template<typename T> vector<T>& operator++ (vector<T> &v){for (auto& i : v) ++i; return v;}
template<typename T> istream& operator>>(istream& is, vector<T> &v){for (auto& i : v) is >> i; return is;}
template<typename T> ostream& operator<<(ostream& os, vector<T> v){for (auto& i : v) os << i << ' '; return os;}
inline int inputInt(){int X=0; bool flag=1; char ch=getchar();while(ch<'0'||ch>'9') {if(ch=='-') flag=0; ch=getchar();}while(ch>='0'&&ch<='9') {X=(X<<1)+(X<<3)+ch-'0'; ch=getchar();}if(flag) return X;return ~(X-1);}
inline void outInt(int X){if(X<0) {putchar('-'); X=~(X-1);}int s[20],top=0;while(X) {s[++top]=X%10; X/=10;}if(!top) s[++top]=0;while(top) putchar(s[top--]+'0');}
inline ll inputLL(){ll X=0; bool flag=1; char ch=getchar();while(ch<'0'||ch>'9') {if(ch=='-') flag=0; ch=getchar();}while(ch>='0'&&ch<='9') {X=(X<<1)+(X<<3)+ch-'0'; ch=getchar();}if(flag) return X;return ~(X-1); }
inline void outLL(ll X){if(X<0) {putchar('-'); X=~(X-1);}ll s[20],top=0;while(X) {s[++top]=X%10; X/=10;}if(!top) s[++top]=0;while(top) putchar(s[top--]+'0');}
const int N = 1e7 + 10;
vector<ll> prime;
bool isprime[N];
ll dir[N], a[N];
int cass;
inline void Get_euler() {
isprime[0] = isprime[1] = 1;
for ( ll i = 2; i < N; i ++ ) {
if( !isprime[i] ) { prime.push_back(i), dir[i] = (i == 2 ? 0 : 2 * i); } // 除了2以外的质数都要和2连一般
for ( ll j = 0; j < prime.size() && prime[j] * i < N; j ++ ) {
isprime[i * prime[j]] = 1;
dir[i * prime[j]] = i * prime[j]; // 不是质数,差分等于它自己
if ( i % prime[j] == 0 ) break;
}
}
for ( ll i = 1; i <= N; i ++ ) a[i] = a[i - 1] + dir[i];
}
CHIVAS_{beginTime
Get_euler();
EACH_CASE ( cass ) {
outLL(a[inputLL()]); puts("");
}
endTime _REGAL;
};
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
99
100
101
102
103
104
105
106
107
108
109
110
111
112
113
114
115
116
117
118
119
120
121
122
# HDU2021多校(1)8_Maximalsubmatrix
# 🔗
https://acm.hdu.edu.cn/showproblem.php?pid=6957
# 💡
重在构造
首先能想到构造成 01 矩阵然后求全1最大面积
然后发现两个连着且同列的递增列不好处理
然后是想如何划分两个列,可以用长度划分,即一个列横过来:...3648... -> ...1212...
然后也同时获得了它的高度
如果在遍历每个点的话可以当做一个直方图来看
那么对直方图的最大矩形面积可以使用单调栈解直方图 (opens new window)
维护最大值即可
# ✅
/*
________ _ ________ _
/ ______| | | | __ | | |
/ / | | | |__| | | |
| | | |___ _ _ _ ___ _ _____ | ___| ______ _____ ___ _ | |
| | | __ \ |_| | | | | | _\| | | ____| | |\ \ | __ | | _ | | _\| | | |
| | | | \ | _ | | | | | | \ | | \___ | | \ \ | |_/ _| | |_| | | | \ | | |
\ \______ | | | | | | \ |_| / | |_/ | ___/ | | | \ \ | /_ \__ | | |_/ | | |
Author : \________| |_| |_| |_| \___/ |___/|_| |_____| _________|__| \__\ |______| | | |___/|_| |_|
____| |
\_____/
*/
//#include <unordered_map>
#include <algorithm>
#include <iostream>
#include <cstring>
#include <utility>
#include <string>
#include <vector>
#include <cstdio>
#include <stack>
#include <queue>
#include <cmath>
#include <map>
#include <set>
#define G 10.0
#define LNF 1e18
#define EPS 1e-6
#define PI acos(-1.0)
#define INF 0x7FFFFFFF
#define ll long long
#define ull unsigned long long
#define LOWBIT(x) ((x) & (-x))
#define LOWBD(a, x) lower_bound(a.begin(), a.end(), x) - a.begin()
#define UPPBD(a, x) upper_bound(a.begin(), a.end(), x) - a.begin()
#define TEST(a) cout << "---------" << a << "---------" << '<br>'
#define CHIVAS_ int main()
#define _REGAL exit(0)
#define SP system("pause")
#define IOS ios::sync_with_stdio(false)
//#define map unordered_map
#define _int(a) int a; cin >> a
#define _ll(a) ll a; cin >> a
#define _char(a) char a; cin >> a
#define _string(a) string a; cin >> a
#define _vectorInt(a, n) vector<int>a(n); cin >> a
#define _vectorLL(a, b) vector<ll>a(n); cin >> a
#define PB(x) push_back(x)
#define ALL(a) a.begin(),a.end()
#define MEM(a, b) memset(a, b, sizeof(a))
#define EACH_CASE(cass) for (cass = inputInt(); cass; cass--)
#define LS l, mid, rt << 1
#define RS mid + 1, r, rt << 1 | 1
#define GETMID (l + r) >> 1
using namespace std;
template<typename T> inline T MAX(T a, T b){return a > b? a : b;}
template<typename T> inline T MIN(T a, T b){return a > b? b : a;}
template<typename T> inline void SWAP(T &a, T &b){T tp = a; a = b; b = tp;}
template<typename T> inline T GCD(T a, T b){return b > 0? GCD(b, a % b) : a;}
template<typename T> inline void ADD_TO_VEC_int(T &n, vector<T> &vec){vec.clear(); cin >> n; for(int i = 0; i < n; i ++){T x; cin >> x, vec.PB(x);}}
template<typename T> inline pair<T, T> MaxInVector_ll(vector<T> vec){T MaxVal = -LNF, MaxId = 0;for(int i = 0; i < (int)vec.size(); i ++) if(MaxVal < vec[i]) MaxVal = vec[i], MaxId = i; return {MaxVal, MaxId};}
template<typename T> inline pair<T, T> MinInVector_ll(vector<T> vec){T MinVal = LNF, MinId = 0;for(int i = 0; i < (int)vec.size(); i ++) if(MinVal > vec[i]) MinVal = vec[i], MinId = i; return {MinVal, MinId};}
template<typename T> inline pair<T, T> MaxInVector_int(vector<T> vec){T MaxVal = -INF, MaxId = 0;for(int i = 0; i < (int)vec.size(); i ++) if(MaxVal < vec[i]) MaxVal = vec[i], MaxId = i; return {MaxVal, MaxId};}
template<typename T> inline pair<T, T> MinInVector_int(vector<T> vec){T MinVal = INF, MinId = 0;for(int i = 0; i < (int)vec.size(); i ++) if(MinVal > vec[i]) MinVal = vec[i], MinId = i; return {MinVal, MinId};}
template<typename T> inline pair<map<T, T>, vector<T> > DIV(T n){T nn = n;map<T, T> cnt;vector<T> div;for(ll i = 2; i * i <= nn; i ++){while(n % i == 0){if(!cnt[i]) div.push_back(i);cnt[i] ++;n /= i;}}if(n != 1){if(!cnt[n]) div.push_back(n);cnt[n] ++;n /= n;}return {cnt, div};}
template<typename T> vector<T>& operator-- (vector<T> &v){for (auto& i : v) --i; return v;}
template<typename T> vector<T>& operator++ (vector<T> &v){for (auto& i : v) ++i; return v;}
template<typename T> istream& operator>>(istream& is, vector<T> &v){for (auto& i : v) is >> i; return is;}
template<typename T> ostream& operator<<(ostream& os, vector<T> v){for (auto& i : v) os << i << ' '; return os;}
inline int inputInt(){int X=0; bool flag=1; char ch=getchar();while(ch<'0'||ch>'9') {if(ch=='-') flag=0; ch=getchar();}while(ch>='0'&&ch<='9') {X=(X<<1)+(X<<3)+ch-'0'; ch=getchar();}if(flag) return X;return ~(X-1);}
inline void outInt(int X){if(X<0) {putchar('-'); X=~(X-1);}int s[20],top=0;while(X) {s[++top]=X%10; X/=10;}if(!top) s[++top]=0;while(top) putchar(s[top--]+'0');}
inline ll inputLL(){ll X=0; bool flag=1; char ch=getchar();while(ch<'0'||ch>'9') {if(ch=='-') flag=0; ch=getchar();}while(ch>='0'&&ch<='9') {X=(X<<1)+(X<<3)+ch-'0'; ch=getchar();}if(flag) return X;return ~(X-1); }
inline void outLL(ll X){if(X<0) {putchar('-'); X=~(X-1);}ll s[20],top=0;while(X) {s[++top]=X%10; X/=10;}if(!top) s[++top]=0;while(top) putchar(s[top--]+'0');}
const int N = 2e3 + 10;
int las[N], Map[N][N]; // Map的替身滚动数组,后期行列式递进矩阵
int l[N], r[N]; // 单调栈的左右边界
stack<int> stk; // 单调栈
inline void solve () {
int n = inputInt(), m = inputInt();
for ( int i = 1; i <= n; i ++ ) { // 输入同时转换
for ( int j = 1; j <= m; j ++ ) {
Map[i][j] = inputInt();
int tmp = Map[i][j];
Map[i][j] = (((i ^ 1) && Map[i][j] >= las[j]) ? Map[i - 1][j] + 1 : 1);
las[j] = tmp;
}
}
int res = 0;
for ( int i = 1; i <= n; i ++ ) {
stk = stack<int>(); // 单调栈求l、r
for ( int j = 1; j <= m; j ++) {
while ( stk.size() && Map[i][j] <= Map[i][stk.top()] ) stk.pop();
l[j] = (stk.size() ? stk.top() + 1 : 1);
stk.push(j);
}
stk = stack<int>();
for ( int j = m; j >= 1; j -- ) {
while ( stk.size() && Map[i][j] <= Map[i][stk.top()] ) stk.pop();
r[j] = (stk.size() ? stk.top() - 1 : m);
stk.push(j);
}
for ( int j = 1; j <= m; j ++ ) res = MAX(res, Map[i][j] * (r[j] - l[j] + 1)); // 维护最大面积
}
outInt(res);
puts("");
}
CHIVAS_{
int cass;
EACH_CASE ( cass ) {
solve();
}
_REGAL;
};
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
99
100
101
102
103
104
105
106
107
108
109
110
111
112
113
114
115
116
117
118
119
120
121
122
123
124
125
126
127
128
129
# HDU2021多校(9)3_Dota2ProCircuit
# 🔗
# 💡
其实可以看作是一类分配问题
比如第i个人想获取最低的名次,意味着分数要超过他的人需要很多
那么一个人如果选取最小的锦标赛排名分就比第i个要大了话,他去取最大的锦标赛排名分就会造成很多浪费
所以在这种情况下每个人要去取刚好超过第i个人的锦标赛排名分
那么我们可以贪心地去遍历
设置一个下标指针表示当前锦标赛排名分
对于a按值从大到小遍历,b从小到大遍历(逆序
如果当前的a[j]+b[id]<=a[i]+b[n]就让id--
直到满足>了就停下来,如果id还可以选,那就答案++
这样选的话可以保证每个人对加上后大于a[i]+b[n]的每个分数都充分利用了
如果当前的a[j]选比b[id]大的只有过大于a[i]+b[n]导致浪费的情况
如果让比b[id]小的去选,不仅会导致a[i]没法用它大于a[i]+b[n],还可能导致剩下的id选不完
如果要排名更靠前
那么整体反转一下即可
但要注意这时我们求的是比a[i]+b[1]小于等于的个数,最后答案是n-cnt+1
# ✅
const int N = 5e3 + 10;
struct node {
int id, val;
}a[N];
int b[N];
pair<int, int> res[N];
int n;
inline void Solve () {
cin >> n;
for ( int i = 1; i <= n; i ++ )
cin >> a[i].val,
a[i].id = i;
for ( int i = 1; i <= n; i ++ )
cin >> b[i];
sort ( a + 1, a + 1 + n, [&](node a, node b){
return a.val < b.val;
});
for ( int i = 1; i <= n; i ++ ) {
int cnt, cur;
cnt = 0, cur = a[i].val + b[1];
for ( int j = 1, idb = 2; j <= n && idb <= n; j ++ ) {
if ( j == i ) continue;
while ( a[j].val + b[idb] > cur && idb <= n ) idb ++;
if ( idb <= n ) cnt ++;
else break;
idb ++;
}
res[a[i].id].first = n - cnt - 1;
cnt = 0, cur = a[i].val + b[n];
for ( int j = n, idb = n - 1; j >= 1 && idb; j -- ) {
if ( j == i ) continue;
while ( a[j].val + b[idb] <= cur && idb ) idb --;
if ( idb ) cnt ++;
else break;
idb --;
}
res[a[i].id].second = cnt;
}
for ( int i = 1; i <= n; i ++ ) cout << res[i].first + 1 << " " << res[i].second + 1 << endl;
}
int main () {
ios::sync_with_stdio(false);
int cass; cin >> cass; while ( cass -- ) {
Solve ();
}
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
# ICPC2019南昌E_BobsProblem
# 🔗
# 💡
白边给了限制,但黑边没有说,所以先把权值加上再说。
要保证这是一个生成树,所以我们先用不多于 个白边和之前的所有黑边将图连通,这些白边从大到小选。
如果无法用不多于 条白边和所有黑边构成生成树,那么就是 ,否则说明我们还可以再选几条边,就让没选过的白边从大到小选几条就行了。
# ✅
const int N = 5e5 + 10;
struct Dsu {
vector<int> nod;
inline Dsu (int n) {
this->nod.resize(n + 1);
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i ++) this->nod[i] = i;
}
inline int find (int x) { return x == nod[x] ? x : nod[x] = find(nod[x]); }
inline void merge (int x, int y) {
x = find(x);
y = find(y);
if (x == y) return;
nod[x] = y;
}
inline bool is_similar (int x, int y) {
return find(x) == find(y);
}
};
inline void Solve () {
int n, m, k; cin >> n >> m >> k;
Dsu dsu(n);
vector<tuple<int, int, int> > wht;
ll res = 0, cnt = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < m; i ++) {
int u, v, w, c; cin >> u >> v >> w >> c;
if (c) {
wht.push_back({u, v, w});
} else {
res += 1ll * w;
cnt += !dsu.is_similar(u, v);
dsu.merge(u, v);
}
}
sort(wht.begin(), wht.end(), [&](tuple<int, int, int> a, tuple<int, int, int> b) {
return get<2>(a) > get<2>(b);
});
vector<tuple<int, int, int> > els;
for (auto [u, v, w] : wht) {
if (k && !dsu.is_similar(u, v)) {
cnt ++;
k --;
dsu.merge(u, v);
res += 1ll * w;
} else els.push_back({u, v, w});
}
if (cnt != n - 1) {
cout << "-1\n";
return;
}
for (auto [u, v, w] : els) {
if (k) {
res += 1ll * w;
k --;
}
}
cout << res << endl;
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
# ICPC2019台北E_TheLeagueOfSequenceDesigners
# 🔗
# 💡
因为有数大小的限制,所以我们想让数列尽可能长,最长就是
我们构建一个这样的数列
那么即可得出
我们设 得出的结果是 ,那么 得出的结果是
列出方程
那么就将 给 分一下就行了
# ✅
inline void Solve () {
int k, l; cin >> k >> l;
if ( l >= 2000 ) { cout << "-1" << endl; return; }
cout << 1999 << endl << -1;
int num0 = (k + 1999) % 1998;
int num1 = 1998 - num0;
int add = (k + 1999) / 1998;
for ( int i = 0; i < 1998; i ++ ) {
if ( i < num0 ) cout << " " << add + 1;
else cout << " " << add;
} cout << endl;
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
# ICPC上海站2020B_MineSweeperII
# 🔗
# 💡
给定两个矩阵,由 和 构成,每个矩阵的价值是所有 一圈的 的数量的和,问可否在不多于 次操作让 矩阵和 矩阵的价值一样
可以看到,每个 做出的贡献都是依靠相对的 ,那么我们对一个矩阵进行翻转那么价值是一样的,而 矩阵变成 矩阵或者 的反矩阵必定有一个次数是小于要求的,我们就看 的差异数,我们就可以知道要变哪个矩阵
# ✅
const int N = 1100;
string a[N];
string b[N];
inline void Solve () {
int n, m; cin >> n >> m;
for ( int i = 0; i < n; i ++ ) cin >> a[i];
for ( int i = 0; i < n; i ++ ) cin >> b[i];
int dirX = 0; // 差异数
for ( int i = 0; i < n; i ++ ) {
for ( int j = 0; j < m; j ++ ) {
dirX += a[i][j] != b[i][j];
}
}
int candel = n * m / 2;
if ( candel < dirX ) {
for ( int i = 0; i < n; i ++ ) {
for ( int j = 0; j < m; j ++ ) a[i][j] == 'X' ? a[i][j] = '.' : a[i][j] = 'X';
cout << a[i] << endl;
}
}
else {
for ( int i = 0; i < n; i ++ ) cout << a[i] << endl;
}
}
int main () {
ios::sync_with_stdio(false);
int cass = 1; while ( cass -- ) {
Solve ();
}
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
# ICPC2020上海M_Gitignore
# 🔗
# 💡
题目是给出我们 个文件路径,让我们保留最后 个,删掉别的所有文件需要的最少次数
这就是个资源管理器,它就像一棵树,每个文件路径都是树上深度为 的点到一个叶子结点的树链
我们可以对这条树链的每一个前缀路径都标为 ,默认是 ,这样我们就可以确定哪些需要删哪些不能删,删掉的标记为 即可
既然要删最少的次数,我们肯定更希望删去每条 链最上面的文件夹
从根结点向下走是一个 的过程,而我们这里可以直接采用遍历要删掉的 个文件的路径即可
为 的时候意味着要删去,我们标记 然后将计数结果 再 break 即可
# ✅
inline void Solve () {
int n, m; cin >> n >> m;
vector<string> del;
for ( int i = 0; i < n; i ++ ) {
string s; cin >> s; s += "/";
del.push_back(s);
}
map<string, int> statu;
for ( int i = 0; i < m; i ++ ) {
string s; cin >> s; s += "/";
string fl;
for ( int j = 0; j < s.size(); j ++ ) {
fl += s[j];
if ( s[j] == '/' ) statu[fl] = 1;
}
}
int res = 0;
for ( int i = 0; i < n; i ++ ) {
string s = del[i];
string fl;
for ( int j = 0; j < s.size(); j ++ ) {
fl += s[j];
if ( s[j] == '/' ) {
if ( !statu[fl] ) {
statu[fl] = -1;
res ++;
break;
} else if ( statu[fl] == -1 ) {
break;
}
}
}
}
cout << res << endl;
}
int main () {
ios::sync_with_stdio(false);
int cass; cin >> cass; while ( cass -- ) {
Solve ();
}
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
# ICPC2021台北J_TransportationNetwork
# 🔗
# 💡
首先要知道如何求这个贡献
每条边的贡献为两端点数相乘再乘上这个点的权值
已知
所以我们想让 尽可能去连接
所以:
如果
那么就让所有的 放在 下面
然后让所有的 连接到一个 点上
如果
那么要考虑一下让 去占完所有的 的话,后面可能会出现很多个 的情况
这种贡献也是 是我们不想出现的
就挑出来一个 让其连接上
然后剩下的所有的 连接到这个 下面,所有的 连接到一个 下面
这里有一个比较轻松点的统计方法
即第二种情况下,可能会出现没有 的情况
我们可以对第一层的 取一个 ,即如果没有 的话就是没有贡献
# ✅
ll n, s, p;
inline ll Solve () {
if (s <= p) {
ll res = 0;
ll s1 = s;
ll u1 = p - s;
ll u2 = n - 1 - p;
res += (n - u2 - 1) * (u2 + 1);
res += (s1 - 1) * (n - 1);
res += 2ll * u1 * (n - 1);
res += u2 * (n - 1);
return res * 2;
} else {
ll res = 0;
ll s1 = p - 1, s2 = s - s1;
ll u1 = min(n - s - 1, 1ll), u2 = n - 1 - s - u1;
res += (u2 + 1) * (n - u2 - 1) * 1;
res += (s2 + 1) * (n - s2 - 1) * 2;
res += (n - u2 - s2) * (n - 1) * 1;
return res * 2;
}
}
int main() {
ios::sync_with_stdio(false);
int cass; cin >> cass; while (cass --) {
cin >> n >> s >> p;
for (int i = 0; i < s; i ++) {
int x; cin >> x;
}
cout<<Solve()<<"\n";
}
return 0;
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
# NCD2019M_GCDSalary
# 🔗
# 💡
原题来看是需要计算两个指数符
这个本身是不难的,但是我们对于 这么大的数显然是存不下的
就算存下了,在乘和比较的时候又会要很慢
我们可以贪一下,如果这个指数符变成加号或者乘号将会非常方便
想一下 的性质,如果前面加一个指数的相反符也就是 ,那么指数就可以提到前面做乘法了
问题转化:
# ✅
inline void Solve () {
int b1, p1, b2, p2; cin >> b1 >> p1 >> b2 >> p2;
double res1 = (double)p1 * log10(b1);
double res2 = (double)p2 * log10(b2);
if ( b1 == 0 && b2 == 0 ) cout << "Lazy" << endl;
else if ( fabs(res1 - res2) < 1e-8 ) cout << "Lazy" << endl;
else if ( res1 - res2 < -1e-8 ) cout << "Congrats" << endl;
else cout << "HaHa" << endl;
}
int main () {
int cass; scanf("%d", &cass); while ( cass -- ) {
Solve ();
}
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16